|
Vidisha Museum
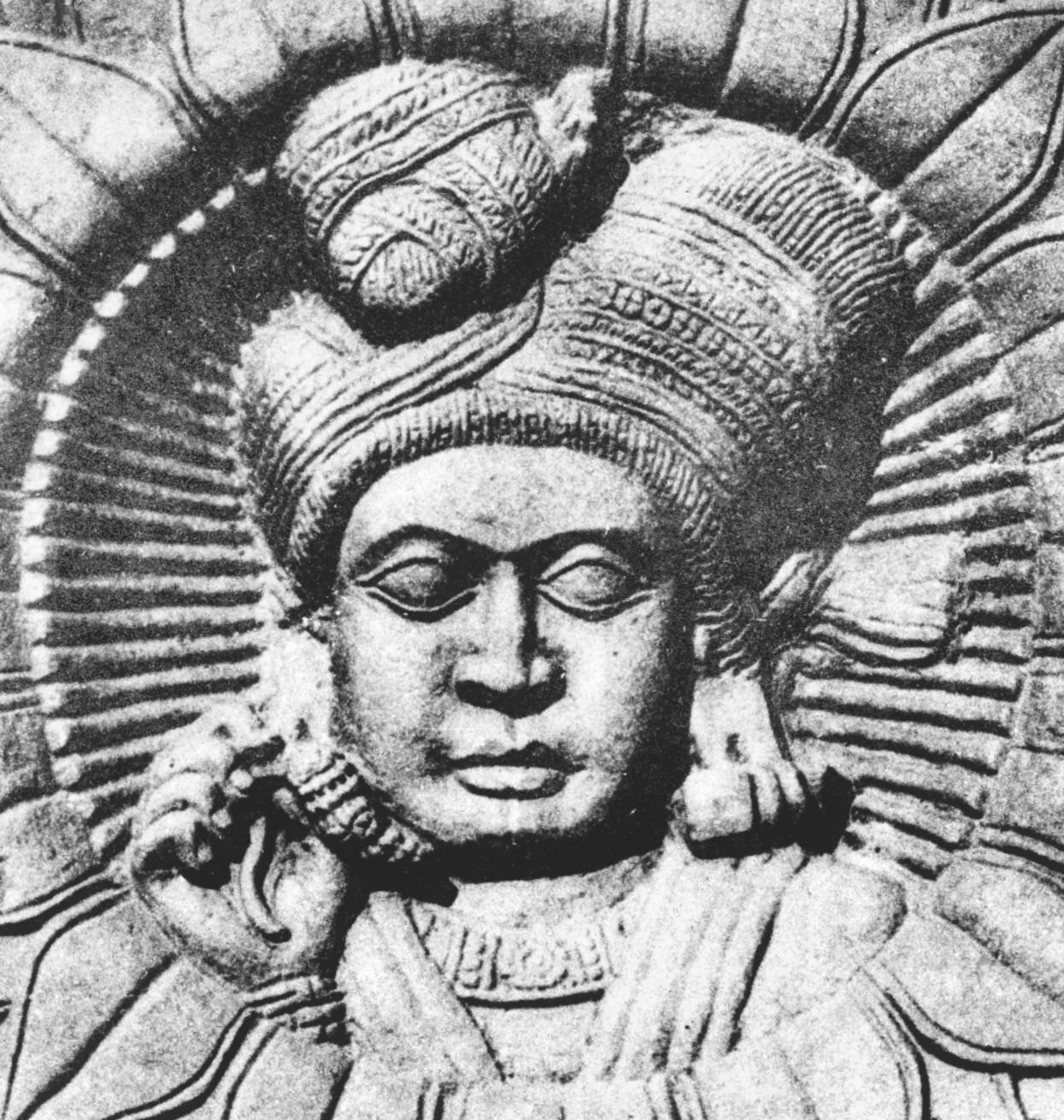
Vidisha Museum or Vidisha District Museum is the main museum of the city of Vidisha, ancient Besnagar. The museum has many sculptures, terracottas and coins, especially from the 9th to the 10 th century CE, as well as Harappan art. A famous statue of a Yaksha, usually dated to the time of the Mauryan Empire The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ... or the Sunga Empire, can be seen. Address: H.N. 204, Block Colony, NH86, Block Colony, Durga Nagar, Vidisha, Madhya Pradesh 464001, India Vidisha District Museum Boar 2.jpg, Vidisha District Museum Boar (side) Vidisha District Museum Canon.jpg, Vidisha District Museum Canon. Vidisha District Museum Chaitya.jpg, Vidisha District Museum Chaitya. Vidisha District Museum decorated pillars.jpg, Vidisha District Museum decorate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidisha
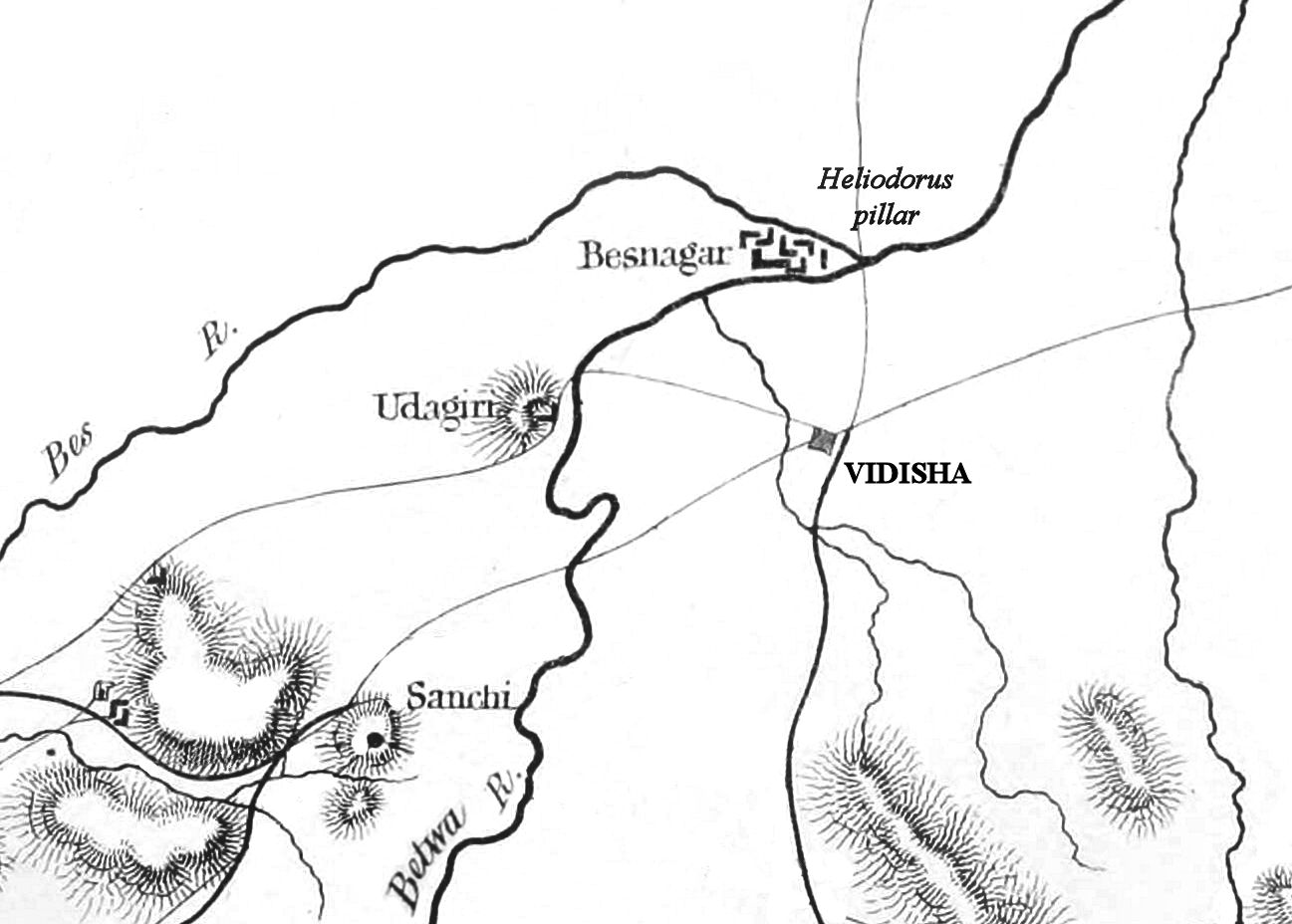
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Museum
An archaeology museum is a museum that specializes in the display of archaeological Types Many archaeology museum are in the open air, such as the Ancient Agora of Athens and the Roman Forum. Others display artifacts inside buildings, such as National Museum of Beirut and Cairo's Museum of Egyptian Antiquities. Still others, display artifacts both outside and inside, such as the Tibes Indigenous Ceremonial Center. Some archaeology museums, such as the Western Australian Museum, may also exhibit maritime archaeological materials. These appear in its Shipwreck Galleries, a wing of the Maritime Museum.MONEY MEIEWIHEPOWEBFJAPVGPQUGFVUIUQEROI See also * Open-air museum * International Council of Museums * International Museum Day (18 May) * List of museums * .museum * Museum education * Museum fatigue * Museum label * Types of museums Type may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc. * Data type, collection of values u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidisha District Museum Yaksha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Besnagar
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harappa
Harappa (; Urdu/ pnb, ) is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal. The Bronze Age Harappan civilisation, now more often called the Indus Valley Civilisation, is named after the site, which takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. The core of the Harappan civilization extended over a large area, from Gujarat in the south, across Sindh and Rajasthan and extending into Punjab and Haryana. Numerous sites have been found outside the core area, including some as far east as Uttar Pradesh and as far west as Sutkagen-dor on the Makran coast of Baluchistan, not far from Iran. The site of the ancient city contains the ruins of a Bronze Age fortified city, which was part of the Harappan civilisation centred in Sindh and the Punjab, and then the Cemetery H culture. The city is believed to have had as many as 23,500 residents and occupied about with clay brick houses at its greatest extent durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaksha
The yakshas ( sa, यक्ष ; pi, yakkha, i=yes) are a broad class of nature-spirits, usually benevolent, but sometimes mischievous or capricious, connected with water, fertility, trees, the forest, treasure and wilderness. They appear in Hindu, Jain and Buddhist texts, as well as ancient and medieval era temples of South Asia and Southeast Asia as guardian deities. The feminine form of the word is or ''yakshini'' ( sa, यक्षिणी ; Pali:Yakkhini). In Hindu, Jain and Buddhist texts, the has a dual personality. On the one hand, a may be an inoffensive nature- fairy, associated with woods and mountains; but there is also a darker version of the , which is a kind of ghost ( bhuta) that haunts the wilderness and waylays and devours travellers, similar to the . Early yakshas Several monumental yakshas are known from the time of the Maurya Empire period. They are variously dated from around the 3rd century BCE to the 1st century BCE. These statues are monumental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. Quote: "Magadha power came to extend over the main cities and communication routes of the Ganges basin. Then, under Chandragupta Maurya (c.321–297 bce), and subsequently Ashoka his grandson, Pataliputra became the centre of the loose-knit Mauryan 'Empire' which during Ashoka's reign (c.268–232 bce) briefly had a presence throughout the main urban centres and arteries of the subcontinent, except for the extreme south." The Maurya Empire was centralized by the conquest of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, and its capital city was located at Pataliputra (modern Patna). Outside this imperial center, the empire's geographical extent was dependent on the loyalty of military commanders who controlled the armed cities sprinkling it. During Asho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunga Empire
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the Maurya Empire. Its capital was Pataliputra, but later emperors such as Bhagabhadra also held court at Besnagar (modern Vidisha) in eastern Malwa. Pushyamitra ruled for 36 years and was succeeded by his son Agnimitra. There were ten Shunga rulers. However, after the death of Agnimitra, the second king of the dynasty, the empire rapidly disintegrated:K.A. Nilkantha Shastri (1970)''A Comprehensive History of India: Volume 2'' p.108: "Soon after Agnimitra there was no 'Sunga empire'." inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any Shunga hegemony.Bhandare, Shailendra. "Numismatics and History: The Maurya-Gupta Interlude in the Gangetic Plain". i''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In Madhya Pradesh
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

