Vidisha District Museum Yaksha on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central
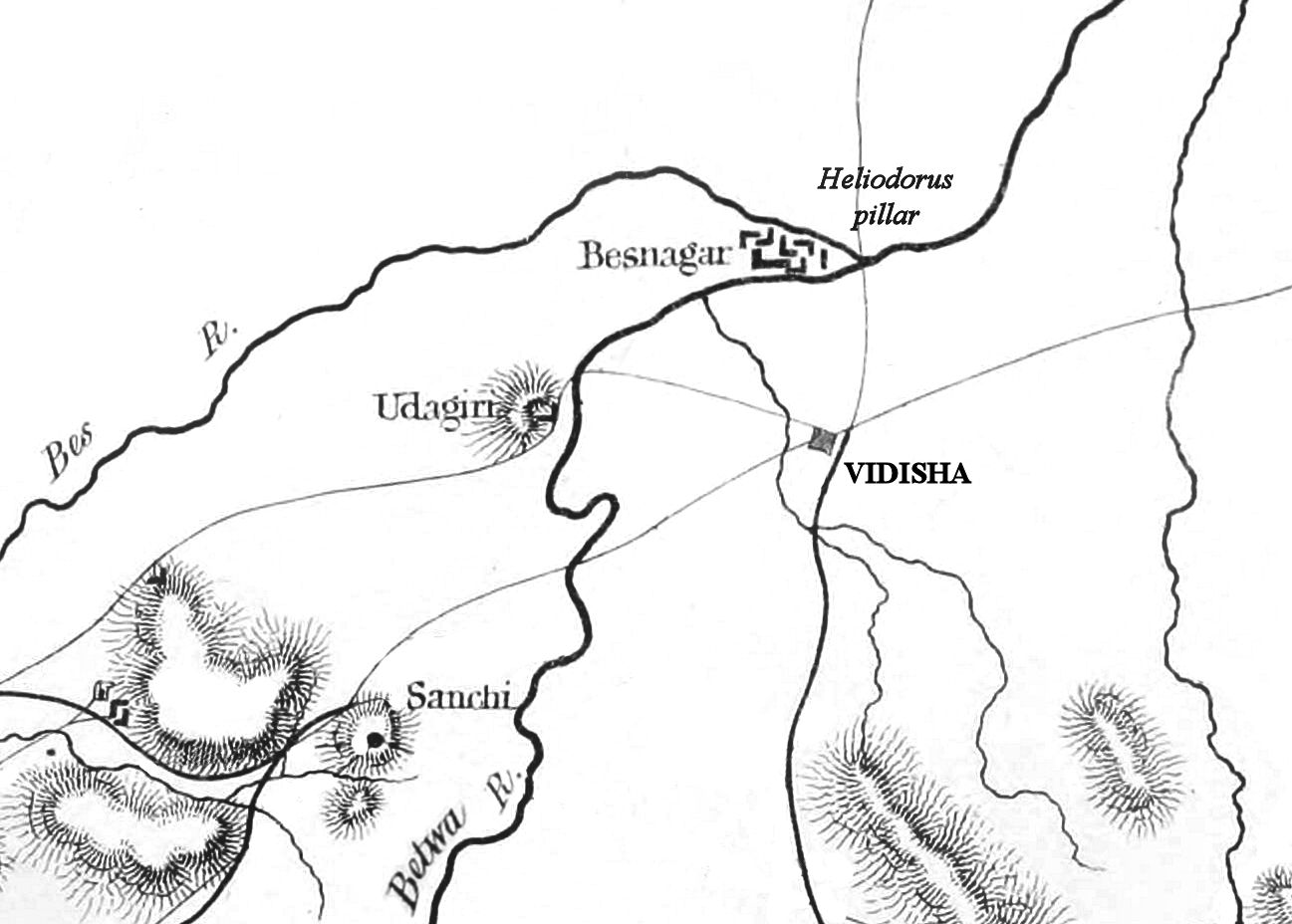 The town is situated east of the
The town is situated east of the
File:Besnagar plan.jpg, Archaeological plan of the old city of Besnagar
File:Besnagar lower levels BSN 3 next to the Heliodorus pillar.jpg, Archaeological layers at Besnagar: the Temple of
 Besnagar was known as Bhelsa during the medieval period. It became famous for the temple of Sun god Bhillasvanin. It was ruled by the Later Gupta king Devagupta and
Besnagar was known as Bhelsa during the medieval period. It became famous for the temple of Sun god Bhillasvanin. It was ruled by the Later Gupta king Devagupta and
 Vidisha is considered to be Puranakshetras Jain tirtha. Vidisha is also believed to be the birthplace of
Vidisha is considered to be Puranakshetras Jain tirtha. Vidisha is also believed to be the birthplace of



 Near the eastern edge of the old town are the remains of a large temple of the late
Near the eastern edge of the old town are the remains of a large temple of the late
 Vidisha Museum or Vidisha District Museum is the main museum of the city of Vidisha.Vidisha District Museum
Vidisha Museum or Vidisha District Museum is the main museum of the city of Vidisha.Vidisha District Museum
/ref> The museum has many sculptures, terracottas and coins, especially from the 9th to the 10th century CE, as well as

Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
.
The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh.
...
state, which was formed in 1948.
Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018.
Demographics
As of the2011 Census of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information ...
, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and females 46.79%. Vidisha has an average literacy rate of 86.88%, higher than the national average of 74.04%: male literacy is 92.29%, and female literacy is 80.98%. In Vidisha, 15% of the population is under 6 years of age.
History
Besnagar
 The town is situated east of the
The town is situated east of the Betwa River
The Betwa (Hindi: बेतवा, Sanskrit: वेत्रवती) is a river in Central and Northern India, and a tributary of the Yamuna. It rises in the Vindhya Range (Raisen) just north of Narmadapuram in Madhya Pradesh and flows north ...
, in the fork of the Betwa and Bes rivers, 9 km from Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen, Raisen town, dist ...
. The town of Besnagar, 3 km from present-day Vidisha on the west side of the river, became an important trade centre in the 6th and 5th centuries BCE, under the Shungas
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the ...
, Nagas, Satavahana
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
s, and Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by se ...
s, and was mentioned in the Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or ''Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravāda'' Buddhism ...
scriptures. The Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
was the governor of Vidisha during his father's lifetime. His Buddhist Empress Vidisha Devi who was also his first wife, was brought up in Vidisha. It finds mention in Kalidasa
Kālidāsa (''fl.'' 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on the Vedas, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata and ...
's '' Meghaduta''.
The ruins of Besnagar were inspected by Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Engineer Group who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly ...
in 1874–1875. Remains of a large defensive wall were found on the western side of the city. Ancient Buddhist railings were also found just outside of the city, which had probably adorned a stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation.
In Buddhism, circumamb ...
. Numerous coins were found, including nine coins of the Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
.
The Heliodorus Pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (near Vidisha, Madhya Pradesh). The pillar was called the ''Garuda-standard'' by Heliodorus, referring to the deity Garuda. The pillar is commonly ...
is a stone column, which was constructed in about 150 BCE. This stone column was erected by the Greek ambassador of the Indo-Greek King Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros ( grc, Ἀντιαλκίδας ὁ Νικηφόρος; epithet means "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who re ...
, who came to the court of Bhagabhadra, a possible Sunga
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the ...
king. Dedicated to Lord Vāsudeva
Vāsudeva ( sa, वासुदेव, ), later incorporated as Vāsudeva-Krishna (, "Krishna, son of Vasudeva"),"While the earliest piece of evidence do not yet use the name Krsna...." in Krishna-Vāsudeva or simply Krishna, was the son of V ...
, this column was constructed in front of the temple of Vāsudeva. The pillar is situated about four kilometers away from the city on Vidisha-Ganj Basoda SH-14, located on the northern bank of the Vais River. It is a 20 feet and 7 inches tall stone pillar, commonly called ''Kham Baba''. The script used in the inscription is Brahmi
Brahmi (; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such ...
but the language is Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
, recording that Heliodorus
Heliodorus is a Greek name meaning "Gift of the Sun". Several persons named Heliodorus are known to us from ancient times, the best known of which are:
*Heliodorus (minister) a minister of Seleucus IV Philopator c. 175 BC
* Heliodorus of Athen ...
erected the pillar as a Garuda Stambha to pay homage to Lord Vasudeva, who was later integrated as a manifestation of Lord Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
.
Vāsudeva
Vāsudeva ( sa, वासुदेव, ), later incorporated as Vāsudeva-Krishna (, "Krishna, son of Vasudeva"),"While the earliest piece of evidence do not yet use the name Krsna...." in Krishna-Vāsudeva or simply Krishna, was the son of V ...
in the forefront, and the Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (near Vidisha, Madhya Pradesh). The pillar was called the ''Garuda-standard'' by Heliodorus, referring to the deity Garuda. The pillar is commonly ...
in the back
File:Besnagar pottery Period V.jpg, Besnagar pottery Period V
File:Besnagar silver punch-marked coins.jpg, Besnagar silver punch-marked coins
Punch-marked coins, also known as ''Aahat coins'', are a type of early coinage of India, dating to between about the 6th and 2nd centuries BC. It was of irregular shape.
History
The study of the relative chronology of these coins has successful ...
.
File:Besnagar Yakshini.jpg, Besnagar Yakshini
''Yakshinis'' or ''yakshis'' (यक्षिणी sa, yakṣiṇī or ''yakṣī''; pi, yakkhiṇī or ''yakkhī'') are a class of female nature spirits in Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain religious mythologies that are different from devas and ...
File:Kalpadruma.jpg, Besnagar Kalpadruma
Kalpavriksha () is a wish-fulfilling divine tree in Indian religions, like Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism. Its earliest descriptions are mentioned in Sanskrit literature. It is also a popular theme in Jain cosmology and Buddhism. ...
File:Besnagar Buddhist railings.jpg, Besnagar Buddhist railings
File:Rail pillars from Besnagar Sunga period.jpg, Besnagar Buddhist railings
File:Besnagar pillar capitals.jpg, Besnagar pillar capitals
File:Heliodorus pillar with elevation.jpg, View of Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (near Vidisha, Madhya Pradesh). The pillar was called the ''Garuda-standard'' by Heliodorus, referring to the deity Garuda. The pillar is commonly ...
File:GangaBeshnagarBhopalState.jpg, Besnagar Ganga statue
Emergence as Bhelsa
 Besnagar was known as Bhelsa during the medieval period. It became famous for the temple of Sun god Bhillasvanin. It was ruled by the Later Gupta king Devagupta and
Besnagar was known as Bhelsa during the medieval period. It became famous for the temple of Sun god Bhillasvanin. It was ruled by the Later Gupta king Devagupta and Rashtrakuta
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
king Krishna III
Krishna III whose Kannada name was Kannara (r. 939 – 967 C.E.) was the last great warrior and able monarch of the Rashtrakuta dynasty of Manyakheta. He was a shrewd administrator and skillful military campaigner. He waged many wars to bring b ...
. The name is first noted in an inscription of 878 AD by a merchant Hatiaka of Paravada community. The 12th century Tri-shashthi-shalaka-purusha-charitra mentions an image of Bhillasvamin at Vidisa, along with a copy of Jivant Swami buried in the sand. Minhajuddin's Tabaqat-i-Nusiri states that the temple was destroyed by Iltutmish
Shams ud-Din Iltutmish ( fa, شمس الدین ایلتتمش; died 30 April 1236, ) was the third of the Mamluk kings who ruled the former Ghurid territories in northern India. He was the first Muslim sovereign to rule from Delhi, and is thus ...
in A D. 1233–34.
In 1293, Alauddin Khalji
Alaud-Dīn Khaljī, also called Alauddin Khilji or Alauddin Ghilji (), born Ali Gurshasp, was an emperor of the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over lar ...
of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
sacked the city as a general of Sultan Jalaluddin. The attack was illustrative of Vidisha's importance in the medieval era. In 1532 Bhilsa was sacked by Bahadur Shah of Gujarat Sultanate. It then passed on to the Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syno ...
Sultans
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it c ...
, the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
and the Scindia
The Scindia dynasty (anglicized from Shinde) is a Hindu Maratha dynasty of maratha origin that ruled the erstwhile State of Gwalior. It had the Patil-ship of Kumberkerrab in Wai. It was founded by Ranoji Scindia, who started as a personal servan ...
s.
Jainism in Vidisha
 Vidisha is considered to be Puranakshetras Jain tirtha. Vidisha is also believed to be the birthplace of
Vidisha is considered to be Puranakshetras Jain tirtha. Vidisha is also believed to be the birthplace of Shitalanatha
Shitalanatha was the tenth tirthankara of the present age according to Jainism. According to Jain beliefs, he became a siddha, a liberated soul which has destroyed all of its karma. Jains believe Shitalanatha was born to King Dradhrath and Quee ...
, the tenth tirthankar. There are 14 temples in Vidisha, among which Bada Mandir, Bajramath Jain temple, Maladevi temple, Gadarmal temple and Pathari Jain temple, built between 9th-10th centuries CE, are the most prominent. These temples are rich in architecture.
Climate
Historic places and monuments



 Near the eastern edge of the old town are the remains of a large temple of the late
Near the eastern edge of the old town are the remains of a large temple of the late Paramara
The Paramara dynasty (IAST: Paramāra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surrounding areas in west-central India between 9th and 14th centuries. They belonged to the Parmara clan of the Rajputs.
The dynasty was established in either th ...
period known as the Bijamaṇḍal. The building was probably started in the second half of the 11th century. That it was never finished is evidenced by the unfinished carved niches and architectural pieces found round the base of the temple plinth. On top of the plinth is a small mosque made using pillars, one of which has an inscription dating probably from the time of king Naravarman (''circa'' 1094–1134). It is a devotional inscription revering Carccikā (i.e. Cāmuṇḍā), of whom he was a devotee. The ''miḥrāb'' suggests the mosque was constructed in the late 14th century. To one side of the Bijamaṇḍal is a store house of the Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexande ...
containing many sculptures collected in the neighbourhood. A step-well of the 7th century is in the same campus and has, beside the entrance, two tall pillars with Kṛṣṇa scenes. These are the earliest Kṛṣṇa scenes in the art of central India. The dimensions of Bijamandal Temple at Vidisha are comparable to those of Konark
Konark is a medium town in the Puri district in the state of Odisha, India. It lies on the coast by the Bay of Bengal, 65 kilometres from the capital of the state, Bhubaneswar. It is the site of the 13th-century Sun Temple, also known as t ...
in Orissa.
Lohangi Pir is a rock formation in Vidisha District that derives its name from Shaykh Jalal Chishti, a saint who was locally known as Lohangi Pir. This small domed building is a tomb, which has two Persian inscriptions on it. One of the inscriptions dates back to 1460 CE, while the other is from 1583 CE. The tank and a large bell-capital dating back to the 1st century BCE can be seen on the nearby hill. Near the tomb are the remains of a medieval temple that survived as a pillared crypt. These are dedicated to Goddess Annapurna. Lohangi is a large rock right in the heart of Vidisha, within walking distance of the railway station, is of religious and historical significance in the region.
Udaygiri is less than 10 km from Vidisha town. It is a series of at least 20 caves, containing both Hindu and Jain sculptures from the Gupta Era, sometime between the 4th and 5th century CE. According to Jain texts, Tirthankara Sheetal Nath attained nirvana here. It is basically a small hill where intricate sculptures have been cut out of the rocks.
Maladevi temple is a grand Portal of ninth century CE, situated on the eastern slope of a hill and built on a huge platform cut out of the hillside and strengthened by a massive retaining wall, Maladevi temple's imposing structure provides a panoramic valley view, in Gyaraspur, about 40 km from Vidisha along NH-86.
Hindola Torana - Hindola means a swing and Torana is an arched gate - is a magnificent artwork of the 9th century or medieval period, situated in Gyaraspur. It is a developed, ornamental and decorated arched gate made of sandstone. On both of its pillars, Lord Vishnu's ten incarnations are engraved. Near it, four carved and sculpted pillars and beams seem to be the ruins of Trimurthy temple set on one raised platform, as Lord Shiva, Lord Ganesha, Goddess Parvati and their servants are sculpted on these pillars and beams. The gate may be an entrance gate for a temple for Vishnu, Shiva or Thirumurthy.
Bajramath Temple
Bajramath Temple is a Jain temple located in Gyaraspur town of Vidisha in state of Madhya Pradesh, India.
About temple
Bajramath Temple is famous for carvings and craftmanship, and are representative of post- Gupta architecture. This tem ...
is situated in Gyaraspur, on NH-146 behind the Sub-Judicial Magistrate and Tehsildar's Office. The temple faces the east, and was a Hindu temple later transformed into a Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
temple. It is just opposite the hill on which Maladevi temple is situated.
Dashavtar Temple is situated on the north of the local lake, where ruins of a group of small Vaishnava shrines can be found. These small Vaishnava shrines are popularly known as Sadhavatara Temple. The temple comprises a large open pillared hall, in which the pillars are dedicated to the ten incarnations of Vishnu. These pillars date back from 8th to 10th century CE. Towards the western bank of the lake lie the ruins of sati pillars that date back to 9th or 10th century CE. One of these pillars is carved with four sculptured faces that depict a seated group of Hara-Gauri.
Girdhari Temple, which is known for its sculptures and fine carvings, is a popular attraction in Sironj. The ancient shrines of Jatashankar and Mahamaya are located close to this temple. Jatashankar Temple is situated 3 km towards the south-west of Sironj in the forest area. On the other hand, Mahamaya Temple is situated 5 km south-west of Sironj.
Udayeshwara Temple, located in Udaipur village of the Basoda Tehsil, is one of the most prominent Hindu shrines in the region. The inscriptions found in this temple suggest that the Udaipur Town was founded by the Parmara King Udayaditya during the 11th century CE. Other inscriptions found at the temple suggest that Parmara King Udayaditya dedicated it to Lord Shiva.
Vidisha District Museum
 Vidisha Museum or Vidisha District Museum is the main museum of the city of Vidisha.Vidisha District Museum
Vidisha Museum or Vidisha District Museum is the main museum of the city of Vidisha.Vidisha District Museum/ref> The museum has many sculptures, terracottas and coins, especially from the 9th to the 10th century CE, as well as
Harrappa
Harappa (; Urdu/ pnb, ) is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal. The Bronze Age Harappan civilisation, now more often called the Indus Valley Civilisation, is named after the site, which takes its name from a mode ...
n art.
Notable people
*Kailash Satyarthi
Kailash Satyarthi (born 11 January 1954) is an Indian social reformer who campaigned against child labor in India and advocated the universal right to education. In 2014, he was the co-recipient of the Nobel Peace Prize, along with Malala You ...
- Born as Kailash Sharma, on 11 January 1954, in the Vidisha district.

Transport
Vidisha is a railway station on the Delhi-Chennai, Delhi-Mumbai main line of the Central Railway, at a distance of 54 km fromBhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
, the capital of Madhya Pradesh. Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen, Raisen town, dist ...
on the Jhansi-Itarsi section of the West Central Railway and Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
to Bina triple electrified broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
lines, from Bina to Katni
Katni officially Murwara is a city on the banks of the Katni River in Madhya Pradesh, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Katni District. It is in the Mahakoshal region of central India. The city is from the divisional headquarters ...
double electrified Lines, Vidisha 102 km from Bina, and Vidisha, 9 km from Sanchi, are more convenient. Vidisha is also well-connected by road.
Education
Vidisha is well known for its educational institutions. Many of the primary and secondary schools are affiliated with the M.P. Board. Some schools choose to be affiliated with Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). There is a Grant-in-Aid Autonomous College called Samrat Ashok Technological Institute.Atal Bihari Vajpayee Government Medical College, Vidisha
Atal Bihari Vajpayee Government Medical College (Hindi: अटल बिहारी वाजपेयी शास्किय चिकित्सा महाविद्यालय) is a government medical college in Vidisha, Madhya Pra ...
is a medical college in Vidisha. It became functional in 2018 and received its first batch of students in the same year. The number of students admitted in 2018 was 150 whereas in 2019 the intake was increased to 180. Students are admitted to the college through NEET-UG
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (Undergraduate) or NEET (UG), formerly the All India Pre-Medical Test (AIPMT), is an all India pre-medical entrance test for students who wish to pursue undergraduate medical ( MBBS), dental ( BDS ...
examination.
References
* * * * * * * {{Authority control Cities in Madhya Pradesh 9th-century Jain temples Jain temples in Madhya Pradesh