|
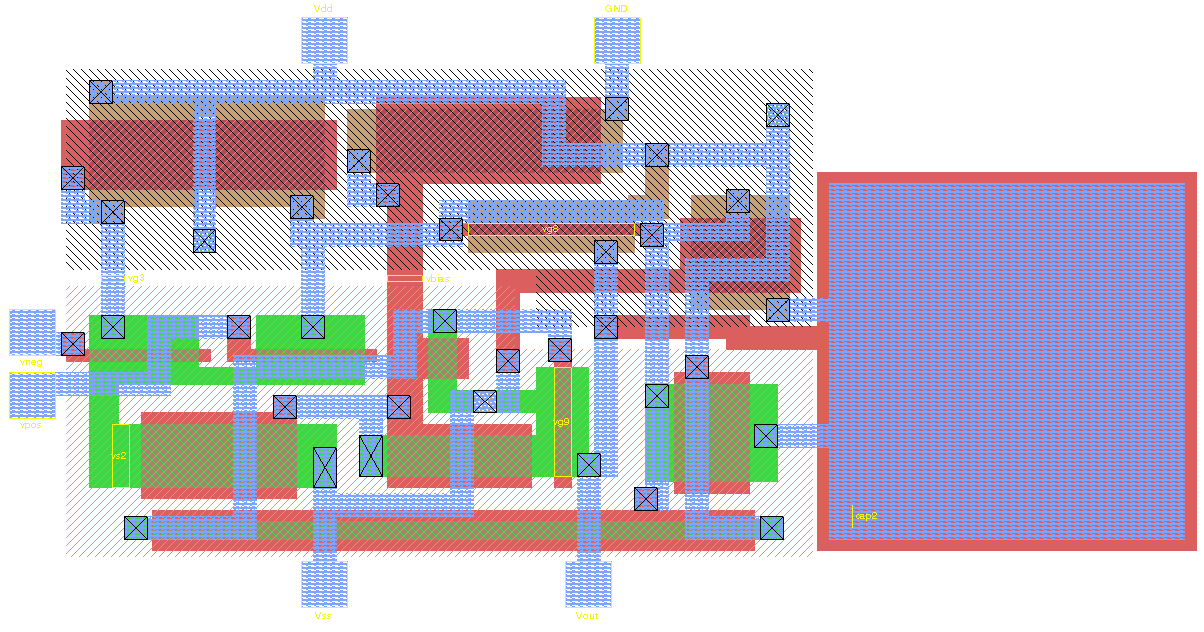
VerilogCSP
In integrated circuit design, VerilogCSP is a set of macros added to Verilog HDL to support Communicating Sequential Processes (CSP) channel communications. These macros are intended to be used in designing digital asynchronous circuits. VerilogCSP also describes nonlinear pipelines A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The Un ... and high-level channel timing properties, such as forward and backward latencies, minimum cycle time, and slack. External links VerilogCSP Homepage References {{Reflist Hardware description languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communicating Sequential Processes
In computer science, communicating sequential processes (CSP) is a formal language for describing patterns of interaction in concurrent systems. It is a member of the family of mathematical theories of concurrency known as process algebras, or process calculi, based on message passing via channels. CSP was highly influential in the design of the occam programming language and also influenced the design of programming languages such as Limbo, RaftLib, Erlang (programming language), Erlang, Go (programming language), Go, Crystal (programming language), Crystal, and Clojure's core.async. CSP was first described by Tony Hoare in a 1978 article, and has since evolved substantially. CSP has been practically applied in industry as a tool for formal specification, specifying and verifying the concurrent aspects of a variety of different systems, such as the T9000 Transputer, as well as a secure e-commerce system. The theory of CSP itself is also still the subject of active research, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit Design
Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular Boolean logic, logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits (ICs). An IC consists of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography. IC design can be divided into the broad categories of Digital data, digital and analog electronics, analog IC design. Digital IC design is to produce components such as microprocessors, FPGAs, memories (Random-access memory, RAM, Read-only memory, ROM, and flash memory, flash) and digital Application-specific integrated circuit, ASICs. Digital design focuses on logical correctness, maximizing circuit density, and placing circuits so that clock and timing signals are routed efficiently. Analog IC design also has specializations in power IC design and Radio frequency, RF IC design. Analog IC design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro (computer Science)
In computer programming, a macro (short for "macro instruction"; ) is a rule or pattern that specifies how a certain input should be mapped to a replacement output. Applying a macro to an input is known as macro expansion. The input and output may be a sequence of lexical tokens or characters, or a syntax tree. Character macros are supported in software applications to make it easy to invoke common command sequences. Token and tree macros are supported in some programming languages to enable code reuse or to extend the language, sometimes for domain-specific languages. Macros are used to make a sequence of computing instructions available to the programmer as a single program statement, making the programming task less tedious and less error-prone. Thus, they are called "macros" because a "big" block of code can be expanded from a "small" sequence of characters. Macros often allow positional or keyword parameters that dictate what the conditional assembler program gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verilog HDL
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits, with the highest level of abstraction being at the register-transfer level. It is also used in the verification of analog circuits and mixed-signal circuits, as well as in the design of genetic circuits. In 2009, the Verilog standard (IEEE 1364-2005) was merged into the SystemVerilog standard, creating IEEE Standard 1800-2009. Since then, Verilog has been officially part of the SystemVerilog language. The current version is IEEE standard 1800-2023. Overview Hardware description languages such as Verilog are similar to software programming languages because they include ways of describing the propagation time and signal strengths (sensitivity). There are two types of assignment operators; a blocking assignment (=), and a non-blocking (>>. A generate–endgenerate construct (similar to VHDL's g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asynchronous Circuit
Asynchronous circuit (clockless or self-timed circuit) is a sequential logic, sequential digital logic electrical network, circuit that does not use a global clock circuit or clock signal, signal generator to synchronize its components. Instead, the components are driven by a handshaking circuit which indicates a completion of a set of instructions. Handshaking works by simple data transfer Communications protocol, protocols. Many synchronous circuits were developed in early 1950s as part of bigger asynchronous systems (e.g. ORDVAC). Asynchronous circuits and theory surrounding is a part of several steps in integrated circuit design, a field of digital electronics engineering. Asynchronous circuits are contrasted with synchronous circuits, in which changes to the signal values in the circuit are triggered by repetitive pulses called a clock signal. Most digital devices today use synchronous circuits. However asynchronous circuits have a potential to be much faster, have a lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipeline (computing)
In computing, a pipeline, also known as a data pipeline, is a set of data processing elements connected in series, where the output of one element is the input of the next one. The elements of a pipeline are often executed in parallel or in time-sliced fashion. Some amount of buffer storage is often inserted between elements. Concept and motivation Pipelining is a commonly used concept in everyday life. For example, in the assembly line of a car factory, each specific task—such as installing the engine, installing the hood, and installing the wheels—is often done by a separate work station. The stations carry out their tasks in parallel, each on a different car. Once a car has had one task performed, it moves to the next station. Variations in the time needed to complete the tasks can be accommodated by "buffering" (holding one or more cars in a space between the stations) and/or by "stalling" (temporarily halting the upstream stations), until the next station becomes avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latency (engineering)
Latency, from a general point of view, is a time delay between the Causality, cause and the effect of some physical change in the system being observed. Lag (video games), Lag, as it is known in Gaming culture, gaming circles, refers to the latency between the input to a simulation and the visual or auditory response, often occurring because of network delay in online games. The original meaning of “latency”, as used widely in psychology, medicine and most other disciplines, derives from “latent”, a word of Latin origin meaning “hidden”. Its different and relatively recent meaning (this topic) of “lateness” or “delay” appears to derive from its superficial similarity to the word “late”, from the old English “laet”. Latency is physically a consequence of the limited velocity at which any Event (relativity), physical interaction can propagate. The magnitude of this velocity is always less than or equal to the speed of light. Therefore, every physical s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |