|
Verderer
Verderers are forestry officials in England who deal with common land in certain former royal hunting areas which are the property of the Crown. The office was developed in the Middle Ages to administer forest law on behalf of the King. Verderers investigated and recorded minor offences such as the taking of venison and the illegal cutting of woodland, and dealt with the day-to-day forest administration. In the modern era, verderers are still to be found in the New Forest, the Forest of Dean, and Epping Forest, where they serve to protect commoning practices, and conserve the traditional landscape and wildlife. Origins Verderers were originally part of the ancient judicial and administrative hierarchy of the vast areas of English forests and Royal Forests set aside by William the Conqueror for hunting. The title Verderer comes from the Norman word ‘vert’ meaning green and referring to woodland. These forests were divided into provinces each having a Chief Justice who travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Forest
The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, featuring in the Domesday Book. It is the home of the New Forest Commoners, whose ancient rights of common pasture are still recognised and exercised, enforced by official Verderer (New Forest), verderers and Agister (New Forest), agisters. In the 18th century, the New Forest became a source of timber for the Royal Navy. It remains a habitat for many rare birds and mammals. The boundaries of the forest have varied over time and depend on the purpose of delimiting them. It is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest. Several areas are Geological Conservation Review sites, including Mark Ash Wood, Shepherd’s Gutter, Cranes Moor, Studley Wood, and Wood Green. There are also a number of Nature Conservation Review sites. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
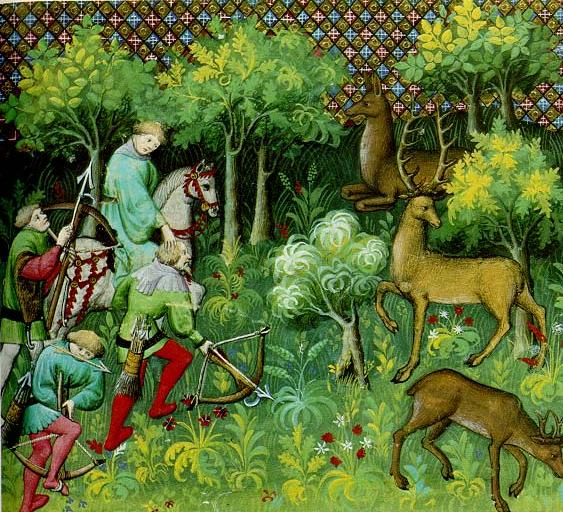
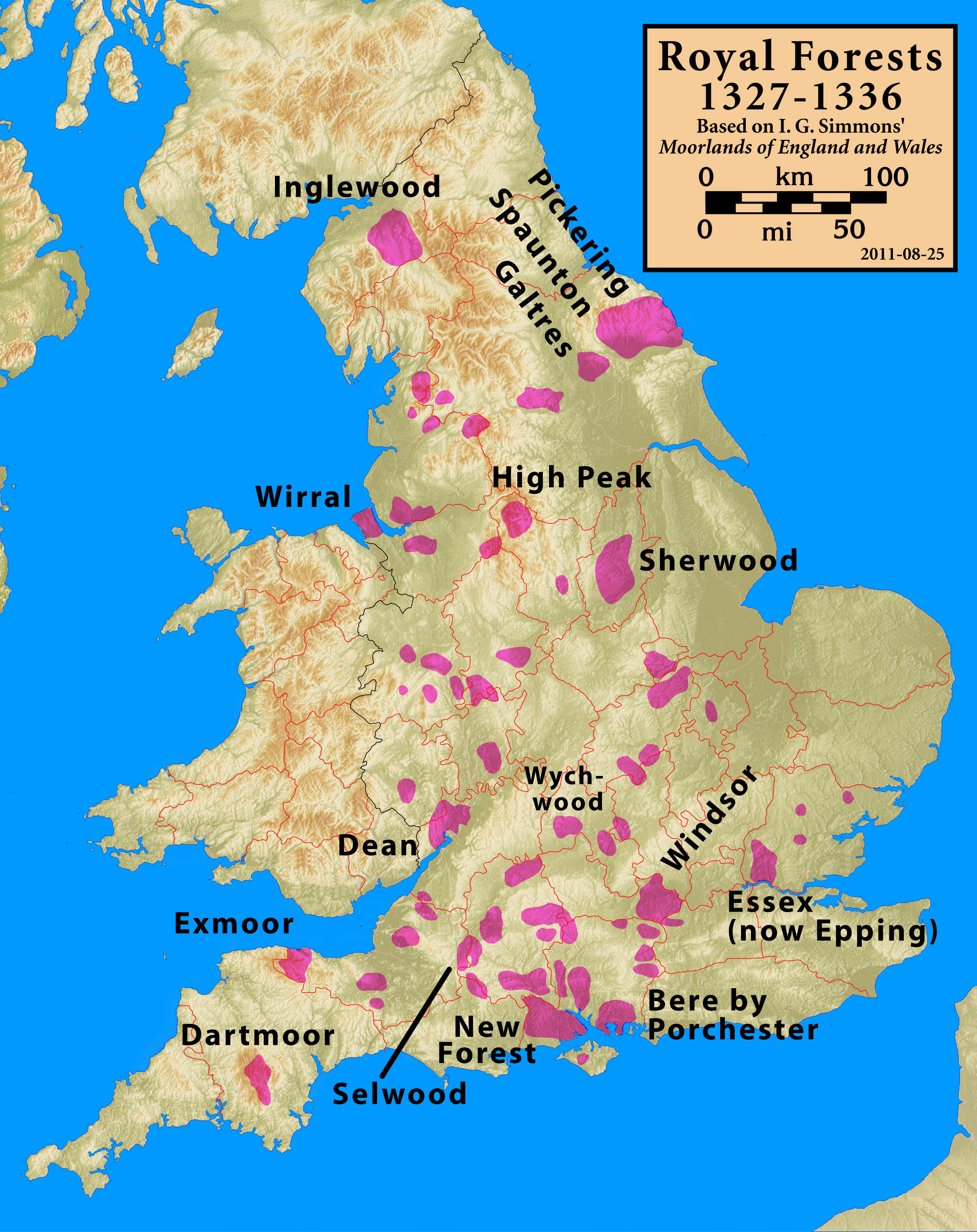
Royal Forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the original medieval sense was closer to the modern idea of a "preserve" – i.e. land legally set aside for specific purposes such as royal hunting – with less emphasis on its composition. There are also differing and contextual interpretations in Continental Europe derived from the Carolingian and Merovingian legal systems. In Anglo-Saxon England, though the kings were great huntsmen, they never set aside areas declared to be "outside" (Latin ''foris'') the law of the land. Historians find no evidence of the Anglo-Saxon monarchs (c. 500 to 1066) creating forests. However, under the Norman kings (after 1066), by royal prerogative forest law was widely applied. The law was designed to protect the " venison and the vert". In this sense, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Land
Common land is collective land (sometimes only open to those whose nation governs the land) in which all persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect wood, or to cut turf for fuel. A person who has a right in, or over, common land jointly with another or others is usually called a commoner. In Great Britain, common land or former common land is usually referred to as a common; for instance, Clapham Common and Mungrisdale Common. Due to enclosure, the extent of common land is now much reduced from the hundreds of square kilometres that existed until the 17th century, but a considerable amount of common land still exists, particularly in upland areas. There are over 8,000 registered commons in England alone. Origins Originally in medieval England the common was an integral part of the manor, and was thus part of the estate held by the lord of the manor under a grant from the Crown or a superior peer (who in turn held hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
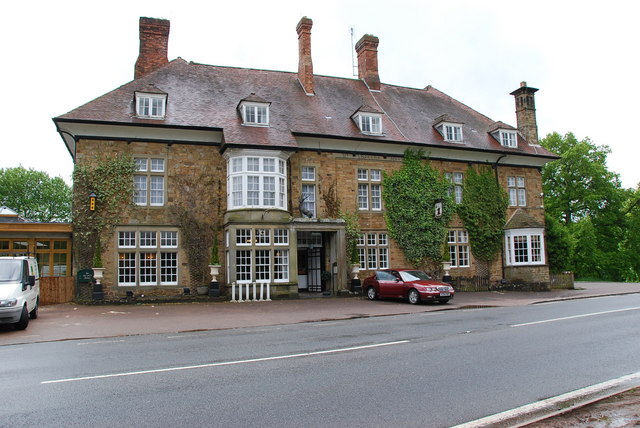
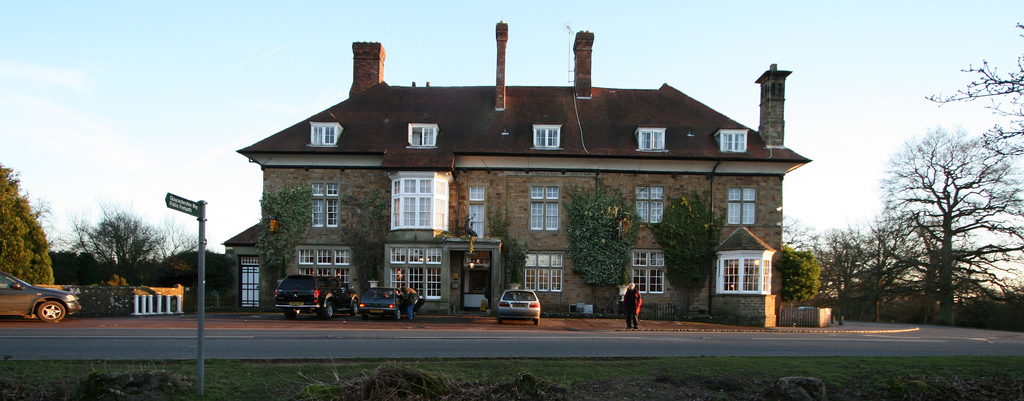
Speech House
The Speech House is a hotel and former administrative building in the Forest of Dean in Gloucestershire Gloucestershire ( , ; abbreviated Glos.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by Herefordshire to the north-west, Worcestershire to the north, Warwickshire to the north-east, Oxfordshire ..., England, lying at the centre of the forest on the road from Coleford to Cinderford. The building was originally constructed as a hunting lodge for Charles II and the Speech House was authorised by the Dean Forest Act 1667 ( 19 & 20 Cha. 2. c. 8) as part of a reorganisation of the open land in the area, and its construction was finished in 1682. It hosts the "Court of the Speech", a sort of parliament for the Verderers and Free Miners managing the forest, game, and mineral resources of the area. It was severely damaged in the Revolution of 1688, but repaired soon thereafter. Around 1840 it began to be used as an inn, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Brady
Sir Antonio Brady (10 November 1811 – 12 December 1881) was an English naturalist, social reformer and British Admiralty official. Brady was born at Deptford on 10 November 1811, being the eldest son of Anthony Brady of the Deptford victualling yard, then storekeeper at the Royal William victualling yard, Plymouth, by his marriage, on 20 December 1810, with Marianne, daughter of Francis Perigal and Mary Ogier. He was educated at Colfe's School, Lewisham, and then entered the Civil Service as a junior clerk in the Victoria victualling yard, Deptford, on 29 November 1828, and, having served there and at Plymouth and Portsmouth, was, through the recommendation of Sir James Graham, promoted to headquarters at Somerset House as a second-class clerk in the accountant-general's office on 26 June 1844. He was gradually promoted until in 1864 he became registrar of contracts, and having subsequently assisted very materially in reorganising the office, he was made the first superintende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Johnston (English Politician)
Andrew Johnston may refer to: * Andrew Johnston (critic) (1968–2008), film and TV critic * Andrew Johnston (English politician) (1835–1895), Liberal Party Member of Parliament for Southern Essex 1868–1874 * Andrew Johnston (golfer) (born 1989), English golfer * Andrew Johnston (poet) (born 1963), New Zealand poet * Andrew Johnston (Scottish politician) ( – 1862), Whig Member of Parliament for Anstruther Burghs 1831–1832 and St Andrews Burghs 1832–1837 * Andrew Johnston (singer) (born 1994), British boy soprano * Andrew Johnston (New Jersey politician) (1694–1762), politician from New Jersey * Andrew Johnston (footballer) (born 1970), Australian rules footballer * Andrew Johnston (surgeon) (1770–1833), president of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland *Andrew Johnston, aka Andrew Griswold, Northern Irish musician with The Dangerfields See also * Andrew Johnson (other) {{hndis, name=Johnston, Andrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Charles Baring
Thomas Charles Baring DL (16 May 1831 – 2 April 1891) was a British banker and Conservative Party politician. Life Baring, informally called "T. C." or "Charley" to distinguish him from the other Thomases in the Baring family, was the son of the Right Reverend Charles Baring, Bishop of Durham, younger son of Sir Thomas Baring, 2nd Baronet. His mother was Mary Ursula, daughter of Charles Sealy. He was educated at Harrow and Wadham College, Oxford, before becoming a partner in the family firm of Baring Brothers & Co. In 1874 Baring gave £30,000 to enable Magdalen Hall in Oxford to be refounded as Hertford College, Oxford by means of an act of parliament. He entered Parliament for Essex South in 1874, a seat he held until 1885, and later represented the City of London from 1887 to 1891. Baring also served as a Justice of the Peace for Essex, Middlesex, London and Westminster, was a member of the Royal Commission on Loss of Life at Sea from 1885 to 1887, and the author o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west; it is sited from Monmouth, from Bristol, and east of the England and Wales border, border with Wales. Gloucester has a population of around 132,000, including suburban areas. It is a port, linked via the Gloucester and Sharpness Canal to the Severn Estuary. Gloucester was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans and became an important city and ''Colonia (Roman), colony'' in AD 97, under Nerva, Emperor Nerva as ''Glevum, Colonia Glevum Nervensis''. It was granted its first charter in 1155 by Henry II of England, Henry II. In 1216, Henry III of England, Henry III, aged only nine years, was crowned with a gilded iron ring in the Chapter House of Gloucester Cathedral. Gloucester's significance in the Middle Ages is unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, historic centre of London, though it forms only a small part of the larger Greater London metropolis. The City of London had a population of 8,583 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, however over 500,000 people were employed in the area as of 2019. It has an area of , the source of the nickname ''the Square Mile''. The City is a unique local authority area governed by the City of London Corporation, which is led by the Lord Mayor of London, Lord Mayor of the City of London. Together with Canary Wharf and the West End of London, West End, the City of London forms the primary central business district of London, which is one of the leading financial centres of the world. The Bank of England and the London Stock Exchange are both ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Fowell Buxton, 3rd Baronet
Sir Thomas Fowell Buxton, 3rd Baronet, (26 January 1837 – 28 October 1915), commonly known as Sir Fowell Buxton, was the Governor of South Australia from 29 October 1895 until 29 March 1899. He was the grandson of Sir Thomas Fowell Buxton, a British MP and social reformer, and the son of Sir Edward North Buxton, also an MP. He attended Harrow School and Trinity College, Cambridge. He raised the part-time 3rd (Truman, Hanbury, Buxton) Tower Hamlets Rifle Volunteer Corps mainly from employees of the family's Black Eagle Brewery in Spitalfields and was commissioned as its captain commandant on 4 May 1860.Ray Westlake, ''Tracing the Rifle Volunteers'', Barnsley: Pen and Sword, 2010, ISBN 978-1-84884-211-3, p. 239. The unit became part of the 1st Administrative Battalion, Tower Hamlets Rifle Volunteer Corps (later 2nd Tower Hamlets Rifles), in which he was promoted to major on 24 July 1863 and lieutenant-colonel on 23 January 1863. Sir Fowell retired from the command on 23 No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epping Forest Act 1878
During the middle of the nineteenth century, a number of initiatives were started to protect the rights of the public to use open spaces and for the areas to be conserved for their specific environmental features. Some notable people of the time devoted themselves to societies such as the Commons Preservation Society, now known as the Open Spaces Society, in order to gain protection for some clearly defined areas . One of these areas was Epping Forest on the outskirts of London. It was an area beginning to suffer encroachments of building development and enclosure. The local people of Loughton were also, by tradition, taking a limited quantity of wood from the forest under what was termed their 'lopping rights'. The enclosure of the lands within the forest bounds was threatening the performance of the annual lopping tradition and thus, a dispute also arose over the removal by private individuals of forest considered to be in public ownership. Following the intervention of a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |