|
Velyki Mosty
Velyki Mosty (, IPA: Help:IPA">vəliki_masti.html" ;"title="Help:IPA.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Help:IPA">vəliki masti">Help:IPA.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Help:IPA">vəliki masti ; ) is a city in Chervonohrad Raion of Lviv Oblast (oblast, region) of Western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Velyki Mosty urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Its population is . In the Kingdom of Poland, the village of Mosty was a royal property, with its own starostas. The village itself was established in 1472, and was part of Belz Voivodeship. In the late 15th century, Mosty was ransacked and destroyed in a Crimean Tatars raid, and in July 1497, during the Moldavian expedition of John I Albert, a unit of Teutonic Knights under Johann von Tiefen, called upon by the Polish king, marched through the village. On 23 July 1549, during the period known as the Polish Golden Age, Mosty received Magdeburg rights. Following the order of King Zygmunt August, a nobleman Andrzej Rokicki became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form.International Phonetic Association (IPA), ''Handbook''. The IPA is used by lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguistics, linguists, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of wiktionary:lexical, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, phonemes, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, and the separation of words and syllables. To represent additional qualities of speech—such as tooth wiktionary:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the state, exercising extensive political rights and power. Szlachta as a class differed significantly from the feudal nobility of Western Europe. The estate was officially abolished in 1921 by the March Constitution."Szlachta. Szlachta w Polsce" ''Encyklopedia PWN'' The origins of the ''szlachta'' are obscure and the subject of several theories. Traditionally, its members owned land (allods), [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygmunt August
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the last male monarch from the Jagiellonian dynasty. Sigismund was the only son of Italian-born Bona Sforza and Sigismund the Old. From the beginning he was groomed and extensively educated as a successor. In 1529 he was crowned '' vivente rege'' while his father was still alive. Sigismund Augustus continued a tolerance policy towards minorities and maintained peaceful relations with neighbouring countries, with the exception of the Northern Seven Years' War which aimed to secure Baltic trade. Under his patronage, culture flourished in Poland; he was a collector of tapestries from the Low Countries and collected military memorabilia as well as swords, armours and jewellery. Sigismund Augustus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the German city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Bohemia, Hungary, Poland and Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries, the Baltic states, and the interior (for example Braunschweig). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Golden Age
The Polish Golden Age was the Renaissance period in Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, roughly corresponding to the period of rule of the King Sigismund I the Old and his son, Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellonian Dynasty monarchs, until his death in 1572. Some historians reckon the Polish Golden Age to have continued to the mid-17th century, when the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was ravaged by the Khmelnytsky Uprising (1648–57) and by the Swedish and Russian invasion. During its Golden Age, the Commonwealth became one of the largest kingdoms of Europe, stretching from modern Estonia in the north to Moldavia in the east and Bohemia in the west. In the 16th century the Commonwealth grew to almost 1 million km2, with a population of 11 million. It prospered from its enormous grain, wood, salt, and cloth exports to Western Europe via the Baltic Sea ports of Gdańsk, Elbląg, Riga, Memel, and Königsberg. The Commonwealth's major cities included Poznań, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Von Tiefen
Johann von Tiefen (died 25 August 1497) was the 35th Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1489 to 1497. Von Tiefen's date of birth is unknown, although it is believed he hailed from Switzerland. His beginnings in the Teutonic Order start in Elbing, where he was the right-hand man of the Grand Hospitaller, Heinrich Reuß von Plauen. In 1474 he became the Komtur of Memel and two years later, the Grand Komtur. He represented the Teutonic Order on several diplomatic missions to many European courts. During the times of Grand Master Martin Truchseß von Wetzhausen, von Tiefen tried to release the pressure between the Teutonic Order and the Kingdom of Poland. In 1480 he became the Komtur of Brandenburg (Frisches Haff) and the Grand Hospitaller of the Order. On June 25, 1487, von Tiefen issued a charter in Drengfurt to establish a church in Alt Jucha. In 1489 the Order's Capitulum named von Tiefen Grand Master. Immediately after being elected, he went to Poland and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having a small voluntary and mercenary military membership, serving as a crusading military order for the protection of Christians in the Holy Land and the Baltics during the Middle Ages. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in german: Orden der Brüder vom Deutschen Haus der He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I Albert
John I Albert ( pl, Jan I Olbracht; 27 December 1459 – 17 June 1501) was King of Poland from 1492 until his death in 1501 and Duke of Głogów (Glogau) from 1491 to 1498. He was the fourth Polish sovereign from the Jagiellonian dynasty, the son of Casimir IV and his wife Elizabeth of Austria. As a kin to the House of Habsburg, John Albert was groomed to become emperor in the Holy Roman Empire, a plan which ultimately failed. He was well-educated and tutored by scholars such as Johannes Longinus and Callimachus, whom he subsequently befriended. Heavily influenced by the Italian Renaissance, John sought to strengthen royal authority at the expense of the Catholic Church and the clergy. In 1487, he led a force against the Ottoman Empire and defeated the Tatars of the Crimean Khanate during the early phase of the Polish–Ottoman War. In the aftermath of the Bohemian–Hungarian War, John unsuccessfully attempted to usurp Hungary from his elder brother Vladislaus but was inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
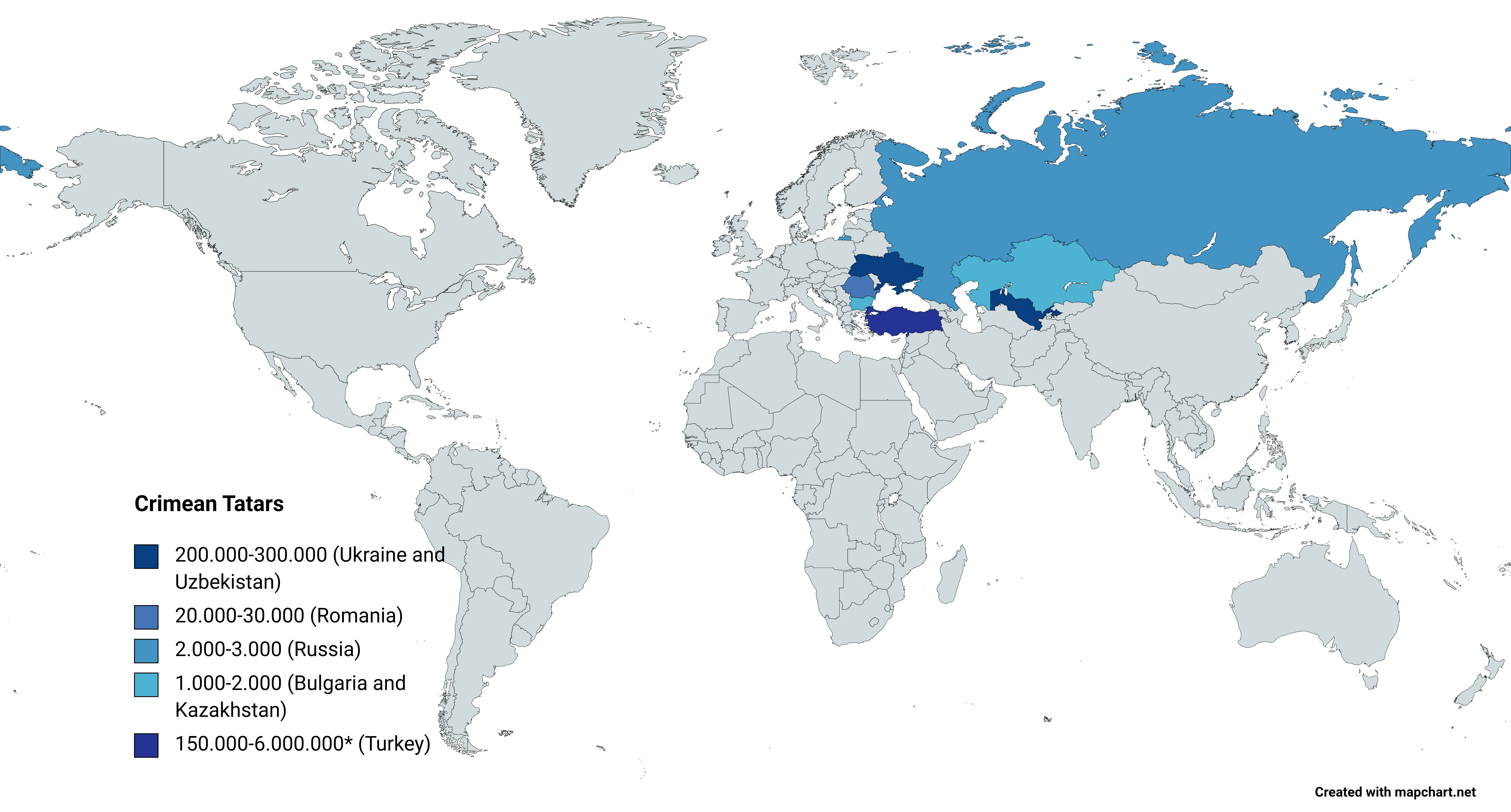
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belz Voivodeship
Bełz Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo bełskie, la, Palatinatus Belzensis) was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from 1462 to the Partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. Together with the Ruthenian Voivodeship it was part of Red Ruthenia, Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown. The voivodeship was created by King Kazimierz Jagiellonczyk, and had four senators in the Senate of the Commonwealth (the Voivode and the Castellan of Belz, as well as Castellans of Lubaczow and Busk). History Bełz Voivodeship was formed in 1462 from the territories of the Duchy of Belz, after the Duchy was annexed by the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. Zygmunt Gloger in his monumental book Historical Geography of the Lands of Old Poland gives a detailed description of the voivodeship: “Belz, on the Zaloka river, was one of the oldest gords of the Czerwien Land. In 981, the province was seized by Vladimir the Great. Recovered by Bolesław Chrobry in 1018, it again b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starosta
The starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', german: link=no, Starost, Hauptmann) is a term of Slavic origin denoting a community elder whose role was to administer the assets of a clan or family estates. The Slavic root of starost translates as "senior". Since the Middle Ages, it has meant an official in a leadership position in a range of civic and social contexts throughout Central and Eastern Europe. In terms of a municipality, a ''starosta'' was historically a senior royal administrative official, equivalent to the County Sheriff or the outdated Seneschal, and analogous to a gubernator. In Poland, a ''starosta'' would administer crown territory or a delineated district called a '' starostwo''. In the early Middle Ages, the ''starosta'' could head a settled urban or rural community or other communities, such as a church starosta, or an ''artel'' starosta, etc. The starosta also functioned as the master of ceremonies. Poland Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_and_the_Columns_of_Gediminas%2C_minted_in_1568.jpg)