|
Allod
In the law of the Middle Ages and early Modern Period and especially within the Holy Roman Empire, an allod (Old Low Franconian ''allōd'' ‘fully owned estate’, from ''all'' ‘full, entire’ and ''ōd'' ‘estate’, Medieval Latin ''allodium''), also allodial land or allodium, is an estate in land over which the allodial landowner (allodiary) had full ownership and right of alienation. Description Historically holders of allods are a type of sovereign. Allodial land is described as territory or a state where the holder asserted right to the land by the grace of god and the sun. For this reason they were historically equal to other princes regardless of what the size of their territory was or what title they used. This definition is confirmed by the acclaimed Jurist Hugo Grotius, the father of international law and the concept of sovereignty. "holders of allodial land are sovereign" because allodial land is by nature free, hereditary, inherited from their forefathers, sove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominium Directum
''Dominium directum et utile'' is a legal Latin term used to refer to the two separate estates in land that a fief was split into under feudal land tenure. This system is more commonly known as ''duplex dominium'' or double domain. This can be contrasted with the modern allodial system, in which ownership is full and not divided into separate estates—a situation known as ''dominium plenum'' "full ownership". Definitions ''Dominium directum et utile'' is composed of: *''Dominium directum'' (or eminent domain, superiority): the landlord's estate consisting of the right to dispose of property and to collect rents (feu-duty) and feudal incidents (fees, services, etc.) accruing from it. *''Dominium utile'' (or utile domain): the tenant's estate encompassing the rights to enjoy (use), make improvements to, or profit from property, and to keep the income or profit; includes e.g. the right to occupy and dwell on land and the right to keep the '' fructus naturales'' and emblements from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominium Utile
''Dominium directum et utile'' is a legal Latin term used to refer to the two separate estates in land that a fief was split into under feudal land tenure. This system is more commonly known as ''duplex dominium'' or double domain. This can be contrasted with the modern allodial system, in which ownership is full and not divided into separate estates—a situation known as ''dominium plenum'' "full ownership". Definitions ''Dominium directum et utile'' is composed of: *''Dominium directum'' (or eminent domain, superiority): the landlord's estate consisting of the right to dispose of property and to collect rents (feu-duty) and feudal incidents (fees, services, etc.) accruing from it. *''Dominium utile'' (or utile domain): the tenant's estate encompassing the rights to enjoy (use), make improvements to, or profit from property, and to keep the income or profit; includes e.g. the right to occupy and dwell on land and the right to keep the '' fructus naturales'' and emblements fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
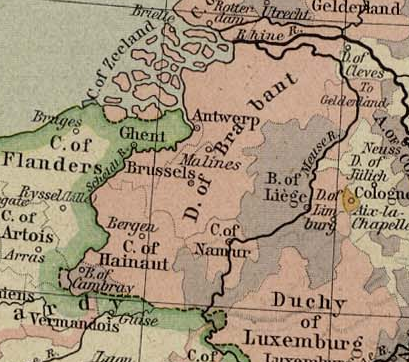
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: '' Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walloon Brabant
Walloon Brabant (french: Brabant wallon ; nl, Waals-Brabant ; wa, Roman Payis) is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the province of Flemish Brabant (Flemish Region) and the provinces of Liège, Namur and Hainaut. Walloon Brabant's capital- and largest city is Wavre. The provincial population was recorded at 403,599 as of January 2019, giving a population density of . Etymology Walloon is a Belgian version of a old West Germanic word reconstructed as *walh (“foreigner, stranger, speaker of Celtic or Latin”). Brabant is from Old Dutch *brākbant (attested in Medieval Latin as pāgus brācbatensis, Bracbantum, Bracbantia), from Frankish, a compound of Proto-Germanic *brēk-, *brekaną (“fallow, originally 'to break'”) + *bant-, *bantō, *banti (“district, region”) Like the terms "Belgium" and "Flanders", the terms "Walloon" and "Brabant" are much older than the modern political entities whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braine-l'Alleud
Braine-l'Alleud (; nl, Eigenbrakel ; wa, Brinne-l'-Alou) is a municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Walloon Brabant, Belgium, about south of Brussels. The municipality consists of the following districts: Braine-l'Alleud (including the hamlet of Sart-Moulin), Lillois-Witterzée, and Ophain-Bois-Seigneur-Isaac. Bordering Flanders, the town is home to a minority of Dutch speakers. The famous Lion of Waterloo, where the eponymous battle took place, is in the territory of Braine-l'Alleud. History Middle Ages Several archaeological finds point to prehistoric settlements in this area. The first historical mention of a parish on Braine-l'Alleud's current territory, then called ''Dudinsart'', dates from 1131, date at which Godfrey I, Duke of Brabant ceded it to the Abbey of Gembloux. The Duke, however, still owned exempt land (or franchise) on this territory, as specified in a legal document by Henry I dated 1197. The name of the municipality changed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a sovereign state and a federal constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
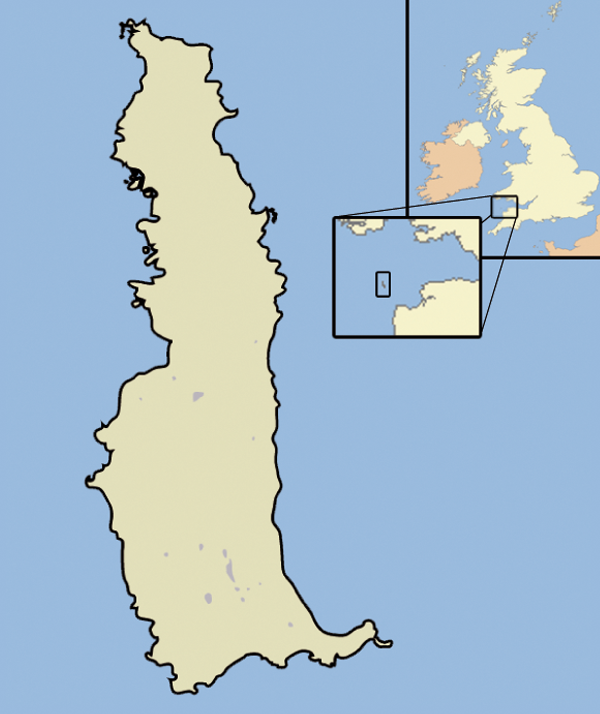
Lundy
Lundy is an English island in the Bristol Channel. It was a micronation from 1925–1969. It forms part of the district of Torridge District, Torridge in the county of Devon. About long and wide, Lundy has had a long and turbulent history, frequently changing hands between the British crown and various usurpers. In the 1920s, one self-proclaimed king, Martin Coles Harman, Martin Harman, tried to issue his own coinage and was fined by the House of Lords. In 1941, two German Heinkel He 111 bombers crash landed on the island, and their crews were captured. In 1969, Lundy was purchased by British millionaire Jack Hayward, who donated it to the National Trust. It is now managed by the Landmark Trust, a conservation charity that derives its income from day trips and holiday lettings, most visitors arriving by boat from Bideford or Ilfracombe. A local tourist curiosity is the special "Puffin" postage stamp, a category known by philatelists as "local carriage labels", a collectors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place approximately northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Norman victory. The background to the battle was the death of the childless King Edward the Confessor in January 1066, which set up a succession struggle between several claimants to his throne. Harold was crowned king shortly after Edward's death, but faced invasions by William, his own brother Tostig, and the Norwegian King Harald Hardrada (Harold III of Norway). Hardrada and Tostig defeated a hastily gathered army of Englishmen at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September 1066, and were in turn defeated by Harold at the Battle of Stamford Bridge five days later. The deaths of Tostig and Hardrada at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Law
The Salic law ( or ; la, Lex salica), also called the was the ancient Frankish civil law code compiled around AD 500 by the first Frankish King, Clovis. The written text is in Latin and contains some of the earliest known instances of Old Dutch. It remained the basis of Frankish law throughout the early Medieval period, and influenced future European legal systems. The best-known tenet of the old law is the principle of exclusion of women from inheritance of thrones, fiefs, and other property. The Salic laws were arbitrated by a committee appointed and empowered by the King of the Franks. Dozens of manuscripts dating from the sixth to eighth centuries and three emendations as late as the ninth century have survived. Salic law provided written codification of both civil law, such as the statutes governing inheritance, and criminal law, such as the punishment for murder. Although it was originally intended as the law of the Franks, it has had a formative influence on the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territorial Lord
A territorial lord (german: Landesherr) was a ruler in the period beginning with the Early Middle Ages who, stemming from his status as being immediate (''unmittelbar''), held a form of authority over a territory known as ''Landeshoheit''. This authority gave him nearly all the attributes of sovereignty. Such a lord had authority or dominion in a state or territory, but this fell short of sovereignty since as a ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, he remained subject to imperial law and supreme authority, including imperial tribunals and imperial war contributions. The territorial lord was generally a member of the high aristocracy ('' Hochadel'') or clergy, who was the title bearer or office holder of an existing or constituent state through the custom of primogeniture or feudal law. In the Holy Roman Empire, the lords of the individual member states, the imperial states or ''Reichsstände'' (excluding the Holy Roman Emperor), were the territorial lords of the regions ruled by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., Order of precedence, precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically Hereditary title, hereditary and Patrilinearity, patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and preceding the High Middle Ages ( 11th to 13th centuries). The alternative term '' late antiquity'', for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while ''Early Middle Ages'' is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and increased migration. In the 19th century the Early Middle Ages were often labelled the ''Dark Ages'', a characterization base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |