|
Vee Formation
The Vic formation is a formation devised for military aircraft and first used during the First World War. It has three or sometimes more aircraft fly in close formation with the leader at the apex and the rest of the flight '' en echelon'' to the left and the right, the whole resembling the letter "V". The formation's name is derived from the term that was then used for "V" in the RAF phonetic alphabet. The formation is still in use but has been superseded or replaced in some circumstances. History At the start of the First World War, little thought had been given to the most efficient formations to use for military aircraft. Groups of fliers, drawn from the various nations' army or navy, would fly in columns, or line, ahead as if they were troops of cavalry or flotillas of ships. That was soon found to be inefficient for several reasons. Firstly, the leaders and their squadrons could not communicate with each other except for the vague instruction to follow the leader. Second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
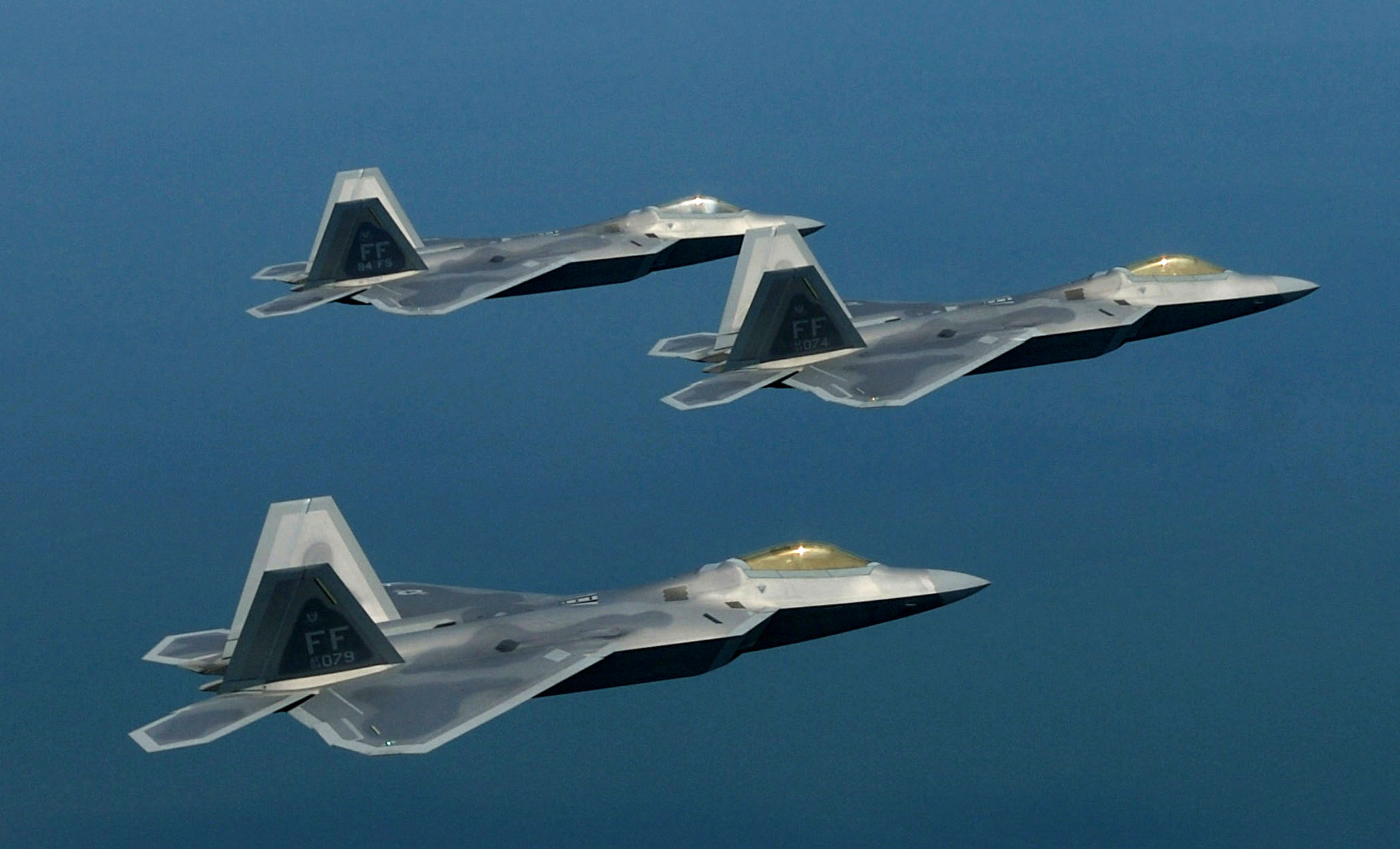
F22 Training Formation
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''. History The origin of 'F' is the Semitic letter '' waw'' that represented a sound like or . Graphically it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club. It may have been based on a comparable Egyptian hieroglyph such as that which represented the word ''mace'' (transliterated as ḥ(dj)): T3 The Phoenician form of the letter was adopted into Greek as a vowel, ''upsilon'' (which resembled its descendant ' Y' but was also the ancestor of the Roman letters ' U', ' V', and ' W'); and, with another form, as a consonant, ''digamma'', which indicated the pronunciation , as in Phoenician. Latin 'F,' despite being pronounced differently, is ultimately descended from digamma and closely resembles it in form. After sound changes eliminat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link=no) or The Uprising ( es, La Sublevación, link=no) among Republicans. was a civil war in Spain fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republicans and the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the left-leaning Popular Front (Spain), Popular Front government of the Second Spanish Republic, and consisted of various socialist, communist, separatist, anarchist, and Republicanism in Spain, republican parties, some of which had opposed the government in the pre-war period. The opposing Nationalists were an alliance of Falangism, Falangists, monarchists, conservatives, and Traditionalism (Spain), traditionalists led by a National Defense Junta, military junt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Warfare Tactics
Aerial may refer to: Music * ''Aerial'' (album), by Kate Bush * ''Aerials'' (song), from the album ''Toxicity'' by System of a Down Bands *Aerial (Canadian band) * Aerial (Scottish band) *Aerial (Swedish band) Performance art * Aerial silk, apparatus used in aerial acrobatics *Aerialist, an acrobat who performs in the air Recreation and sport *Aerial (dance move) *Aerial (skateboarding) * Aerial adventure park, ropes course with a recreational purpose * Aerial cartwheel (or side aerial), gymnastics move performed in acro dance and various martial arts *Aerial skiing, discipline of freestyle skiing *Front aerial, gymnastics move performed in acro dance Technology Antennas *Aerial (radio), a radio ''antenna'' or transducer that transmits or receives electromagnetic waves **Aerial (television), an over-the-air television reception antenna Mechanical *Aerial fire apparatus, for firefighting and rescue *Aerial work platform, for positioning workers Optical *Aeria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II (1941–1945). It was created on 20 June 1941 as successor to the previous United States Army Air Corps and is the direct predecessor of the United States Air Force, today one of the six armed forces of the United States. The AAF was a component of the United States Army, which on 2 March 1942 was divided functionally by executive order into three autonomous forces: the Army Ground Forces, the United States Army Services of Supply (which in 1943 became the Army Service Forces), and the Army Air Forces. Each of these forces had a commanding general who reported directly to the Army Chief of Staff. The AAF administered all parts of military aviation formerly distributed among the Air Corps, General Headquarters Air Force, and the gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Bader
Group Captain Sir Douglas Robert Steuart Bader, (; 21 February 1910 – 5 September 1982) was a Royal Air Force flying ace during the Second World War. He was credited with 22 aerial victories, four shared victories, six probables, one shared probable and 11 enemy aircraft damaged. Bader joined the RAF in 1928, and was commissioned in 1930. In December 1931, while attempting some aerobatics, he crashed and lost both his legs. Having been on the brink of death, he recovered, retook flight training, passed his check flights and then requested reactivation as a pilot. Although there were no regulations applicable to his situation, he was retired against his will on medical grounds. After the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939, however, Douglas Bader returned to the RAF and was accepted as a pilot. He scored his first victories over Dunkirk during the Battle of France in 1940. He then took part in the Battle of Britain and became a friend and supporter of Air Vice Marshal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
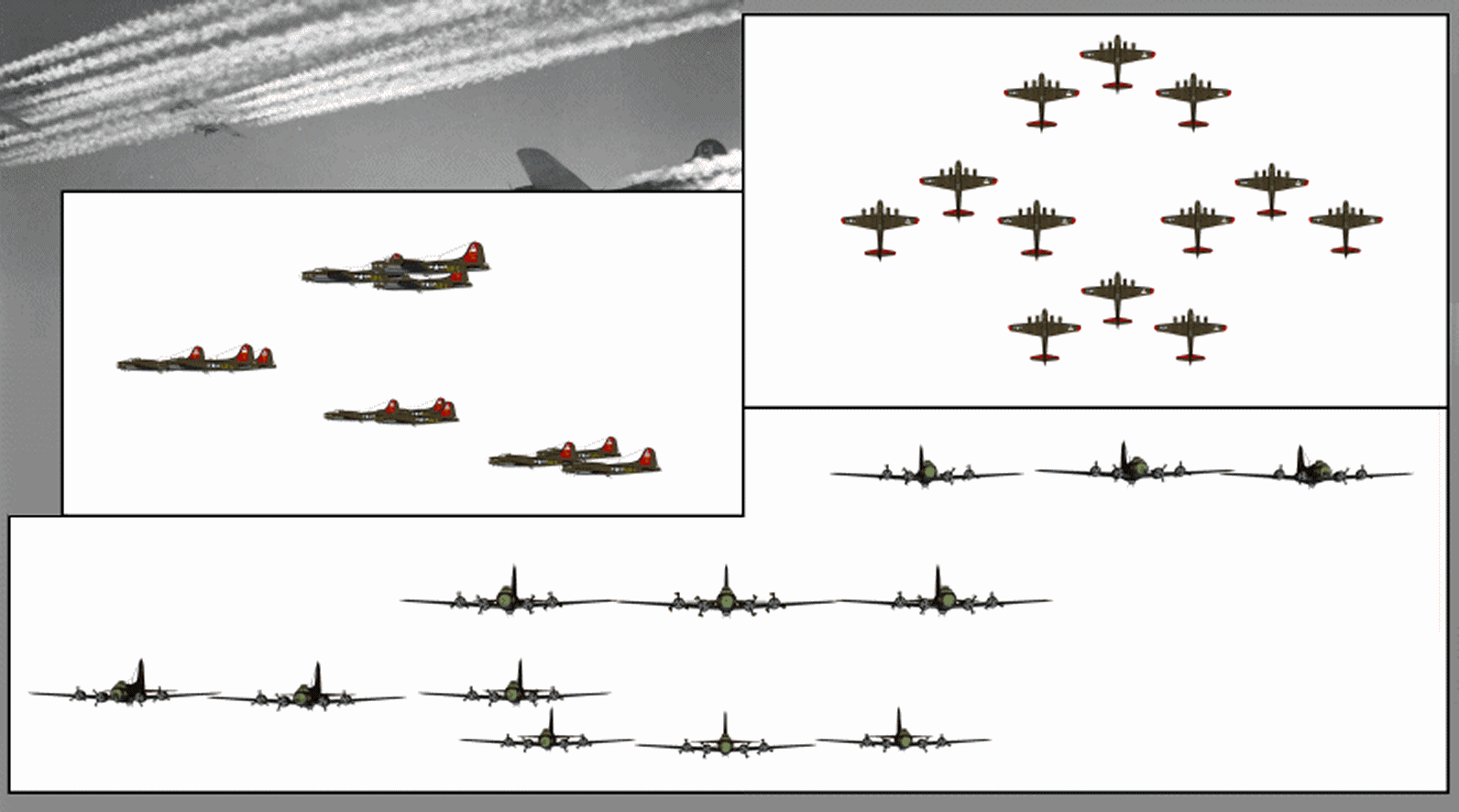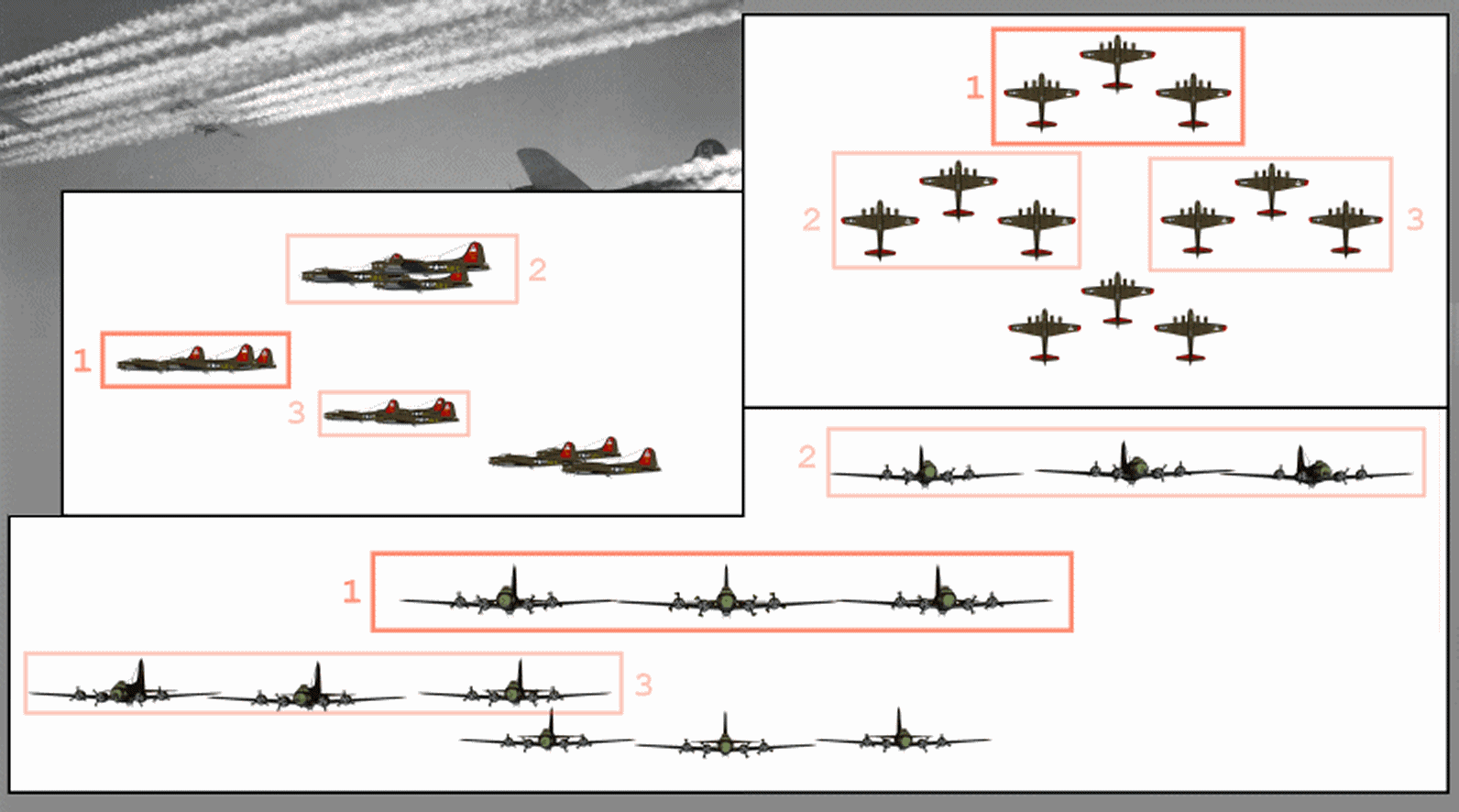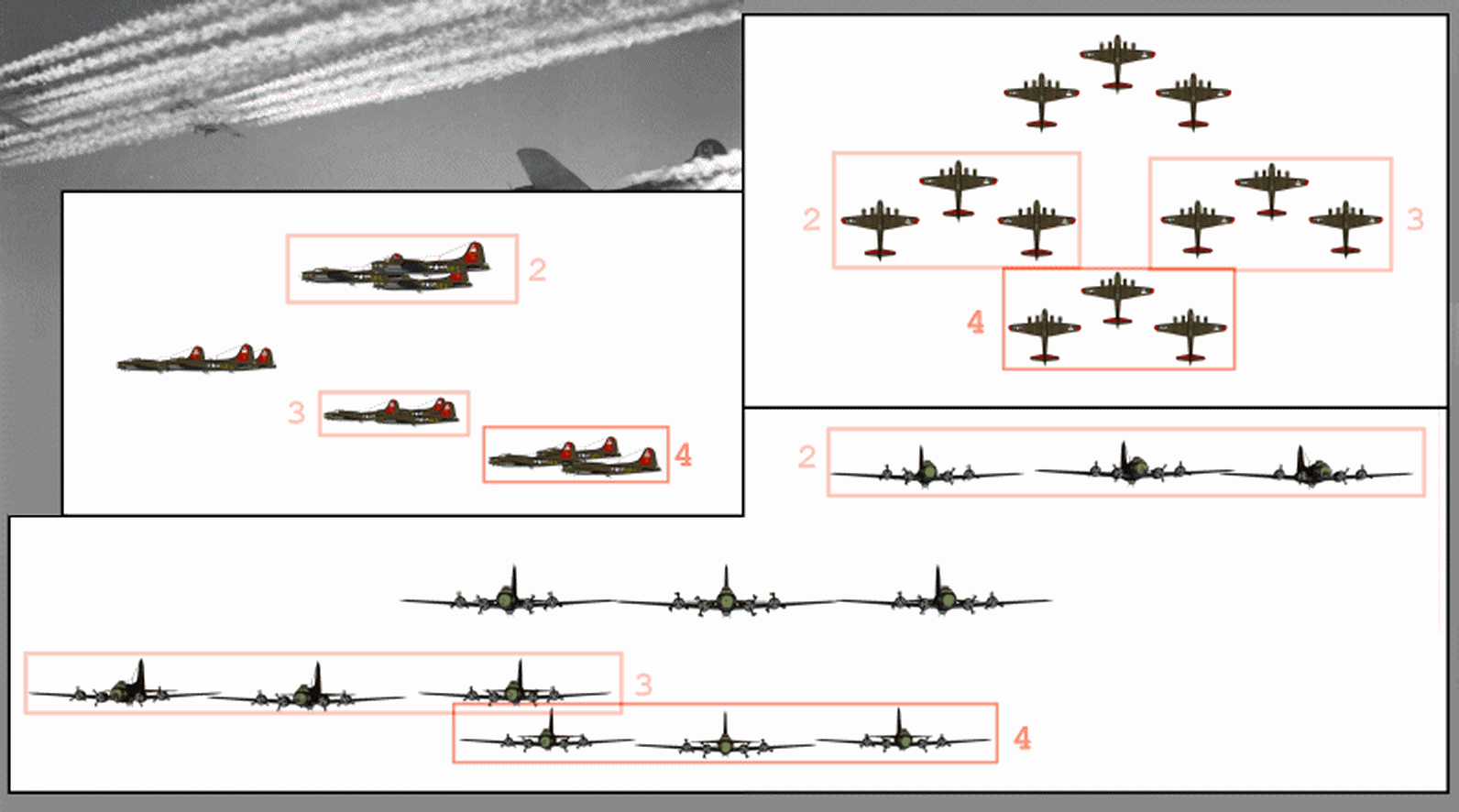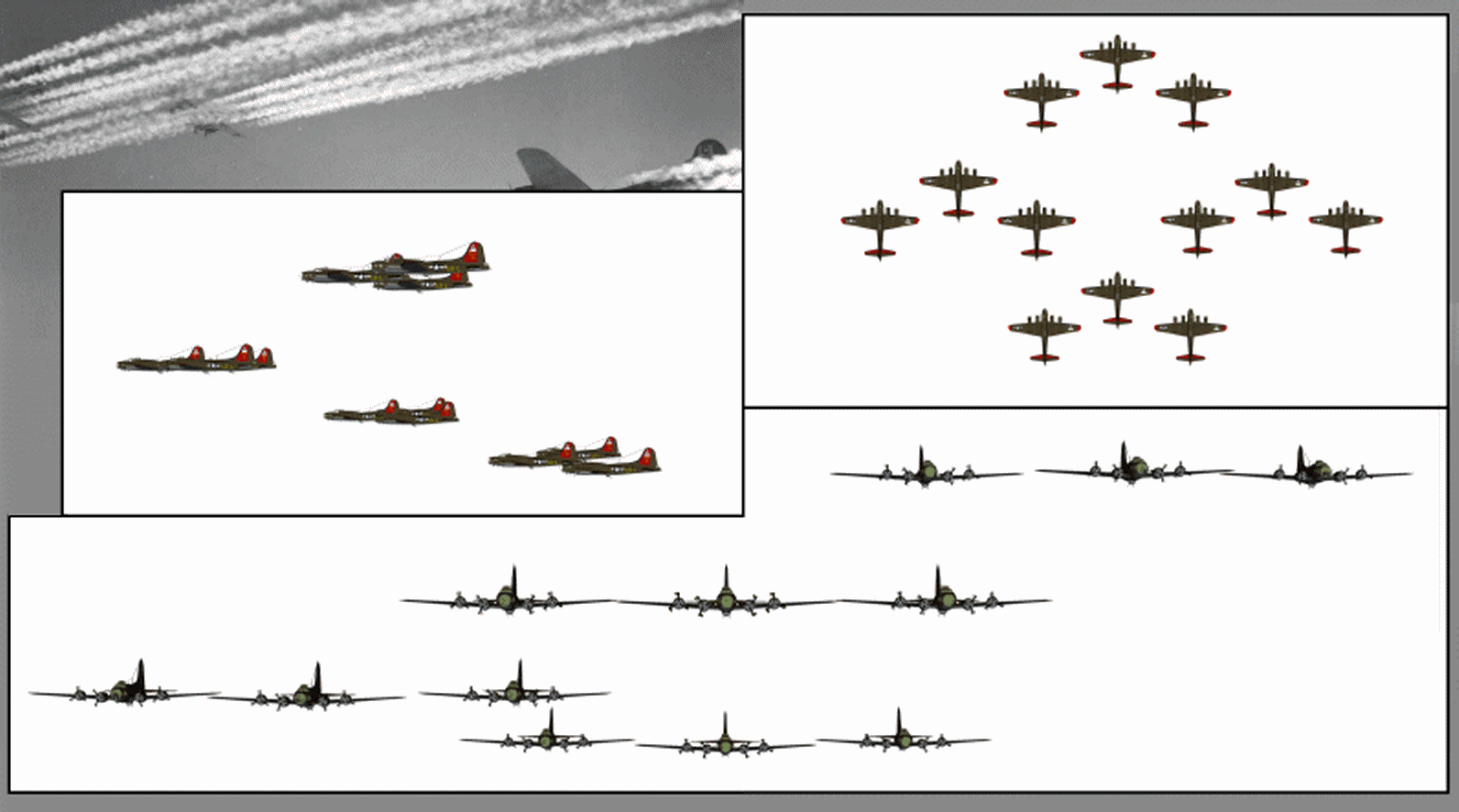
Combat Box
The combat box was a tactical formation used by heavy (strategic) bombers of the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II. The combat box was also referred to as a "staggered formation". Its defensive purpose was in massing the firepower of the bombers' guns, while offensively it concentrated the release of bombs on a target. Initially formations were created in keeping with the pre-war Air Corps doctrine that massed bombers could attack and destroy targets in daylight without fighter escort, relying on interlocking fire from their defensive machine guns, almost exclusively the "light barrel" Browning AN/M2 .50 calibre (12.7 mm) gun. However the use of high altitudes by USAAF bombers resulted in factors that demanded a tighter bomb pattern and the combat box continued in use even after the advent of fighter escort – and especially starting in the spring of 1944 over Europe, with USAAF fighters flying far ahead of the combat boxes in air supremacy mode instead against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II (1941–1945). It was created on 20 June 1941 as successor to the previous United States Army Air Corps and is the direct predecessor of the United States Air Force, today one of the six armed forces of the United States. The AAF was a component of the United States Army, which on 2 March 1942 was divided functionally by executive order into three autonomous forces: the Army Ground Forces, the United States Army Services of Supply (which in 1943 became the Army Service Forces), and the Army Air Forces. Each of these forces had a commanding general who reported directly to the Army Chief of Staff. The AAF administered all parts of military aviation formerly distributed among the Air Corps, General Headquarters Air Force, and the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defended the United Kingdom (UK) against large-scale attacks by Nazi Germany's air force, the Luftwaffe. It was the first major military campaign fought entirely by air forces."92 Squadron – Geoffrey Wellum." ''Battle of Britain Memorial Flight'' via ''raf.mod.uk.''. Retrieved: 17 November 2010, archived 2 March 2009. The British officially recognise the battle's duration as being from 10 July until 31 October 1940, which overlaps the period of large-scale night attacks known as |
Fighter Command
RAF Fighter Command was one of the commands of the Royal Air Force. It was formed in 1936 to allow more specialised control of fighter aircraft. It served throughout the Second World War. It earned near-immortal fame during the Battle of Britain in 1940, when the Few held off the Luftwaffe attack on Britain. The Command continued until 17 November 1943, when it was disbanded and the RAF fighter force was split into two categories; defence and attack. The defensive force became Air Defence of Great Britain (ADGB) and the offensive force became the RAF Second Tactical Air Force. Air Defence of Great Britain was renamed back to Fighter Command in October 1944 and continued to provide defensive patrols around Great Britain. It was disbanded for the second time in 1968, when it was subsumed into the new Strike Command. Origins On 20 May 1926, the forerunner of Fighter Command was established as a group within Inland Area. On 1 June 1926, Fighting Area was transferred to the Air D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |