|
Varifold
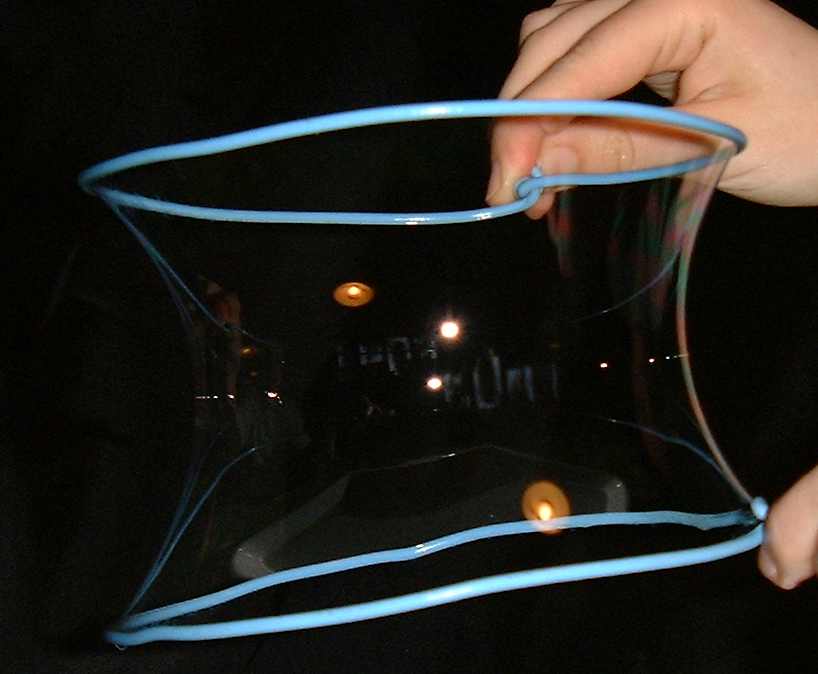
In mathematics, a varifold is, loosely speaking, a measure-theoretic generalization of the concept of a differentiable manifold, by replacing differentiability requirements with those provided by rectifiable sets, while maintaining the general algebraic structure usually seen in differential geometry. Varifolds generalize the idea of a rectifiable current, and are studied in geometric measure theory. Historical note Varifolds were first introduced by Laurence Chisholm Young in , under the name "''generalized surfaces''". Frederick J. Almgren Jr. slightly modified the definition in his mimeographed notes and coined the name ''varifold'': he wanted to emphasize that these objects are substitutes for ordinary manifolds in problems of the calculus of variations. The modern approach to the theory was based on Almgren's notesThe first widely circulated exposition of Almgren's ideas is the book : however, the first systematic exposition of the theory is contained in the mimeograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current (mathematics)
In mathematics, more particularly in functional analysis, differential topology, and geometric measure theory, a ''k''-current in the sense of Georges de Rham is a functional on the space of compactly supported differential ''k''-forms, on a smooth manifold ''M''. Currents formally behave like Schwartz distributions on a space of differential forms, but in a geometric setting, they can represent integration over a submanifold, generalizing the Dirac delta function, or more generally even directional derivatives of delta functions (multipoles) spread out along subsets of ''M''. Definition Let \Omega_c^m(M) denote the space of smooth ''m''-forms with compact support on a smooth manifold M. A current is a linear functional on \Omega_c^m(M) which is continuous in the sense of distributions. Thus a linear functional T : \Omega_c^m(M)\to \R is an ''m''-dimensional current if it is continuous in the following sense: If a sequence \omega_k of smooth forms, all supported in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurence Chisholm Young
Laurence Chisholm Young (14 July 1905 – 24 December 2000) was a British mathematician known for his contributions to measure theory, the calculus of variations, optimal control theory, and potential theory. He was the son of William Henry Young and Grace Chisholm Young, both prominent mathematicians. He moved to the US in 1949 but never sought American citizenship. The concept of Young measure is named after him: he also introduced the concept of the generalized curve and a concept of generalized surface which later evolved in the concept of varifold. The Young integral also is named after him and has now been generalised in the theory of rough paths. Life and academic career Laurence Chisholm Young was born in Göttingen,. the fifth of the six children of William Henry Young and Grace Chisholm Young.. He held positions of Professor at the University of Cape Town, South Africa, and at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. He was also a chess grandmaster. Selected publicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radon Measure
In mathematics (specifically in measure theory), a Radon measure, named after Johann Radon, is a measure on the σ-algebra of Borel sets of a Hausdorff topological space ''X'' that is finite on all compact sets, outer regular on all Borel sets, and inner regular on open sets. These conditions guarantee that the measure is "compatible" with the topology of the space, and most measures used in mathematical analysis and in number theory are indeed Radon measures. Motivation A common problem is to find a good notion of a measure on a topological space that is compatible with the topology in some sense. One way to do this is to define a measure on the Borel sets of the topological space. In general there are several problems with this: for example, such a measure may not have a well defined support. Another approach to measure theory is to restrict to locally compact Hausdorff spaces, and only consider the measures that correspond to positive linear functionals on the space of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Society
The American Mathematical Society (AMS) is an association of professional mathematicians dedicated to the interests of mathematical research and scholarship, and serves the national and international community through its publications, meetings, advocacy and other programs. The society is one of the four parts of the Joint Policy Board for Mathematics and a member of the Conference Board of the Mathematical Sciences. History The AMS was founded in 1888 as the New York Mathematical Society, the brainchild of Thomas Fiske, who was impressed by the London Mathematical Society on a visit to England. John Howard Van Amringe was the first president and Fiske became secretary. The society soon decided to publish a journal, but ran into some resistance, due to concerns about competing with the American Journal of Mathematics. The result was the ''Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society'', with Fiske as editor-in-chief. The de facto journal, as intended, was influential in in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateau's Problem
In mathematics, Plateau's problem is to show the existence of a minimal surface with a given boundary, a problem raised by Joseph-Louis Lagrange in 1760. However, it is named after Joseph Plateau who experimented with soap films. The problem is considered part of the calculus of variations. The existence and regularity problems are part of geometric measure theory. History Various specialized forms of the problem were solved, but it was only in 1930 that general solutions were found in the context of mappings (immersions) independently by Jesse Douglas and Tibor Radó. Their methods were quite different; Radó's work built on the previous work of René Garnier and held only for rectifiable simple closed curves, whereas Douglas used completely new ideas with his result holding for an arbitrary simple closed curve. Both relied on setting up minimization problems; Douglas minimized the now-named Douglas integral while Radó minimized the "energy". Douglas went on to be awarded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Measure Theory
In mathematics, geometric measure theory (GMT) is the study of geometric properties of sets (typically in Euclidean space) through measure theory. It allows mathematicians to extend tools from differential geometry to a much larger class of surfaces that are not necessarily smooth. History Geometric measure theory was born out of the desire to solve Plateau's problem (named after Joseph Plateau) which asks if for every smooth closed curve in \mathbb^3 there exists a surface of least area among all surfaces whose boundary equals the given curve. Such surfaces mimic soap films. The problem had remained open since it was posed in 1760 by Lagrange. It was solved independently in the 1930s by Jesse Douglas and Tibor Radó under certain topological restrictions. In 1960 Herbert Federer and Wendell Fleming used the theory of currents with which they were able to solve the orientable Plateau's problem analytically without topological restrictions, thus sparking geometric measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Operator
In mathematics, a chain complex is an algebraic structure that consists of a sequence of abelian groups (or modules) and a sequence of homomorphisms between consecutive groups such that the image of each homomorphism is included in the kernel of the next. Associated to a chain complex is its homology, which describes how the images are included in the kernels. A cochain complex is similar to a chain complex, except that its homomorphisms are in the opposite direction. The homology of a cochain complex is called its cohomology. In algebraic topology, the singular chain complex of a topological space X is constructed using continuous maps from a simplex to X, and the homomorphisms of the chain complex capture how these maps restrict to the boundary of the simplex. The homology of this chain complex is called the singular homology of X, and is a commonly used invariant of a topological space. Chain complexes are studied in homological algebra, but are used in several areas of mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectifiable Set
In mathematics, a rectifiable set is a set that is smooth in a certain measure-theoretic sense. It is an extension of the idea of a rectifiable curve to higher dimensions; loosely speaking, a rectifiable set is a rigorous formulation of a piece-wise smooth set. As such, it has many of the desirable properties of smooth manifolds, including tangent spaces that are defined almost everywhere. Rectifiable sets are the underlying object of study in geometric measure theory. Definition A Borel subset E of Euclidean space \mathbb^n is said to be m-rectifiable set if E is of Hausdorff dimension m, and there exist a countable collection \ of continuously differentiable maps :f_i:\mathbb^m \to \mathbb^n such that the m-Hausdorff measure \mathcal^m of :E\setminus \bigcup_^\infty f_i\left(\mathbb^m\right) is zero. The backslash here denotes the set difference. Equivalently, the f_i may be taken to be Lipschitz continuous without altering the definition. Other authors have different defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiable Manifold
In mathematics, a differentiable manifold (also differential manifold) is a type of manifold that is locally similar enough to a vector space to allow one to apply calculus. Any manifold can be described by a collection of charts (atlas). One may then apply ideas from calculus while working within the individual charts, since each chart lies within a vector space to which the usual rules of calculus apply. If the charts are suitably compatible (namely, the transition from one chart to another is differentiable), then computations done in one chart are valid in any other differentiable chart. In formal terms, a differentiable manifold is a topological manifold with a globally defined differential structure. Any topological manifold can be given a differential structure locally by using the homeomorphisms in its atlas and the standard differential structure on a vector space. To induce a global differential structure on the local coordinate systems induced by the homeomorphisms, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orientability
In mathematics, orientability is a property of some topological spaces such as real vector spaces, Euclidean spaces, surfaces, and more generally manifolds that allows a consistent definition of "clockwise" and "counterclockwise". A space is orientable if such a consistent definition exists. In this case, there are two possible definitions, and a choice between them is an orientation of the space. Real vector spaces, Euclidean spaces, and spheres are orientable. A space is non-orientable if "clockwise" is changed into "counterclockwise" after running through some loops in it, and coming back to the starting point. This means that a geometric shape, such as , that moves continuously along such a loop is changed into its own mirror image . A Möbius strip is an example of a non-orientable space. Various equivalent formulations of orientability can be given, depending on the desired application and level of generality. Formulations applicable to general topological manifolds o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausdorff Measure
In mathematics, Hausdorff measure is a generalization of the traditional notions of area and volume to non-integer dimensions, specifically fractals and their Hausdorff dimensions. It is a type of outer measure, named for Felix Hausdorff, that assigns a number in ,∞to each set in \R^n or, more generally, in any metric space. The zero-dimensional Hausdorff measure is the number of points in the set (if the set is finite) or ∞ if the set is infinite. Likewise, the one-dimensional Hausdorff measure of a simple curve in \R^n is equal to the length of the curve, and the two-dimensional Hausdorff measure of a Lebesgue-measurable subset of \R^2 is proportional to the area of the set. Thus, the concept of the Hausdorff measure generalizes the Lebesgue measure and its notions of counting, length, and area. It also generalizes volume. In fact, there are ''d''-dimensional Hausdorff measures for any ''d'' ≥ 0, which is not necessarily an integer. These measures are fundamenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |