|
Vanadium Compounds
Vanadium compounds are compounds formed by the element vanadium (V). The chemistry of vanadium is noteworthy for the accessibility of the four adjacent oxidation states 2–5, whereas the chemistry of the other group 5 elements, niobium and tantalum, are somewhat more limited to the +5 oxidation state. In aqueous solution, vanadium forms metal aquo complexes of which the colours are lilac (H2O)6sup>2+, green (H2O)6sup>3+, blue O(H2O)5sup>2+, yellow-orange oxides O(H2O)5sup>3+, the formula for which depends on pH. Vanadium(II) compounds are reducing agents, and vanadium(V) compounds are oxidizing agents. Vanadium(IV) compounds often exist as vanadyl derivatives, which contain the VO2+ center. Ammonium vanadate(V) (NH4VO3) can be successively reduced with elemental zinc to obtain the different colors of vanadium in these four oxidation states. Lower oxidation states occur in compounds such as V(CO)6, and substituted derivatives. Vanadium pentoxide is a commercially important c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
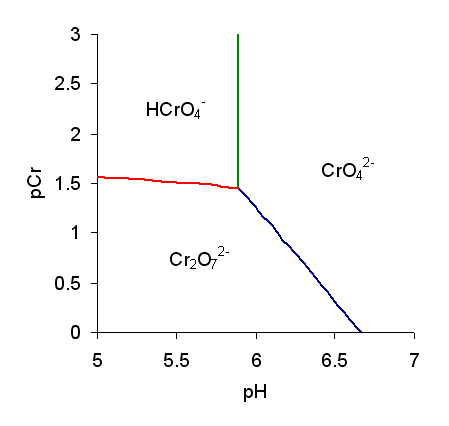
Predominance Diagram
A predominance diagram purports to show the conditions of concentration and pH where a chemical species has the highest concentration in solutions in which there are multiple acid-base equilibria. The lines on a predominance diagram indicate where adjacent species have the same concentration. Either side of such a line one species or the other predominates, that is, has higher concentration relative to the other species. To illustrate a predominance diagram, part of the one for chromate is shown at the right. pCr stands for minus the logarithm of the chromium concentration and pH stands for minus the logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. There are two independent equilibria, with equilibrium constants defined as follows. A third equilibrium constant can be derived from ''K''1 and ''K''D. The species and are only formed at very low pH so they do not appear on this diagram. Published values for log ''K''1 and log ''K''D are 5.89 and 2.05, respectively. Using these values ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diene
In organic chemistry a diene ( ) (diolefin ( ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition. Classes Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. #Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. #Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(IV) Chloride
Vanadium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula V Cl4. This bright red liquid serves as a useful reagent for the preparation of other vanadium compounds. Synthesis, bonding, basic properties With one more valence electron than diamagnetic TiCl4, VCl4 is a paramagnetic liquid. It is one of only a few paramagnetic compounds that is liquid at room temperature. VCl4 is prepared by chlorination of vanadium metal. VCl5 does not form in this reaction; Cl2 lacks the oxidizing power to attack VCl4. VCl5 can however be prepared indirectly from VF5 at −78 °C. In contrast, the heavier analogues NbCl5 and TaCl5 are stable and not particularly oxidizing. VF5 can be prepared directly by fluorination of vanadium metal, reflecting the increased oxidizing power of F2 vs Cl2. Indicative of its oxidizing power, VCl4 releases Cl2 at its boiling point (standard pressure) to afford VCl3. Reactions Consistent with its high oxidizing power, VCl4 reacts with HBr a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halides
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, astatide, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX (X = F, Cl, Br or I). Many salts are halides; the ''hal-'' syllable in ''halide'' and ''halite'' reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature. A halide ion is a halogen atom bearing a negative charge. The halide anions are fluoride (), chloride (), bromide (), iodide () and astatide (). Such ions are present in all ionic halide salts. Halide minerals contain halides. All these halides are colourless, high melting crystalline solids having high negative enthalpies of formation. Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoperoxidase
Bromide peroxidase (, ''bromoperoxidase'', ''haloperoxidase (ambiguous)'', ''eosinophil peroxidase'') is a family of enzymes with systematic name ''bromide:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase''. These enzymes catalyses the following chemical reaction: : HBr + H2O2 \rightleftharpoons HOBr + H2O The HOBr is a potent brominating agent. The many organobromine compounds observed in marine environments are the products of reaction with this oxidized form of bromine. Bromo peroxidases of red and brown marine algae (''Rhodophyta'' and ''Phaeophyta'') contain vanadate (vanadium bromoperoxidase). Otherwise vanadium is unusual cofactor in biology. By virtue of this family of enzymes, a variety of brominated natural products have been isolated from marine sources. Related chloroperoxidase enzymes effect chlorination. In the nomenclature of haloperoxidase, bromoperoxidases classically are unable to oxidize chloride at all. For example, eosinophil peroxidase appears to prefer bromide ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidic Oxide
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution (and the generation of carbonic acid) when dissolved. The acidity of an oxide can be reasonably assumed by its accompanying constituents. Less electronegative elements tend to form basic oxides such as sodium oxide and magnesium oxide, whereas more electronegative elements tend to produce acidic oxides as seen with carbon dioxide and phosphorus pentoxide. Some oxides like aluminium oxides are amphoteric. Acidic oxides are of environmental concern. Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are considered air pollutants as they react with atmospheric water vapour to produce acid rain. Examples Carbonic acid is an illustrative example of the Lewis acidity of an aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decavanadate
Sodium decavanadate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Na6 10O28H2O)n. These are sodium salts of the orange-colored decavanadate anion 10O28sup>6−. Numerous other decavanadate salts have been isolated and studied since 1956 when it was first characterized. Preparation The preparation of decavanadate is achieved by acidifying an aqueous solution of ortho-vanadate: :10 Na3 O4 + 24 HOAc → Na6 10O28 + 12 H2O + 24 NaOAc The formation of decavanadate is optimized by maintaining a pH range of 4–7. Typical side products include metavanadate, O3sup>−, and hexavanadate, 6O16sup>2−, ions. Structure The decavanadate ion consists of 10 fused VO6 octahedra and has D2h symmetry. The structure of Na6 10O28�18H2O has been confirmed with X-ray crystallography. The decavanadate anions contains three sets of equivalent V atoms (see fig. 1). These include two central VO6 octahedra (Vc) and four each peripheral tetragonal-pyramidal VO5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadate
In chemistry, a vanadate is an anionic coordination complex of vanadium. Often vanadate refers to oxoanions of vanadium, most of which exist in its highest oxidation state of +5. The complexes and are referred to as hexacyanovanadate(III) and nonachlorodivanadate(III), respectively. A simple vanadate ion is the tetrahedral orthovanadate anion, (which is also called vanadate(V)), which is present in e.g. sodium orthovanadate and in solutions of in strong base ( pH > 13). Conventionally this ion is represented with a single double bond, however this is a resonance form as the ion is a regular tetrahedron with four equivalent oxygen atoms. Additionally a range of polyoxovanadate ions exist which include discrete ions and "infinite" polymeric ions. There are also vanadates, such as rhodium vanadate, , which has a statistical rutile structure where the and ions randomly occupy the positions in the rutile lattice, that do not contain a lattice of cations and balancing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

4-3D-balls.png)
