|
Valgarðr á Velli
Valgarðr á Velli was an 11th-century skald in the service of King Harald Hardrada of Norway. Little is known about his life or origin but his name suggests he may have been a kinsman, perhaps a son, of Mörðr Valgarðsson of Völlr, a chieftain who plays a role in ''Njáls saga''. He is listed in '' Skáldatal'' among the court poets of Harald Hardrada. Extant poetry The Norse sources attribute 11 stanzas or half-stanzas of ''dróttkvætt'' poetry to Valgarðr. There are three in '' Skáldskaparmál'' where they are used to illustrate the use of certain ''heiti'' (poetic synonyms). Of these, one mentions that Sicily was laid waste. Two others are descriptions of destruction by fire in an unknown context. There are 8 stanzas or half-stanzas preserved in the kings' sagas where they are used as sources of historical information on events in the life of Harald Hardrada. The first chronologically is preserved only in ''Fagrskinna'' and relates to events in 1042 as Harald joined an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fríssbók F
Codex Frisianus or Fríssbók (shelfmark AM 45 fol. in the Arnamagnæanske samling) is a manuscript of the early fourteenth century (c. 1300–1325). Among its 124 folios, it contains '' Heimskringla'' (without the Saga of Saint Olaf) and ''Hákonar saga Hákonarsonar''. Origins and history The manuscript might have been written in Iceland and soon moved into Norway or have been composed in Norway.Hollander, Lee M., ''Snorri Sturluson. Heimskringla: history of the kings of Norway'' (Austin: University of Texas Press for the American-Scandinavian Foundation, 2005), p. xxiv. It was found in Bergen in 1550 and brought to Denmark before 1600, when it was acquired by the collector Otto Friis, from whom it takes its name. It then came into the possession of Jens Rosenkrantz before being bought in 1695 by Árni Magnússon. The latter gave it at his death (1730) to the University of Copenhagen The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varangian
The Varangians (; non, Væringjar; gkm, Βάραγγοι, ''Várangoi'';Varangian " Online Etymology Dictionary : варяже, varyazhe or варязи, varyazi) were , conquerors, traders and settlers, mostly from . Between the 9th and 11th centuries, Varangians ruled the state of |
Raptio
''Raptio'' (in archaic or literary English rendered as ''rape'') is a Latin term for the large-scale abduction of women, i.e. kidnapping for marriage, concubinage or sexual slavery. The equivalent German term is ''Frauenraub'' (literally ''wife robbery''). Bride kidnapping is distinguished from ''raptio'' in that the former is the abduction of one woman by one man (and his friends and relatives), whereas the latter is the abduction of many women by groups of men, possibly in a time of war. Terminology The English word ''rape'' retains the Latin meaning in literary language, but the meaning is obscured by the more current meaning of "sexual violation". The word is akin to ''rapine'', ''rapture'', ''raptor'', ''rapacious'' and ''ravish'', and referred to the more general violations, such as looting, destruction, and capture of citizens, that are inflicted upon a town or country during war, e.g. the Rape of Nanking. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' gives the definition "the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roskilde
Roskilde ( , ) is a city west of Copenhagen on the Danish island of Zealand. With a population of 51,916 (), the city is a business and educational centre for the region and the 10th largest city in Denmark. It is governed by the administrative council of Roskilde Municipality. Roskilde has a long history, dating from the pre-Christian Viking Age. Its UNESCO-listed Gothic cathedral, now housing 39 tombs of the Danish monarchs, was completed in 1275, becoming a focus of religious influence until the Reformation. With the development of the rail network in the 19th century, Roskilde became an important hub for traffic with Copenhagen, and by the end of the century, there were tobacco factories, iron foundries and machine shops. Among the largest private sector employers today are the IT firm BEC (Bankernes EDB Central) and seed company DLF. The Risø research facility is also becoming a major employer, extending interest in sustainable energy to the clean technology sphere. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sjælland
Zealand ( da, Sjælland ) at 7,031 km2 is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020. It is the 13th-largest island in Europe by area and the 4th most populous. It is connected to Sprogø and Funen by the Great Belt Fixed Link and to Amager by several bridges in Copenhagen. Indirectly, through the island of Amager and the Øresund Bridge, it is also linked to Scania in Sweden. In the south, the Storstrøm Bridge and the Farø Bridges connect it to Falster, and beyond that island to Lolland, from where the Fehmarnbelt Tunnel to Germany is planned. Copenhagen, the capital of Denmark, with a population between 1.3 and 1.4 million people in 2020, is located mostly on the eastern shore of Zealand and partly on the island of Amager. Other cities on Zealand include Roskilde, Hillerød, Næstved, Helsingør, Slagelse, Køge, Holbæk a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus The Good
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson''; Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus Olavsson''; – 25 October 1047), better known as Magnus the Good (Old Norse: ''Magnús góði'', Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus den gode''), was King of Norway from 1035 and King of Denmark from 1042 until his death in 1047. Magnus was an illegitimate son of King Olaf II of Norway, and fled with his mother Alfhild when his father was dethroned in 1028. He returned to Norway in 1035 and was crowned king at the age of 11. In 1042, he was also crowned king of Denmark. Magnus ruled the two countries until 1047, when he died under unclear circumstances. After his death, his kingdom was split between Harald Hardrada in Norway and Sweyn Estridsson in Denmark. Early life Magnus was an illegitimate son of King Olaf Haraldsson (later St. Olaf), by his English concubine Alfhild,Carl Frederik Bricka, ''Dansk Biografisk Lexikon'', vol. XI aar – Müllner 1897p.44 originally a slave (thrall) of Olaf's que ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flateyjarbók
''Flateyjarbók'' (; "Book of Flatey") is an important medieval Icelandic manuscript. It is also known as GkS 1005 fol. and by the Latin name ''Codex Flateyensis''. It was commissioned by Jón Hákonarson and produced by the priests and scribes Jón Þórðarson and Magnús Þórhallsson. Description ''Flateyjarbók'' is the largest medieval Icelandic manuscript, comprising 225 written and illustrated vellum leaves. It contains mostly sagas of the Norse kings as found in the ''Heimskringla'', specifically the sagas about Olaf Tryggvason, St. Olaf, Sverre, Hákon the Old, Magnus the Good, and Harald Hardrada. But they appear here expanded with additional material not found elsewhere (some of it being very old) along with other unique differences. Most—but not all—of the additional material is placed within the royal sagas, sometimes interlaced. Additionally, the manuscript contains the only copy of the eddic poem '' Hyndluljóð'', a unique set of annals from creation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
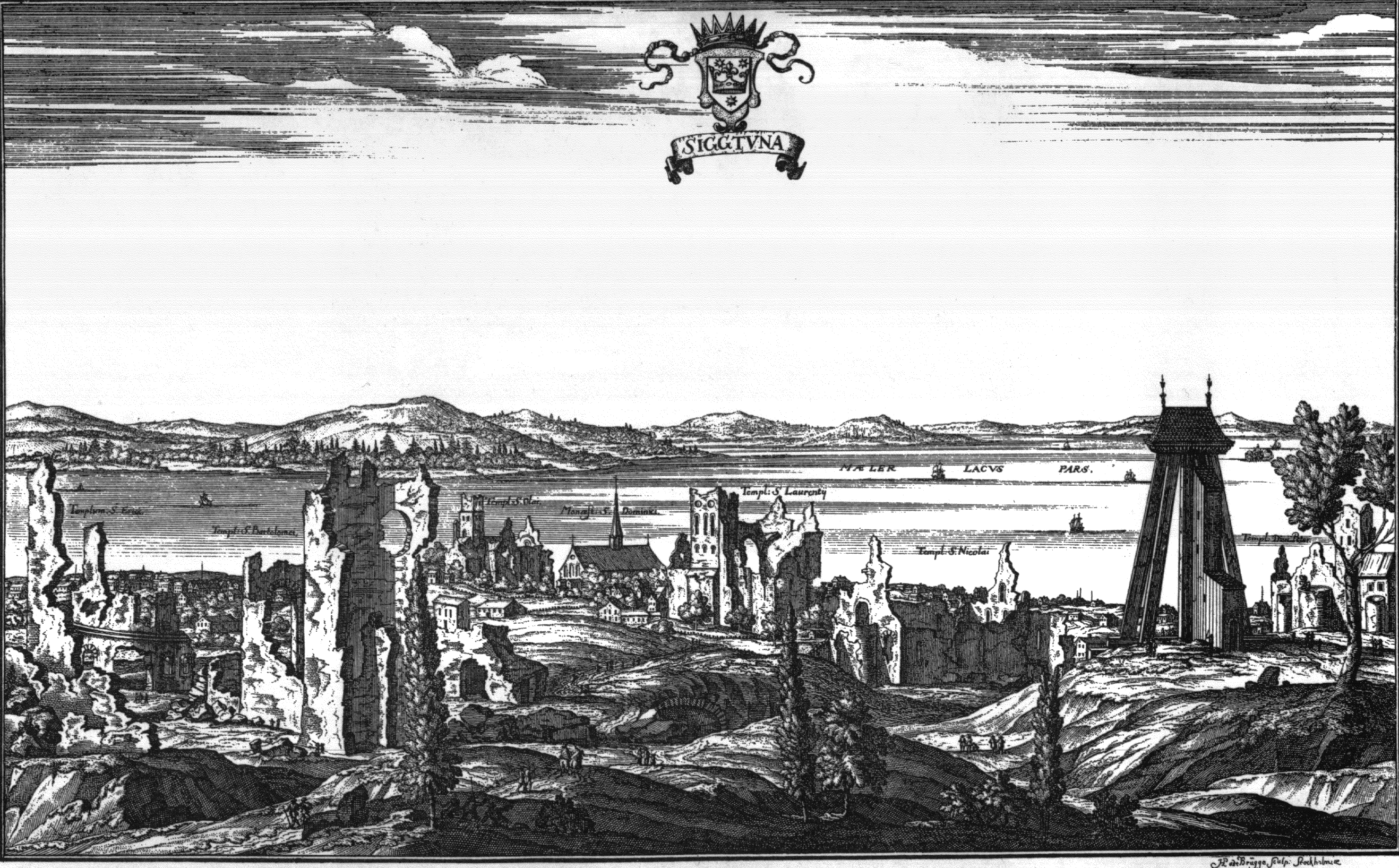
Sigtuna
Sigtuna () is a locality situated in Sigtuna Municipality, Stockholm County, Sweden with 8,444 inhabitants in 2010. It is the namesake of the municipality even though the seat is in Märsta. Sigtuna is for historical reasons often still referred to as a ''stad''. Modern-day Sigtuna, a harbor town that was established around 980, developed approximately 4 kilometres east of Old Sigtuna (which, according to Norse mythology, was previously the home of Odin). Sigtuna has a medieval-style town centre with restaurants, cafes and small shops. The old church ruins, runic stones and the old main street (''Stora gatan'') are popular attractions for tourists, especially in the summertime. The small streets with low-built wooden houses lead up to several handicrafts shops and the old tiny town hall (''Sigtuna Rådhus''). There are restaurants and ''Sigtuna Stadshotell'', a hotel in the town centre. Geography Sigtuna is situated at the bay Skarven, stretching around Upplands-Bro and a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garðaríki
(anglicized Gardariki or Gardarike) or is the Old Norse term used in medieval times for the states of Kievan Rus. As the Varangians dealt mainly with Northern Kievan Rus' lands, their sagas regard the city of (, Veliky Novgorod) as the capital of . Other local towns mentioned in the sagas are (Old Ladoga), (Polotsk), (Smolensk), (Suzdal), (Murom), and (Rostov). Three of the Varangian runestones, G 114, Sö 338, and U 209, refer to Scandinavian men who had been in . Etymology The word , which first appeared in Icelandic sagas in the twelfth century, could stem from the words and according to the common Scandinavian pattern for state formations ''X+ríki'', therefore this term could be translated into English as "the kingdom of Garðar". The name itself was used in skaldic poems, runic inscriptions and early sagas up to the twelfth century to refer to the lands to the east of Scandinavia populated by the Rus' people. is a plural form of the Old Norse word whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hulda-Hrokkinskinna
''Hulda-Hrokkinskinna'' is one of the kings' sagas. Written after 1280 it relates the history of the Norwegian kings from Magnús góði, who acceded to the throne in 1035, to Magnús Erlingsson, who died in 1177. The saga is based on Snorri Sturluson's ''Heimskringla'' but supplemented by prose and poetry from a version of ''Morkinskinna'' which is no longer extant. Thunberg, Carl L. (2011). ''Särkland och dess källmaterial''. Göteborgs universitet. CLTS. pp. 59-67. . ''Hulda-Hrokkinskinna'' is especially valuable in places where the preserved ''Morkinskinna'' manuscript is defective. It preserves eight verses of skaldic poetry found nowhere else by the poets Arnórr Þórðarson, Þjóðólfr Arnórsson, Bölverkr Arnórsson and Þórarinn stuttfeldr. The saga is preserved in two manuscripts. ''Hulda'' ("the hidden manuscript") or ''AM 66 fol.'' is an Icelandic manuscript from the last part of the 14th century. It consists of 142 leaves while the first six (the first qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derived from the first two words of one of the manuscripts (''kringla heimsins'', "the circle of the world"). ''Heimskringla'' is a collection of sagas about Swedish and Norwegian kings, beginning with the saga of the legendary Swedish dynasty of the Ynglings, followed by accounts of historical Norwegian rulers from Harald Fairhair of the 9th century up to the death of the pretender Eystein Meyla in 1177. The exact sources of the Snorri's work are disputed, but they include earlier kings' sagas, such as Morkinskinna, Fagrskinna and the 12th-century Norwegian synoptic histories and oral traditions, notably many skaldic poems. He explicitly names the now lost work ''Hryggjarstykki'' as his source for the events of the mid-12th century. Although Sno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morkinskinna
''Morkinskinna'' is an Old Norse kings' saga, relating the history of Norwegian kings from approximately 1025 to 1157. The saga was written in Iceland around 1220, and has been preserved in a manuscript from around 1275. The name ''Morkinskinna'' means "mouldy parchment" and is originally the name of the manuscript book in which the saga has been preserved. The book itself, GKS 1009 fol, is currently in the Royal Danish Library in Copenhagen. It was brought to Denmark from Iceland by Þormóður Torfason ( Tormod Torfæus) in 1662. The saga was published in English in 2000 in a translation by Theodore M. Andersson and Kari Ellen Gade. Contents The saga starts in 1025 or 1026 and in its received form, ends suddenly in 1157, after the death of King Sigurðr II. Originally, the work may have been longer, possibly continuing until 1177, when the narratives of ''Fagrskinna'' and ''Heimskringla'', which use ''Morkinskinna'' as one of their sources, end. Apart from giving the main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |