|
Vahe Gurzadyan
Vahagn "Vahe" Gurzadyan ( hy, Վահագն Գուրզադյան; born 21 November 1955) is an Armenian mathematical physicist and a professor and head of Cosmology Center at Yerevan Physics Institute, Yerevan , Armenia, best known for co-writing "Concentric circles in WMAP data may provide evidence of violent pre-Big-Bang activity" paper with his colleague, Roger Penrose, and collaborating on Roger Penrose's recent book ''Cycles of Time''. Gurzadyan was born in Yerevan, Armenia (then Soviet Union), graduated Yerevan State University (1977), postgraduate student in theoretical physics department, Lebedev Physics Institute, Moscow (1977–1980; 1980 PhD.), DSci in theoretical and mathematical physics (1988). In 1989 he lectured on dynamical systems in four universities in Japan (Tokyo, Kyoto, Hiroshima, Fukui), and subsequently held visiting positions at the University of Sussex (1996–1997) and, since 2001, at Sapienza University of Rome. His father Grigor Gurzadyan, an Armen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and industrial center of the country, as its primate city. It has been the Historical capitals of Armenia, capital since 1918, the Historical capitals of Armenia, fourteenth in the history of Armenia and the seventh located in or around the Ararat Plain. The city also serves as the seat of the Araratian Pontifical Diocese, which is the largest diocese of the Armenian Apostolic Church and one of the oldest dioceses in the world. The history of Yerevan dates back to the 8th century BCE, with the founding of the fortress of Erebuni Fortress, Erebuni in 782 BCE by King Argishti I of Urartu, Argishti I of Urartu at the western extreme of the Ararat Plain. Erebuni was "designed as a great administrative an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galaxies – in either observational astronomy, observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, Sun, solar astronomy, the Star formation, origin or stellar evolution, evolution of stars, or the galaxy formation and evolution, formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers usually fall under either of two main types: observational astronomy, observational and theoretical astronomy, theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of Astronomical object, celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformal Cyclic Cosmology
Conformal cyclic cosmology (CCC) is a cosmological model in the framework of general relativity and proposed by theoretical physicist Roger Penrose. In CCC, the universe iterates through infinite cycles, with the future timelike infinity (i.e. the latest end of any possible timescale evaluated for any point in space) of each previous iteration being identified with the Big Bang singularity of the next. Penrose popularized this theory in his 2010 book ''Cycles of Time: An Extraordinary New View of the Universe''. Basic construction Penrose's basic construction is to connect a countable sequence of open Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker metric (FLRW) spacetimes, each representing a Big Bang followed by an infinite future expansion. Penrose noticed that the past conformal boundary of one copy of FLRW spacetime can be "attached" to the future conformal boundary of another, after an appropriate conformal rescaling. In particular, each individual FLRW metric g_ is multiplied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arecibo
Arecibo (; ) is a city and municipality on the northern coast of Puerto Rico, on the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, located north of Utuado and Ciales; east of Hatillo; and west of Barceloneta and Florida. It is about west of San Juan, the capital city. Arecibo is the largest municipality in Puerto Rico by area, and it is the core city of the Arecibo Metropolitan Statistical Area and part of the greater San Juan Combined Statistical Area. It is spread over 18 ''barrios'' and Arecibo Pueblo (the downtown area and the administrative center of the city). Its population in 2020 was 87,754. The Arecibo Observatory, which housed the Arecibo telescope, the world's largest radio telescope until July 2016, is located in the municipality. The Arecibo telescope collapsed on December 1, 2020. Arecibo is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Arecibo. Etymology and nicknames The name ''Arecibo'' comes from the Taíno chief Xamaica Arasibo, cacique of the ''yucayeque'' (Taíno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolmogorov Complexity
In algorithmic information theory (a subfield of computer science and mathematics), the Kolmogorov complexity of an object, such as a piece of text, is the length of a shortest computer program (in a predetermined programming language) that produces the object as output. It is a measure of the computational resources needed to specify the object, and is also known as algorithmic complexity, Solomonoff–Kolmogorov–Chaitin complexity, program-size complexity, descriptive complexity, or algorithmic entropy. It is named after Andrey Kolmogorov, who first published on the subject in 1963 and is a generalization of classical information theory. The notion of Kolmogorov complexity can be used to state and prove impossibility results akin to Cantor's diagonal argument, Gödel's incompleteness theorem, and Turing's halting problem. In particular, no program ''P'' computing a lower bound for each text's Kolmogorov complexity can return a value essentially larger than ''P'''s own leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann János Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in both pure and applied mathematics". He integrated pure and applied sciences. Von Neumann made major contributions to many fields, including mathematics (foundations of mathematics, measure theory, functional analysis, ergodic theory, group theory, lattice theory, representation theory, operator algebras, matrix theory, geometry, and numerical analysis), physics (quantum mechanics, hydrodynamics, ballistics, nuclear physics and quantum statistical mechanics), economics ( game theory and general equilibrium theory), computing ( Von Neumann architecture, linear programming, numerical meteo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Paradox
The Fermi paradox is the discrepancy between the lack of conclusive evidence of advanced extraterrestrial life and the apparently high a priori likelihood of its existence, and by extension of obtaining such evidence. As a 2015 article put it, "If life is so easy, someone from somewhere must have come calling by now." Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi's name is associated with the paradox because of a casual conversation in the summer of 1950 with fellow physicists Edward Teller, Herbert York, and Emil Konopinski. While walking to lunch, the men discussed recent UFO reports and the possibility of faster-than-light travel. The conversation moved on to other topics, until during lunch Fermi blurted out, "But where is everybody?" (although the exact quote is uncertain). There have been many attempts to resolve the Fermi paradox, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Panspermia
Information panspermia is the concept of life forms travelling across the universe by means of transmission of compressed information representing said life forms e.g. via genome coding, which can then enable the recovery of intelligent life. Name The concept was invented and coined by Vahe Gurzadyan, and then listed by Stephen Webb as Solution 23 to the Fermi paradox: "The Armenian mathematical physicist Vahe Gurzadyan has posited an interesting hypothesis: we might inhabit a Galaxy 'full of traveling life streams' strings of bits beamed throughout space." Background Kolmogorov complexity is defined as the length of the computer program which enables the complete recovery of an object. Gurzadyan showed that the complexity of the human genome is relatively low due to non-random parts in the genomic sequences. Moreover, he noticed that since the genomic information on the terrestrial life, starting from bacteria up to humans, contains essential common parts, the entire terrestri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Synchrotron Radiation Facility
The European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) is a joint research facility situated in Grenoble, France, supported by 22 countries (13 member countries: France, Germany, Italy, the UK, Spain, Switzerland, Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, Finland, Norway, Sweden, Russia; and 9 associate countries: Austria, Portugal, Israel, Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia, India and South Africa). Some 8,000 scientists visit this particle accelerator each year, conducting upwards of 2,000 experiments and producing around 1,800 scientific publications. History Inaugurated in September 1994, it has an annual budget of around 100 million euros, employs over 630 people and is host to more than visiting scientists each year. In 2009, the ESRF began a first major improvement in its capacities. With the creation of the new ultra-stable experimental hall of 8,000 m2 in 2015, its X-rays are 100 times more powerful, with a power of 100 billion times that of hospital radiography d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Invariance
In a relativistic theory of physics, a Lorentz scalar is an expression, formed from items of the theory, which evaluates to a scalar, invariant under any Lorentz transformation. A Lorentz scalar may be generated from e.g., the scalar product of vectors, or from contracting tensors of the theory. While the components of vectors and tensors are in general altered under Lorentz transformations, Lorentz scalars remain unchanged. A Lorentz scalar is not always immediately seen to be an invariant scalar in the mathematical sense, but the resulting scalar value is invariant under any basis transformation applied to the vector space, on which the considered theory is based. A simple Lorentz scalar in Minkowski spacetime is the ''spacetime distance'' ("length" of their difference) of two fixed events in spacetime. While the "position"-4-vectors of the events change between different inertial frames, their spacetime distance remains invariant under the corresponding Lorentz transformation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
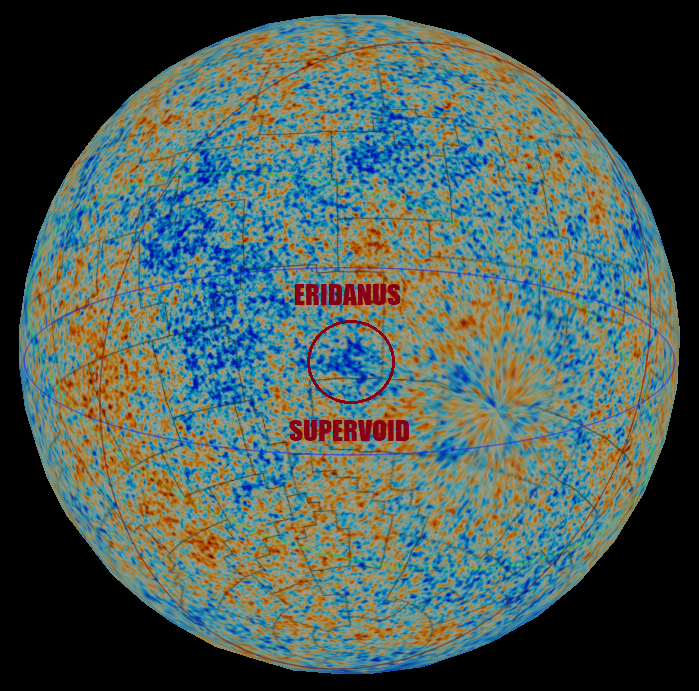
CMB Cold Spot
The CMB Cold Spot or WMAP Cold Spot is a region of the sky seen in microwaves that has been found to be unusually large and cold relative to the expected properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR). The "Cold Spot" is approximately 70 µK (0.00007 K) colder than the average CMB temperature (approximately 2.7 K), whereas the root mean square of typical temperature variations is only 18 µK.After the dipole anisotropy, which is due to the Doppler shift of the microwave background radiation due to our peculiar velocity relative to the comoving cosmic rest frame, has been subtracted out. This feature is consistent with the Earth moving at some 627 km/s towards the constellation Virgo. At some points, the "cold spot" is 140 µK colder than the average CMB temperature. The radius of the "cold spot" subtends about 5°; it is centered at the galactic coordinate , (equatorial: ''α'' = , ''δ'' = ). It is, therefore, in the Souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |