|
Vaginal Melanoma
Vaginal melanoma is a rare malignancy that originates from Melanocyte, melanocytes in the vaginal epithelium. It is also known as a melanocytic tumor or as a malignant melanoma. It is aggressive and infrequently cured. The median overall survival is 16 months. Vaginal melanoma accounts 5.5% of all Vaginal cancer, vaginal cancers and only 1% of all melanomas diagnosed in women. Vaginal melanomas are frequently diagnosed in advanced stages of the disease. The prognosis is poor and the most important risk factor is the presence of lymph node metastases. Presentation This cancer most often develops on the lowest third of the vagina. It is darkly pigmented and of an irregular T-shape, but Amelanotic melanoma, amelanotic melanomas have been described in 7% of cases. Melanoma of the vagina can be several centimeters in size. Histology When the tissue is assessed, the histological characteristics include: * the shape of the cells appear similar to epithelial and spindle-shaped * the growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse. Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. Cancers usually show tumour heterogeneity, containing multiple subclones. They also frequently have reduced expression of DNA repair enzymes due to epigenetic methylation of DNA repair genes or altered microRNAs that control DNA repair gene expression. Tumours can be detected through the visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S100 Protein
The S100 proteins are a family of low molecular-weight proteins found in vertebrates characterized by two calcium-binding sites that have helix-loop-helix (" EF-hand-type") conformation. At least 21 different S100 proteins are known. They are encoded by a family of genes whose symbols use the ''S100'' prefix, for example, ''S100A1'', ''S100A2'', ''S100A3''. They are also considered as damage-associated molecular pattern molecules (DAMPs), and knockdown of aryl hydrocarbon receptor downregulates the expression of S100 proteins in THP-1 cells. Structure Most S100 proteins consist of two identical polypeptides (homodimeric), which are held together by noncovalent bonds. They are structurally similar to calmodulin. They differ from calmodulin, though, on the other features. For instance, their expression pattern is cell-specific, i.e. they are expressed in particular cell types. Their expression depends on environmental factors. In contrast, calmodulin is a ubiquitous and univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Diseases
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral openin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynaecological Neoplasia
Gynecologic oncology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on cancers of the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer. As specialists, they have extensive training in the diagnosis and treatment of these cancers. In the United States, 82,000 women are diagnosed with gynecologic cancer annually. In 2013, an estimated 91,730 were diagnosed. The Society of Gynecologic Oncology and the European Society of Gynaecological Oncology are professional organizations for gynecologic oncologists, and the Gynecologic Oncology Group is a professional organization for gynecological oncologists as well as other medical professionals who deal with gynecologic cancersThe Foundation for Women's Canceris the major U.S. organization that raises awareness and research funding and provides educational programs and materials about gynecologic cancers. There is low quality evidence which demonstrates women with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
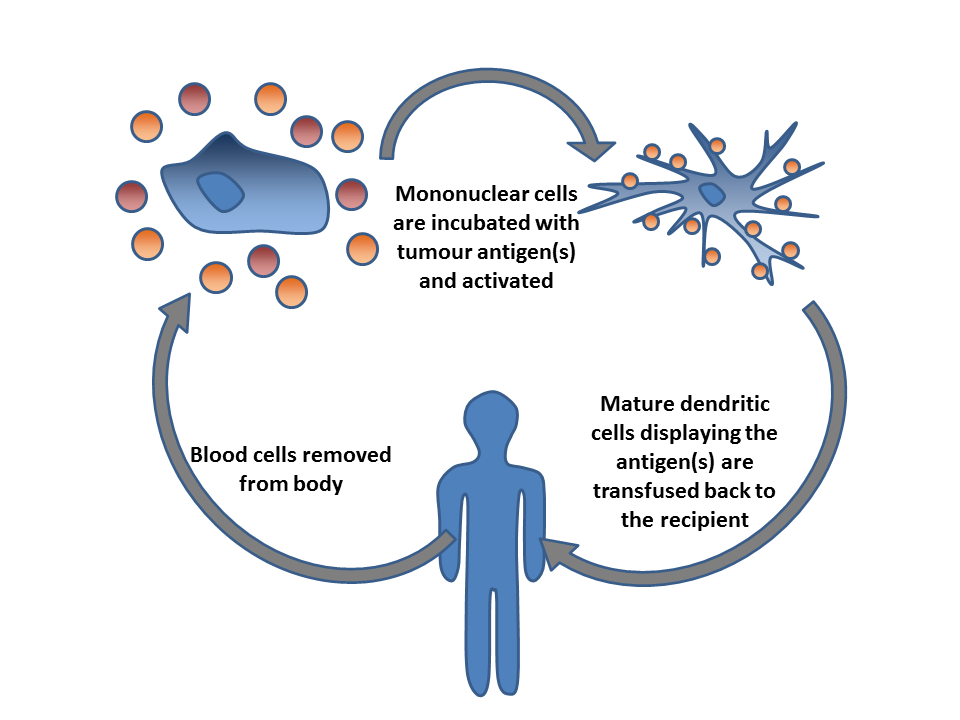
PD-1 Inhibitor
Cancer immunotherapy (sometimes called immuno-oncology) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspecialty of oncology. Cancer immunotherapy exploits the fact that cancer cells often have tumor antigens, molecules on their surface that can be detected by the antibody proteins of the immune system, binding to them. The tumor antigens are often proteins or other macromolecules (e.g., carbohydrates). Normal antibodies bind to external pathogens, but the modified immunotherapy antibodies bind to the tumor antigens marking and identifying the cancer cells for the immune system to inhibit or kill. Clinical success of cancer immunotherapy is highly variable between different forms of cancer; for instance, certain subtypes of gastric cancer react well to the approach whereas immunotherapy is not effective for o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTLA-4
CTLA-4 or CTLA4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), also known as CD152 ( cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed in regulatory T cells but only upregulated in conventional T cells after activation – a phenomenon which is particularly notable in cancers. It acts as an "off" switch when bound to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. The CTLA-4 protein is encoded by the ''Ctla-4'' gene in mice and the ''CTLA-4'' gene in humans. History CTLA-4 was first identified in 1991 as a second receptor for the T cell costimulation ligand B7. In November 1995, the labs of Tak Wah Mak and Arlene H. Sharpe independently published their findings on the discovery of the function of CTLA-4 as a negative regulator of T-cell activation, by knocking out the gene in mice. Previous studies from several labs had used methods which could n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men, they most commonly occur on the back. About 25% of melanomas develop from moles. Changes in a mole that can indicate melanoma include an increase in size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness, or skin breakdown. The primary cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light (UV) exposure in those with low levels of the skin pigment melanin. The UV light may be from the sun or other sources, such as tanning devices. Those with many moles, a history of affected family members, and poor immune function are at greater risk. A number of rare genetic conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, also increase the risk. Diagnosis is by biopsy and analysis of any skin lesio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRAF (gene)
BRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf. The B-Raf protein is involved in sending signals inside cells which are involved in directing cell growth. In 2002, it was shown to be mutated in some human cancers. Certain other inherited ''BRAF'' mutations cause birth defects. Drugs that treat cancers driven by ''BRAF'' mutations have been developed. Two of these drugs, vemurafenib and dabrafenib are approved by FDA for treatment of late-stage melanoma. Vemurafenib was the first approved drug to come out of fragment-based drug discovery. Function B-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of growth signal transduction protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ ERKs signaling pathway, which affects cell division, differentiation, and secretion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEK Inhibitor
A MEK inhibitor is a chemical or drug that inhibits the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase enzymes MEK1 and/or MEK2. They can be used to affect the MAPK/ERK pathway which is often overactive in some cancers. (See MAPK/ERK pathway#Clinical significance.) Hence MEK inhibitors have potential for treatment of some cancers, especially BRAF-mutated melanoma, and KRAS/BRAF mutated colorectal cancer. Approved for clinical use * Binimetinib (MEK162), approved by the FDA in June 2018 in combination with encorafenib for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive melanoma. * Cobimetinib or XL518, approved by US FDA in Nov 2015 for use in combination with vemurafenib (Zelboraf(R)), for treatment of advanced melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation. * Selumetinib, had a phase 2 clinical trial for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) which demonstrated an improvement in PFS, and is now in phase III development in KRAS mutation positiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRAF Inhibitor
BRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf. The B-Raf protein is involved in sending signals inside cells which are involved in directing cell growth. In 2002, it was shown to be mutated in some human cancers. Certain other inherited ''BRAF'' mutations cause birth defects. Drugs that treat cancers driven by ''BRAF'' mutations have been developed. Two of these drugs, vemurafenib and dabrafenib are approved by FDA for treatment of late-stage melanoma. Vemurafenib was the first approved drug to come out of fragment-based drug discovery. Function B-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of growth signal transduction protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ ERKs signaling pathway, which affects cell division, differentiation, and secretion. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checkpoint Inhibitor
Checkpoint inhibitor therapy is a form of cancer immunotherapy. The therapy targets immune checkpoints, key regulators of the immune system that when stimulated can dampen the immune response to an immunologic stimulus. Some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulating immune checkpoint targets. Checkpoint therapy can block inhibitory checkpoints, restoring immune system function. The first anti-cancer drug targeting an immune checkpoint was ipilimumab, a CTLA4 blocker approved in the United States in 2011. Currently approved checkpoint inhibitors target the molecules CTLA4, PD-1, and PD-L1. PD-1 is the transmembrane programmed cell death 1 protein (also called PDCD1 and CD279), which interacts with PD-L1 ( PD-1 ligand 1, or CD274). PD-L1 on the cell surface binds to PD-1 on an immune cell surface, which inhibits immune cell activity. Among PD-L1 functions is a key regulatory role on T cell activities. It appears that (cancer-mediated) upregulation of PD-L1 on the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLANA
Protein melan-A also known as melanoma antigen recognized by T cells 1 or MART-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MLANA'' or "MALENA" gene. A fragment of the protein, usually consisting of the nine amino acids 27 to 35, is bound by MHC class I complexes which present it to T cells of the immune system. These complexes can be found on the surface of melanoma cells. Decameric peptides (26-35) are being investigated as cancer vaccines. Discovery and nomenclature The names MART-1 and melan-A were coined by two groups of researchers who independently sequenced the gene for this antigen in 1994. Both names are currently in common use. Kawakami et al. at the National Cancer Institute coined the term MART-1, which stands for "melanoma antigen recognized by T-cells." Coulie et al. of Belgium called the gene melan-A, presumably an abbreviation for "melanocyte antigen." Clinical significance MART-1/melan-A is a protein antigen that is found on the surface of melanocyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |