|
Vadim Delaunay
Vadim Nikolaevich Delaunay ( rus, Вади́м Никола́евич Делоне́, p=vɐˈdʲim nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ dʲɪlɐˈnʲɛ, a=Vadim Nikolayevich Dyelonye.ru.vorb.oga; December 22, 1947, Moscow – June 13, 1983, Paris) was a Soviet poet and dissident, who participated in the 1968 Red Square demonstration of protest against military suppression of the Prague Spring. Biography Delaunay was born to a Russian-French family of Soviet Intelligentsia. He was the son of Nikolai Borisovich Delone, a Soviet physicist. His grandfather, Boris Delaunay, was a prominent Soviet mathematician and creator of the Delaunay triangulation. Among his ancestors was marquis Bernard-René de Launay, the last governor of the Bastille, murdered by the attackers on that castle. Delaunay studied at Moscow matshkola ("Mathematical School") No. 2, one of the best in the country at that time, then at the Department of Philology at the Moscow Pedagogical Institute. As a student, he also work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow, Russia
Moscow ( , American English, US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the Moscow metropolitan area, metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the List of largest cities, world's largest cities; being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
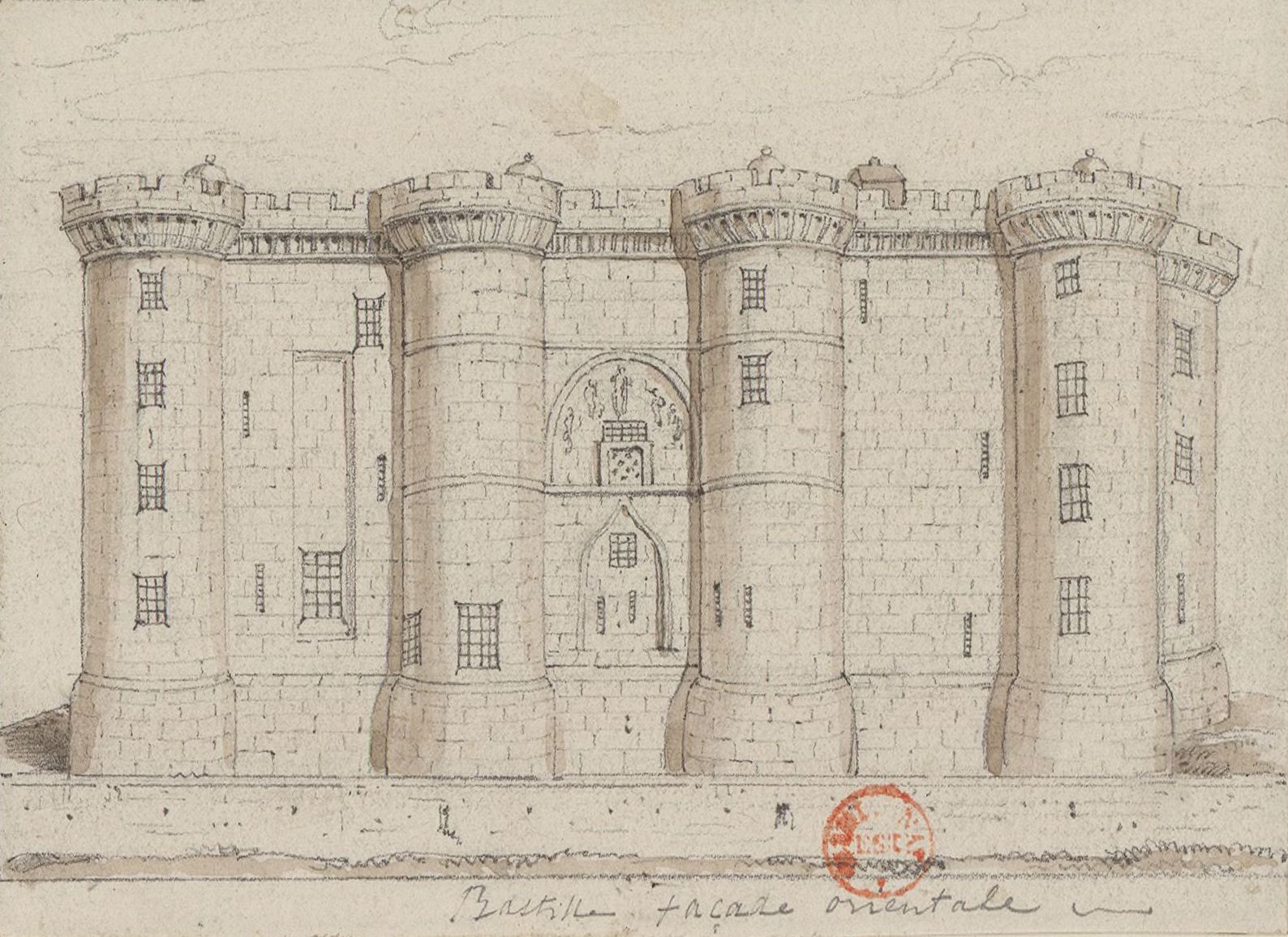
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have many common aspects with slavery and with prisons (especially prison farms). Conditions at labor camps vary widely depending on the operators. Convention no. 105 of the United Nations International Labour Organization (ILO), adopted internationally on 27 June 1957, abolished camps of forced labor. In the 20th century, a new category of labor camps developed for the imprisonment of millions of people who were not criminals ''per se'', but political opponents (real or imagined) and various so-called undesirables under communist and fascist regimes. Some of those camps were dubbed "reeducation facilities" for political coercion, but most others served as backbones of industry and agriculture for the benefit of the state, especially in times of war. Precursors Early-modern states could exploit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Bukovsky
Vladimir Konstantinovich Bukovsky (russian: link=no, Влади́мир Константи́нович Буко́вский; 30 December 1942 – 27 October 2019) was a Russian-born British human rights activist and writer. From the late 1950s to the mid-1970s, he was a prominent figure in the Soviet dissident movement, well known at home and abroad. He spent a total of twelve years in the psychiatric prison-hospitals, labour camps, and prisons of the Soviet Union. After being expelled from the Soviet Union in late 1976, Bukovsky remained in vocal opposition to the Soviet system and the shortcomings of its successor regimes in Russia. An activist, a writer, Jacket and a neurophysiologist,. he is celebrated for his part in the campaign to expose and halt the political abuse of psychiatry in the Soviet Union. A member of the international advisory council of the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation, a director of the Gratitude Fund (set up in 1998 to commemorate and sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might be imposed for these offences, and some general provisions (such as definitions and prohibitions on retroactive prosecution). Criminal codes are relatively common in civil law jurisdictions, which tend to build legal systems around codes and principles which are relatively abstract and apply them on a case-by-case basis. Conversely they are not as common in common law jurisdictions. The proposed introduction of a criminal code in England and Wales was a significant project of the Law Commission from 1968 to 2008. Due to the strong tradition of legal precedent in the jurisdiction and consequently the large number of binding legal judgements and ambiguous 'common law offences', as well as the often inconsistent nature of English law, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial Of The Four
The Trial of the Four, also Galanskov–Ginzburg trial, was the 1968 trial of Yuri Galanskov, Alexander Ginzburg, Alexey Dobrovolsky and Vera Lahkova for their involvement in samizdat publications. The trial took place in Moscow City Court on January 8–12. All four defendants were sentenced to terms in labour camps. The trial played a major part in consolidating the emerging human rights movement in the Soviet Union. Defendants Yury Galanskov was a second-year student at the Historical Archives Institute and worked at the State Literary Museum in Moscow. From 1959 onwards he took part in readings by young poets in Mayakovsky Square. His poems were published in '' Sintaksis'', a typescript poetry anthology edited by Alexander Ginzburg. In 1966, Galanskov compiled and issued the typewritten literary collection '' Phoenix-66''. Alexander Ginzburg was a first-year student at the Historical Archives Institute who also worked at the State Literary Museum. In 1959–1960 he helped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Galanskov
Yuri Timofeyevich Galanskov (russian: Ю́рий Тимофе́евич Галанско́в, 19 June 1939, Moscow - 4 November 1972, Mordovia) was a Russian poet, historian, human rights activist and dissident. For his political activities, such as founding and editing samizdat almanac ''Phoenix'', he was incarcerated in prisons, camps and forced treatment psychiatric hospitals ''(Psikhushkas)''. He died in a labor camp. Early publications Yuri Galanskov began his dissident activities in 1959, as a participant in the poetry readings in Mayakovsky Square. Several of his works were published in the samizdat anthology '' Sintaksis''. After Alexander Ginzburg was arrested in 1960 for publishing ''Sintaksis'', Yuri Galanskov became the leader of dissident publishing in the Soviet Union. Galanskov’s first publication, ''Phoenix'' came in 1961, and contained direct criticism of the Soviet government, partly in the form of poetry. ''Phoenix'' published works by Boris Pasternak, Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushkin Square
Pushkinskaya Square or Pushkin Square () is a pedestrian open space in the Tverskoy District in central Moscow. Historically, it was known as ''Strastnaya Square'' before being renamed for Alexander Pushkin in 1937. It is located at the junction of the Boulevard Ring (Tverskoy Boulevard to the southwest and Strastnoy Boulevard to the northeast) and Tverskaya Street, northwest of the Kremlin. It is not only one of the busiest city squares in Moscow, but also one of the busiest in the world. The former Strastnaya Square name originates from the Passion Monastery (russian: Страстной монастырь, Strastnoy Monastery), which was demolished in the 1930s. At the center of the square is a statue of Pushkin, funded by public subscription and unveiled by Ivan Turgenev and Fyodor Dostoyevsky in 1880. In 1950, Joseph Stalin Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samizdat
Samizdat (russian: самиздат, lit=self-publishing, links=no) was a form of dissident activity across the Eastern Bloc in which individuals reproduced censored and underground makeshift publications, often by hand, and passed the documents from reader to reader. The practice of manual reproduction was widespread, because most typewriters and printing devices required official registration and permission to access. This was a grassroots practice used to evade official Soviet censorship. Name origin and variations Etymologically, the word ''samizdat'' derives from ''sam'' (, "self, by oneself") and ''izdat'' (, an abbreviation of , , "publishing house"), and thus means "self-published". The Ukrainian language has a similar term: ''samvydav'' (самвидав), from ''sam'', "self", and ''vydavnytstvo'', "publishing house". A Russian poet Nikolay Glazkov coined a version of the term as a pun in the 1940s when he typed copies of his poems and included the note ''Samsebyaizd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literaturnaya Gazeta
''Literaturnaya Gazeta'' (russian: «Литературная Газета», ''Literary Gazette'') is a weekly cultural and political newspaper published in Russia and the Soviet Union. It was published for two periods in the 19th century, and was revived in 1929. Overview The current newspaper shares its title with a 19th century publication, and claims to be a continuation of the original publication. The first paper to bear the name of ''Literaturnaya Gazeta'' was founded by a literary group led by Anton Delvig and Alexander Pushkin, whose profile to this day adorns the paper's masthead. The first issue appeared on January 1, 1830. The paper appeared regularly until June 30, 1831, reappearing in 1840–1849. Pushkin himself published some of his most famous works in this paper. ''Literaturnaya Gazeta'' was the first to publish Gogol, and published works by Baratynsky, Belinsky, Nekrasov and many other Russian authors. After the Russian Revolution, the Soviet literary e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freelance
''Freelance'' (sometimes spelled ''free-lance'' or ''free lance''), ''freelancer'', or ''freelance worker'', are terms commonly used for a person who is self-employed and not necessarily committed to a particular employer long-term. Freelance workers are sometimes represented by a company or a temporary agency that resells freelance labor to clients; others work independently or use professional associations or websites to get work. While the term ''independent contractor'' would be used in a different register of English to designate the tax and employment classes of this type of worker, the term "freelancing" is most common in culture and creative industries, and use of this term may indicate participation therein. Fields, professions, and industries where freelancing is predominant include: music, writing, acting, computer programming, web design, graphic design, translating and illustrating, film and video production, and other forms of piece work that some cultural the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State Pedagogical University
Moscow State Pedagogical University or Moscow State University of Education is an educational and scientific institution in Moscow, Russia, with eighteen faculties and seven branches operational in other Russian cities. The institution had undergone a series of name changes since its establishment in 1872. History The university originates in the Moscow Higher Courses for Women founded by Vladimir Guerrier in 1872. It was subsequently reconstituted several times. In 1918 it admitted men and became the Second Moscow State University, then was reformed without its Medical and Chemical Technology schools as the Moscow State Pedagogical Institute, which for a time was known as the Moscow State V. I. Lenin Pedagogical Institute. In 1990, the Institute regained the status of university and thus its present name. Guerrier Courses (1872–1888) In May 1872 the Russian Minister of Education, Count Dmitry Tolstoy, consented to the opening by Professor Guerrier of " Higher Women's Cours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |