|
Vacuum Tower Telescope
The Vacuum Tower Telescope is an evacuated-optics solar telescope located at the Teide Observatory on Tenerife in the Canary Islands. It is operated by the Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik (KIS). It was built between 1983 and 1986, with first light in 1988. It has a 70-centimetre (28-inch) diameter primary mirror and a focal length of . Thanks to an adaptive optics system ''KAOS'' (''K''iepenheuer-institute ''A''daptive ''O''ptic ''S''ystem), in operation since spring 2000, it is able to resolve details down to 0.2 arc seconds (150 km) on the Sun's surface. Description The VTT and the GREGOR are operated by four German institutes: the Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, the Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik (Freiburg, chair), the Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung (Lindau), and the Universitäts-Sternwarte Göttingen. The telescope is used for scientific observations from mid April through mid December. Typically 30 to 40 observing campaigns ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tower Telescope, Teide Observatory
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressure by around 20%. But hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teide Observatory 2018 065
Teide, or Mount Teide, ( es, El Teide, Pico del Teide, , "Peak of Teide") is a volcano on Tenerife in the Canary Islands, Spain. Its summit (at ) is the highest point in Spain and the highest point above sea level in the islands of the Atlantic. If measured from the ocean floor, its height of makes Teide the third-highest volcano in the world, and is described by UNESCO and NASA as Earth's third-tallest volcanic structure. However, as Teide was formed just 170,000 years ago due to volcanic activity following a catastrophic landslide, Teide's base is actually situated in the Las Cañadas crater (the remains of an older, eroded, extinct volcano) at a height of around above sea level. Teide's elevation above sea level makes Tenerife the tenth highest island in the world. Teide is an active volcano: its most recent eruption occurred in late 1909 from the El Chinyero vent on the northwestern Santiago rift. The United Nations Committee for Disaster Mitigation designated Teide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
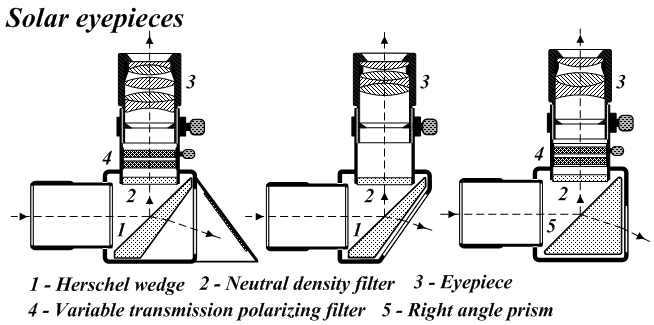
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teide Observatory
Teide Observatory ( es, Observatorio del Teide), IAU code 954, is an astronomical observatory on Mount Teide at , located on Tenerife, Spain. It has been operated by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias since its inauguration in 1964. It became one of the first major international observatories, attracting telescopes from different countries around the world because of the good astronomical seeing conditions. Later the emphasis for optical telescopes shifted more towards Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on La Palma. Telescopes Solar telescopes *Solar Vacuum Tower Telescope (VTT): 70 cm diameter. Operated by the Kiepenheuer Institute of Solar Physics, Freiburg (Germany). Installed in 1989. *THEMIS Solar Telescope: 90 cm diameter, built 1996, operated by Italy and France. *GREGOR Solar Telescope: 1.5 m, operated by a German consortium. In operation since May 2012. *A node of the Birmingham Solar Oscillations Network (BiSON), operated by the University of Birm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of January 2022, it is also the most populous island of Spain and of Macaronesia. Approximately five million tourists visit Tenerife each year; it is the most visited island in the archipelago. It is one of the most important tourist destinations in Spain and the world, hosting one of the world's largest carnivals, the Carnival of Santa Cruz de Tenerife. The capital of the island, , is also the seat of the island council (). That city and are the co-capitals of the autonomous community of the Canary Islands. The two cities are both home to governmental institutions, such as the offices of the presidency and the ministries. This has been the arrangement since 1927, when the Crown ordered it. (After the 1833 territorial division of Spain, until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocco. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and they are the most populous special territory of the European Union. The seven main islands are (from largest to smallest in area) Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera, and El Hierro. The archipelago includes many smaller islands and islets, including La Graciosa, Alegranza, Isla de Lobos, Montaña Clara, Roque del Oeste, and Roque del Este. It also includes a number of rocks, including those of Salmor, Fasnia, Bonanza, Garachico, and Anaga. In ancient times, the island chain was often referred to as "the Fortunate Isles". The Canary Islands are the southernmost region of Spain, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiepenheuer-Institut Für Sonnenphysik
The Leibniz Institute for Solar Physics (aka: KIS; german: Leibniz-Institut für Sonnenphysik), formerly known as Kiepenheuer Institute for Solar Physics (KIS) is a research institute located in Freiburg, Germany. As a member of the Leibniz Association, the institute conducts basic research in astronomy and astrophysics with a particular focus on solar physics. The institute's structure and operation is based on three strategic pillars: 1) fundamental research, 2) operation of the German solar telescope infrastructure on Tenerife, and 3) applied research in data science and operation of the Science Data Center. Institute's Professors appointed and habilitated at the University of Freiburg offer lectures at various university degree levels and train young scientists. History The institute was founded in 1943 as the 'Fraunhofer Institute' by Karl-Otto Kiepenheuer. Kiepenheuer was director of the institute from 1943 until his death in 1975. The institute was renamed as the 'Kiepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instituto De Astrofísica De Canarias
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is an astrophysical research institute located in the Canary Islands, Spain. It was founded in 1975 at the University of La Laguna. It operates two astronomical observatories in the Canary Islands: Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on La Palma, and Teide Observatory on Tenerife. The current director of the IAC is Rafael Rebolo López. In 2016, English scientist A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosoph ... Stephen Hawking was appointed Honorary Professor of the IAC, the first such appointment made by the institute. See also * Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía References External links IAC HomepageEuropean Northern Observatory Tenerife Research institutes in Spain Astronomy institutes and departments Ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Mirror
A primary mirror (or primary) is the principal light-gathering surface (the objective) of a reflecting telescope. Description The primary mirror of a reflecting telescope is a spherical or parabolic shaped disks of polished reflective metal (speculum metal up to the mid 19th century), or in later telescopes, glass or other material coated with a reflective layer. One of the first known reflecting telescopes, Newton's reflector of 1668, used a 3.3 cm polished metal primary mirror. The next major change was to use silver on glass rather than metal, in the 19th century such was with the Crossley reflector. This was changed to vacuum deposited aluminum on glass, used on the 200-inch Hale telescope. Solid primary mirrors have to sustain their own weight and not deform under gravity, which limits the maximum size for a single piece primary mirror. Segmented mirror configurations are used to get around the size limitation on single primary mirrors. For example, the Giant Mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power. In most photography and all telescopy, where the subject is essentially infinitely far away, longer focal length (lower opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array. Adaptive optics should not be confused with active optics, which works on a longer timescale to correct the primary mirror geometry. Other methods can achieve resolving power exceeding the limit imposed by atmospheric distortion, such as speckle imaging, aperture synthesis, and lucky imaging, or by moving outside the atmosphere with space telescopes, such as the Hubble Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GREGOR Solar Telescope
GREGOR is a solar telescope, equipped with a 1.5 m primary mirror, located at 2,390 m altitude at the Teide Observatory on Tenerife in the Canary Islands. It replaces the older Gregory Coudé Telescope and was inaugurated on May 21, 2012. First light, using a 1 metre test mirror, was on .First light was obtained with a 1-meter test-mirror due to manufacturing issues with the main mirror GREGOR is the third-largest solar telescope in the world, after the Big Bear Observatory and the McMath-Pierce solar telescope. It is aimed at observing the solar photosphere and chromosphere at visible and infrared wavelengths. GREGOR sports a high-order adaptive optics (AO) system with a 256-actuator deformable mirrors and a 156-subaperture Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor. Efforts are underway to implement multi-conjugate AO in 2014. 2014-2020 2020 upgrade Initial astigmatism was fixed during an upgrade with some corrective optics: two off-axis parabolic mirrors. See also * * * * *Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |