|
GREGOR Solar Telescope
GREGOR is a solar telescope, equipped with a 1.5 m primary mirror, located at 2,390 m altitude at the Teide Observatory on Tenerife in the Canary Islands. It replaces the older Gregory Coudé Telescope and was inaugurated on May 21, 2012. First light, using a 1 metre test mirror, was on .First light was obtained with a 1-meter test-mirror due to manufacturing issues with the main mirror GREGOR is the third-largest solar telescope in the world, after the Big Bear Observatory and the McMath-Pierce solar telescope. It is aimed at observing the solar photosphere and chromosphere at visible and infrared wavelengths. GREGOR sports a high-order adaptive optics (AO) system with a 256-actuator deformable mirrors and a 156-subaperture Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor. Efforts are underway to implement multi-conjugate AO in 2014. 2014-2020 2020 upgrade Initial astigmatism was fixed during an upgrade with some corrective optics: two off-axis parabolic mirrors. See also * * * * *Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
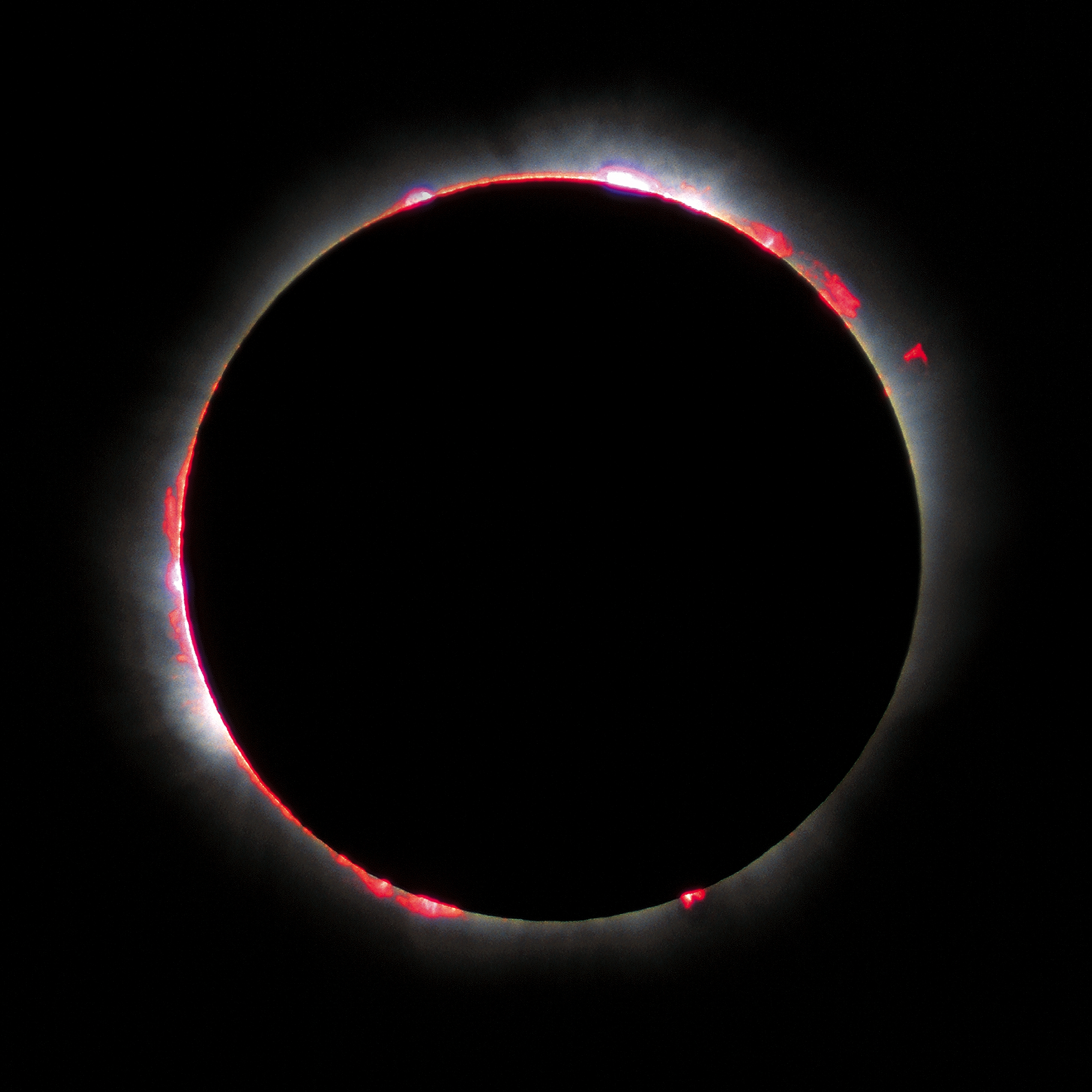
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the deepest region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Composition of the Sun The Sun is composed primarily of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leibniz Institute For Astrophysics Potsdam
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) is a German research institute. It is the successor of the Berlin Observatory founded in 1700 and of the Astrophysical Observatory Potsdam (AOP) founded in 1874. The latter was the world's first observatory to emphasize explicitly the research area of astrophysics. The AIP was founded in 1992, in a re-structuring following the German reunification. The AIP is privately funded and member of the Leibniz Association. It is located in Babelsberg in the state of Brandenburg, just west of Berlin, though the Einstein Tower solar observatory and the great refractor telescopeGreat Refractor telescope at Telegrafenberg on Telegrafenberg i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Solar Telescopes
This is a list of solar telescopes built in various countries around the world. A solar telescope is a specialized telescope that is used to observe the Sun. This list contains ground-based professional observatory telescopes at optical wavelengths in chronological order. Solar telescopes often have multiple focal lengths, and use a various combination of mirrors such as coelostats, lenses, and tubes for instruments including spectrographs, cameras, or coronagraphs. There are many types of instruments that have been designed to observe Earth's Sun, for example, in the 20th century solar towers were common. Ground telescopes Optical telescopes Telescopes for the Sun have existed for hundreds of years, this list is not complete and only goes back to 1900. Potential future optical telescopes Radio telescopes Other types of solar telescopes There are much smaller commercial and/or amateur telescopes such as ''Coronado Filters'' from founder and designer David Lunt, bought by Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformable Mirror
Deformable mirrors (DM) are mirrors whose surface can be deformed, in order to achieve wavefront control and correction of optical aberrations. Deformable mirrors are used in combination with wavefront sensors and real-time control systems in adaptive optics. In 2006 they found a new use in femtosecond pulse shaping. The shape of a DM can be controlled with a speed that is appropriate for compensation of dynamic aberrations present in the optical system. In practice the DM shape should be changed much faster than the process to be corrected, as the correction process, even for a static aberration, may take several iterations. A DM usually has many degrees of freedom. Typically, these degrees of freedom are associated with the mechanical actuators and it can be roughly taken that one actuator corresponds to one degree of freedom. Deformable mirror parameters Number of actuators determines the number of degrees of freedom (wavefront inflections) the mirror can correct. It is ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array. Adaptive optics should not be confused with active optics, which works on a longer timescale to correct the primary mirror geometry. Other methods can achieve resolving power exceeding the limit imposed by atmospheric distortion, such as speckle imaging, aperture synthesis, and lucky imaging, or by moving outside the atmosphere with space telescopes, such as the Hubble Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color") is the second layer of a star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively. In the Sun's atmosphere, the chromosphere is roughly in height, or slightly more than 1% of the Sun's radius at maximum thickness. It possesses a homogeneous layer at the boundary with the photosphere. Hair-like jets of plasma, called spicules, rise from this homogeneous region and through the chromosphere, extending up to into the corona above. The chromosphere has a characteristic red color due to electromagnetic emissions in the ''H''α spectral line. Information about the chromosphere is primarily obtained by analysis of its emitted electromagnetic radiation. Chromospheres have also been observed on stars other than the Sun. On large stars, chromospheres sometimes make up a significant proportion of the entire star. For example, the chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teide Observatory
Teide Observatory ( es, Observatorio del Teide), IAU code 954, is an astronomical observatory on Mount Teide at , located on Tenerife, Spain. It has been operated by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias since its inauguration in 1964. It became one of the first major international observatories, attracting telescopes from different countries around the world because of the good astronomical seeing conditions. Later the emphasis for optical telescopes shifted more towards Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on La Palma. Telescopes Solar telescopes *Solar Vacuum Tower Telescope (VTT): 70 cm diameter. Operated by the Kiepenheuer Institute of Solar Physics, Freiburg (Germany). Installed in 1989. *THEMIS Solar Telescope: 90 cm diameter, built 1996, operated by Italy and France. *GREGOR Solar Telescope: 1.5 m, operated by a German consortium. In operation since May 2012. *A node of the Birmingham Solar Oscillations Network (BiSON), operated by the University of Birm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bear Observatory
Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO) is a university-based solar observatory in the United States. It is operated by New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT). BBSO has a clear aperture Goode Solar Telescope (GST), which has no obscuration in the optical train. BBSO is located on the north side of Big Bear Lake in the San Bernardino Mountains of southwestern San Bernardino County, California, U.S., approximately east of downtown Los Angeles. The telescopes and instruments at the observatory are designed and employed specifically for studying the activities and phenomena of the Sun. Establishment The observatory location was chosen for its location on the high-altitude Big Bear Lake in the San Bernardino Mountains. The combination of high altitude and the daytime stabilizing influence of the lake were found to be ideal of solar observation.The observatory was built The location at Big Bear Lake is optimal due to the clarity of the sky and the presence of a body of water. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phys
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |