|
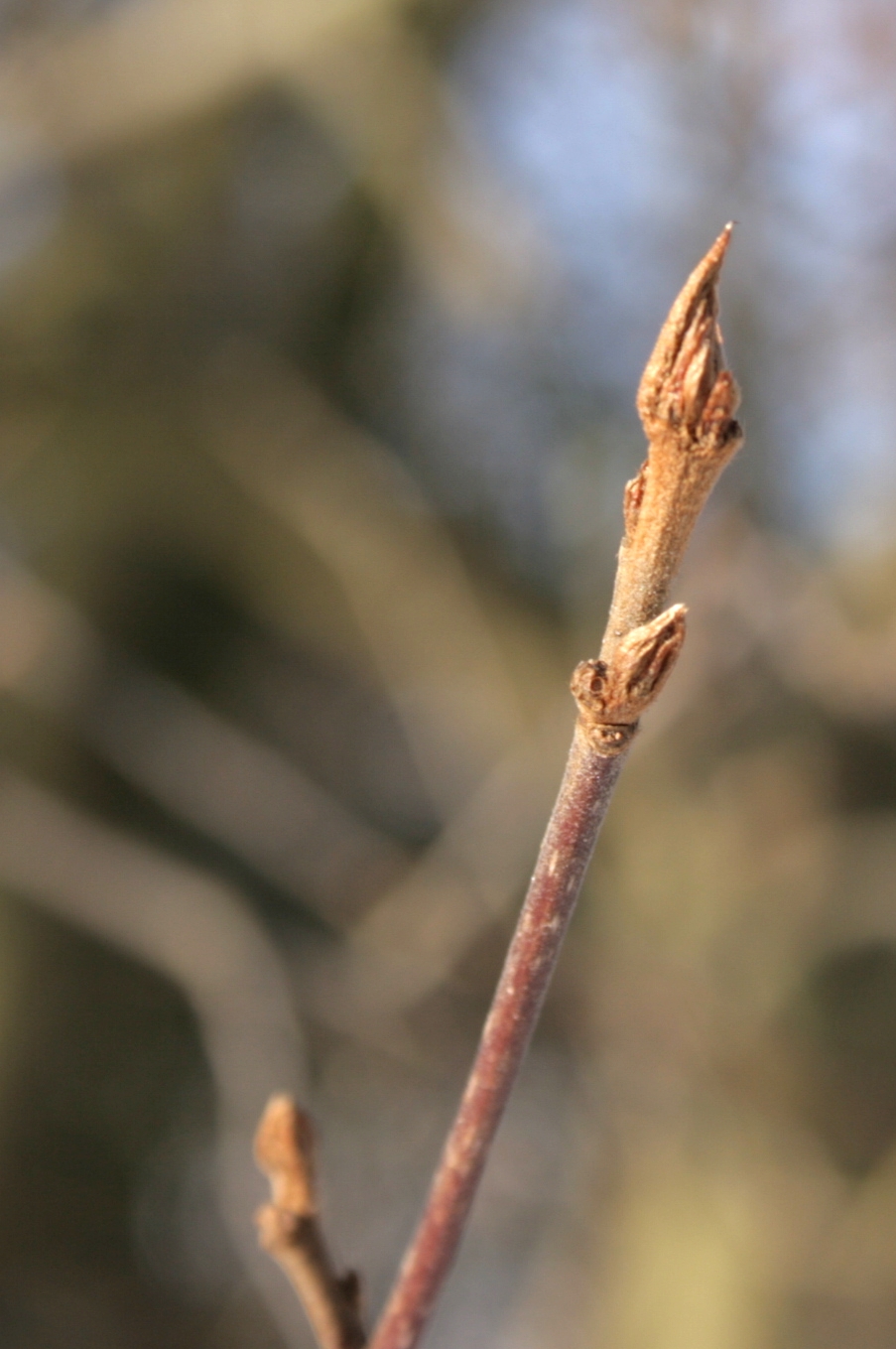
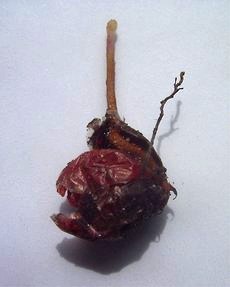
Vaccinium Oxycoccos
''Vaccinium oxycoccos'' is a species of flowering plant in the heath family. It is known as small cranberry, marshberry, bog cranberry, swamp cranberry, or, particularly in Britain, just cranberry. It is widespread throughout the cool temperate northern hemisphere, including northern Europe, northern Asia and northern North America. Description This cranberry is a small, prostrate shrub with vine-like stems that root at the nodes. The leaves are leathery and lance-shaped, up to long. Flowers arise on nodding stalks a few centimeters tall. The corolla is white or pink and flexed backward away from the center of the flower. The fruit is a red berry which has spots when young. It measures up to wide. The plant forms associations with mycorrhizae. It mainly reproduces vegetatively. Distribution and habitat ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'' is a widespread and common species occurring broadly across cooler climates in the temperate northern hemisphere. It is an indicator of moist to wet soi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum Rubellum
''Sphagnum rubellum'', the red peat moss, is a widespread species of moss in the family Sphagnaceae The Sphagnaceae is a family of moss with only one living genus ''Sphagnum ''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term ..., native to the cool temperate parts of North America and Eurasia. It is slower growing than its close relative '' Sphagnum capillifolium''. References rubellum Flora of North America Flora of Europe Flora of temperate Asia Plants described in 1855 {{Bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (Commonwealth English The use of the English language in current and former member countries of the Commonwealth of Nations was largely inherited from British colonisation, with some exceptions. English serves as the medium of inter-Commonwealth relations. Many ...), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but above the forest floor. Only a small percentage of light penetrates the canopy so understory vegetation is generally shade-tolerant. The understory typically consists of trees stunted through lack of light, other small trees with low light requirements, saplings, shrubs, vines and undergrowth. Small trees such as holly and dogwood are understory specialists. In Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest, temperate deciduous forests, many understory plants start into growth earlier in the year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally. The rhizome also retains the ability to allow new shoots to grow upwards. A rhizome is the main stem of the plant that runs underground horizontally. A stolon is similar to a rhizome, but a stolon sprouts from an existing stem, has long internodes, and generates new shoots at the end, such as in the strawberry plant. In general, rhizomes have short internodes, send out roots from the bottom of the nodes, and generate new upward-growing shoots from the top of the nodes. A stem tuber is a thickened part of a rhizome or stolon that has been enlarged for use as a storage organ. In general, a tuber is high in starch, e.g. the potato, which is a modified stolon. The term "tuber" is often used imprecisely and is sometimes appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not plants. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( foliose); grow crust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carex
''Carex'' is a vast genus of more than 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges (or seg, in older books). Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus ''Carex'' may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of ''Carex'' is known as caricology. Description All species of ''Carex'' are perennial, although some species, such as '' C. bebbii'' and '' C. viridula'' can fruit in their first year of growth, and may not survive longer. They typically have rhizomes, stolons or short rootstocks, but some species grow in tufts ( caespitose). The culm – the flower-bearing stalk – is unbranched and usually erect. It is usually distinctly triangular in section. The leaves of ''Carex'' comprise a blade, which extends away from the stalk, and a sheath, which encloses part of the stalk. The blade is normally long and flat, but may be folded, inrolled, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eriophorum
''Eriophorum'' (cottongrass, cotton-grass or cottonsedge) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cyperaceae, the sedge family. They are found throughout the arctic, subarctic, and temperate portions of the Northern Hemisphere in acid bog habitats, being particularly abundant in Arctic tundra regions.Flora Europaea''Eriophorum''/ref> They are herbaceous perennial plants with slender, grass-like leaves. The seed heads are covered in a fluffy mass of cotton-like fibers which are carried on the wind to aid dispersal. The cotton grass also maintains a height of 12 inches and around 2 inches in water. In cold Arctic regions, these masses of translucent fibres also serve as 'down' – increasing the temperature of the reproductive organs during the Arctic summer by trapping solar radiation. Paper and the wicks of candles have been made of its fiber, and pillows stuffed with the same material. The leaves were formerly used in treating diarrhea, and the spongy pith of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosera
''Drosera'', which is commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species. 2 volumes. These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilaginous glands covering their leaf surfaces. The insects are used to supplement the poor mineral nutrition of the soil in which the plants grow. Various species, which vary greatly in size and form, are native to every continent except Antarctica.McPherson, S.R. 2008. ''Glistening Carnivores''. Redfern NaturalHistory Productions Ltd., Poole. Charles Darwin performed much of the early research into ''Drosera'', engaging in a long series of experiments with Drosera rotundifolia which were the first to confirm carnivory in plants. In an 1860 letter, Darwin wrote, “…at the present moment, I care more about ''Drosera'' than the origin of all the species in the world.” Both the botanical name (from the Greek δρόσος: ''drosos'' = "dew, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhamnus Frangula
''Frangula alnus'', commonly known as alder buckthorn, glossy buckthorn, or breaking buckthorn, is a tall deciduous shrub in the family Rhamnaceae. Unlike other "buckthorns", alder buckthorn does not have thorns. It is native to Europe, northernmost Africa, and western Asia, from Ireland and Great Britain north to the 68th parallel in Scandinavia, east to central Siberia and Xinjiang in western China, and south to northern Morocco, Turkey, and the Alborz in Iran and Caucasus Mountains; in the northwest of its range (Ireland, Scotland), it is rare and scattered. It is also introduced and naturalised in eastern North America.Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins .Flora Europaea''Frangula alnus''/ref>Den virtuella floran(in Swedish, with detailed maps)Stace, Clive, et al. ''Interactive Flora of NW Europe''''Frangula alnus''/ref> Description Alder buckthorn is a non-spiny deciduous shrub, growing to , occasionally to tall. It is usually multistemmed, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhododendron Canadense
''Rhododendron canadense'', the rhodora or Canada rosebay, is a deciduous flowering shrub that is native to northeastern North America. Classification Today's botanists consider the rhodora to be a distant relative of the other North American members of its genus, but the difference in floral structure did lead 19th century taxonomists to assign the plant its own genus ''Rhodora''. Its closest relative is '' Rhododendron vaseyi'' from the Appalachian Mountains, which differs in having seven stamens. DNA sequencing shows that ''R. vaseyi'' is not related to ''R. canadense'', but more to '' R. albrechtii''. Description It reaches a mature height of 0.5–1.2 m (approximately 1–3 feet). In early spring, it produces pinkish-purple flowers in clusters of 2–6 together; each flower is 2–3 cm (approximately 1 inch) in diameter, with a five-lobed purple corolla. The flowers are unusual in comparison with other species of the genus ''Rhododendron'' found in northeaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubus Chamaemorus
''Rubus chamaemorus'' is a species of flowering plant in the rose family Rosaceae, native to cool temperate regions, alpine and arctic tundra and boreal forest. This herbaceous perennial produces amber-colored edible fruit similar to the blackberry. English common names include cloudberry, nordic berry, bakeapple (in Newfoundland and Labrador), knotberry and knoutberry (in England), aqpik or low-bush salmonberry (in Alaska – not to be confused with salmonberry, '' Rubus spectabilis''), and averin or evron (in Scotland). Description Unlike most ''Rubus'' species, the cloudberry is dioecious, and fruit production by a female plant requires pollination from a male plant. The cloudberry grows to high. The leaves alternate between having 5 and 7 soft, handlike lobes on straight, branchless stalks. After pollination, the white (sometimes reddish-tipped) flowers form raspberry-sized aggregate fruits which are more plentiful in wooded rather than sun-exposed habitats. Consisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhododendron Groenlandicum
''Rhododendron groenlandicum'' (bog Labrador tea, muskeg tea, swamp tea, or in northern Canada, Hudson's Bay tea; formerly ''Ledum groenlandicum'' or ''Ledum latifolium'') is a flowering shrub with white flowers and evergreen leaves that is used to make a herbal tea. Description It is a low shrub growing to tall—rarely up to —with evergreen leaves long and broad. The leaves are wrinkled on top, densely hairy white to red-brown underneath, and have a leathery texture, curling at the edges. The tiny white flowers grow in hemispherical clusters and are very fragrant and sticky. Distribution and habitat It is reported from Greenland, as well as from every province and territory in Canada and in the northeastern and northwestern United States (New England, New York, Pennsylvania, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Idaho, Washington, and Alaska). It grows in bogs, muskegs, and open tundra, as well as occasionally on wet shores and rocky alpine slopes. Toxicity The pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarracenia Purpurea
''Sarracenia purpurea'', the purple pitcher plant, northern pitcher plant, turtle socks, or side-saddle flower, is a carnivorous plant in the family Sarraceniaceae. Description Like other species of '' Sarracenia'', ''S. purpurea'' obtains most of its nutrients through prey capture. However, prey acquisition is said to be inefficient, with less than 1% of the visiting prey captured within the pitcher. Even so, anecdotal evidence by growers often shows that pitchers quickly fill up with prey during the warm summer months. Prey fall into the pitcher and drown in the rainwater that collects in the base of each leaf. Prey items, such as flies, ants, spiders, and even moths or hornets, are then digested by an invertebrate community, made up mostly by the mosquito '' Wyeomyia smithii'' and the midge '' Metriocnemus knabi''. The relationship between ''W. smithii'' and ''S. purpurea'' is an example of commensalism. ''S. purpurea'' also traps juvenile spotted salamanders with enough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |