|
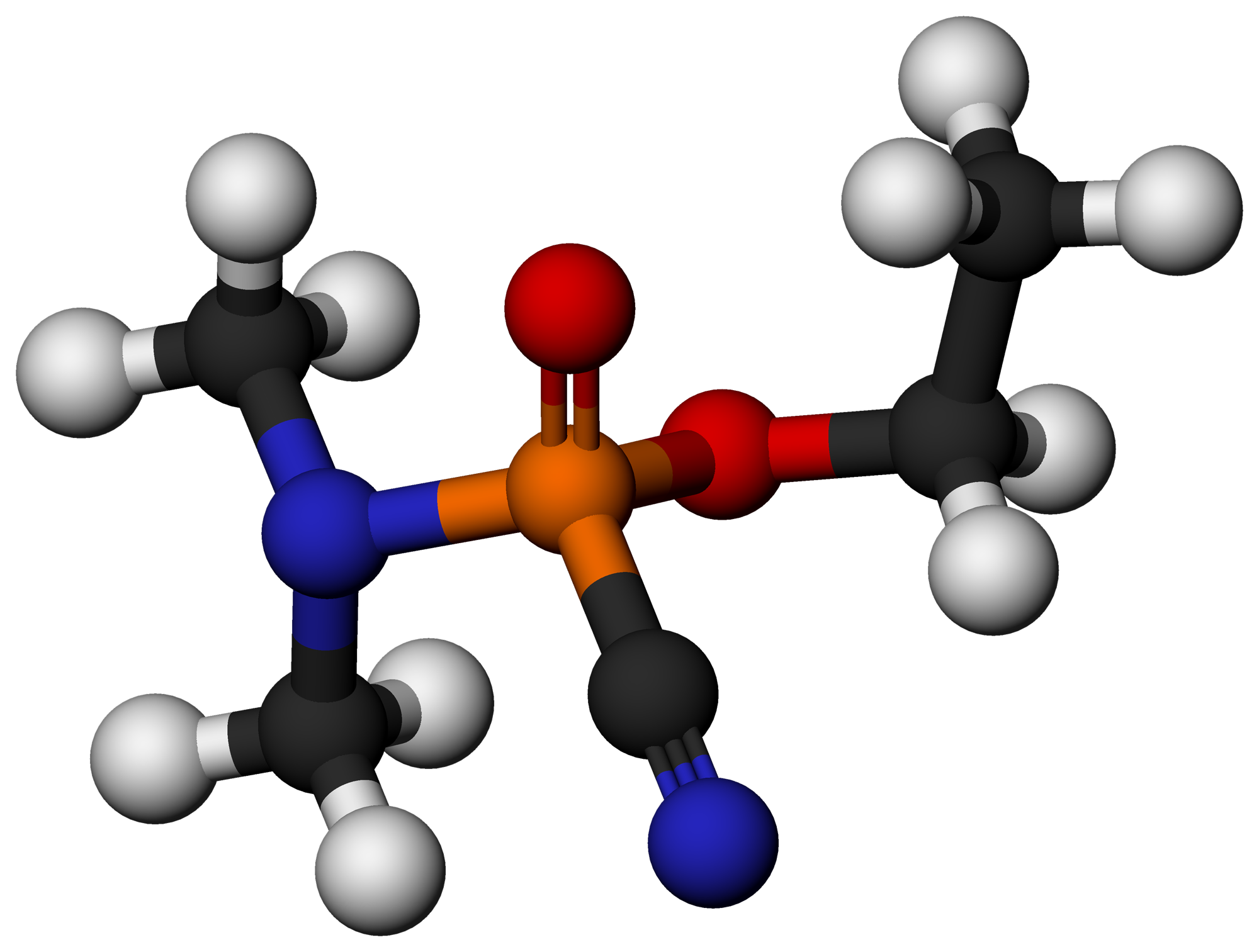
VS (nerve Agent)
VS is a nerve agent of the V-series. Its chemical structure is very similar to the VX nerve agent, but the methyl group on the phosphorus atom is replaced by an ethyl group. See also *VX (nerve agent) VX is an extremely toxic synthetic chemical compound in the organophosphorus class, specifically, a thiophosphonate. In the class of nerve agents, it was developed for military use in chemical warfare after translation of earlier discoverie ... References V-series nerve agents Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Diisopropylamino compounds Ethyl esters {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nerve agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to such agents wear a full body suit in addition to a respirato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nerve agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to such agents wear a full body suit in addition to a respirato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VX (nerve Agent)
VX is an extremely toxic synthetic chemical compound in the organophosphorus class, specifically, a thiophosphonate. In the class of nerve agents, it was developed for military use in chemical warfare after translation of earlier discoveries of organophosphate toxicity in pesticide research. In recent years, VX was found to be the agent used in the assassination of Kim Jong-nam. In its pure form, VX is an oily, relatively non-volatile liquid that is amber-like in colour. Because of its low volatility, VX persists in environments where it is dispersed. VX, short for "venomous agent X", is one of the best known of the V nerve agents and was first discovered at Porton Down by Ranajit Ghosh in England during the early 1950s based on research first done by Gerhard Schrader, a chemist working for IG Farben in Germany during the 1930s. It is now one of a broader V-series of agents which are classified as nerve agents and have been used as a chemical weapon in various recorded dead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Group
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group (abbr. Et) is an alkyl substituent with the formula , derived from ethane (). ''Ethyl'' is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry's nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated two-carbon moiety in a molecule, while the prefix "''eth-''" is used to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule. Ethylation Ethylation is the formation of a compound by introduction of the ethyl group. The most widely practiced example of this reaction is the ethylation of benzene with ethylene to yield ethylbenzene, a precursor to styrene, which is a precursor to polystyrene. Approximately 24.7 million tons of ethylbenzene were produced in 1999. :: Many ethyl-containing compounds are generated by electrophilic ethylation, i.e. treatment of nucleophiles with sources of Et+. Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate t3OF4 is such a reagent. For good nucleophiles, less electrophilic reagents are employed, such as ethyl h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-series Nerve Agents
{{disambiguation ...
V series or V-series may refer to: * Cadillac V series, a line of high-performance vehicles * List of ITU-T V-series recommendations, on data communication over the telephone network * LG V series, a line of high-end Android devices * V series of Sony Ericsson phones, exclusive to Vodafone * V-series of nerve agents: ** VE (nerve agent) ** VG (nerve agent) ** VM (nerve agent) ** VR (nerve agent) ** VS (nerve agent) ** VX (nerve agent) * V (TV series), the name of several TV series * V Series (Sweden), a TV channel See also * U series (other) * W series (other) W series or W-series may refer to: * Dodge W series, 4x4 versions of Dodge D series * GMC W series or Chevrolet W series – versions of the Isuzu Elf trucks * Kawasaki W series, motorcycles * NRIST W-series UAV, Chinese unmanned aerial vehicle l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |