|
VALBOND
In molecular mechanics, VALBOND is a method for computing the angle bending energy that is based on valence bond theory. It is based on ''orbital strength functions'', which are maximized when the orbital hybridisation, hybrid orbitals on the atom are orthogonality#Orthogonal functions, orthogonal. The hybridization of the bonding orbitals are obtained from empirical formulas based on Bent's rule, which relates the preference towards p character with electronegativity. The VALBOND functions are suitable for describing the energy of bond angle distortion not only around the equilibrium angles, but also at very large distortions. This represents an advantage over the simpler harmonic oscillator approximation used by many force fields, and allows the VALBOND method to handle hypervalent molecules and complex (chemistry), transition metal complexes. The VALBOND energy term has been combined with force field (chemistry), force fields such as CHARMM and UFF to provide a complete functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Field (chemistry)
In the context of chemistry and molecular modelling, a force field is a computational method that is used to estimate the forces between atoms within molecules and also between molecules. More precisely, the force field refers to the functional form and parameter sets used to calculate the potential energy of a system of atoms or coarse-grained particles in molecular mechanics, molecular dynamics, or Monte Carlo simulations. The parameters for a chosen energy function may be derived from experiments in physics and chemistry, calculations in quantum mechanics, or both. Force fields are interatomic potentials and utilize the same concept as force fields in classical physics, with the difference that the force field parameters in chemistry describe the energy landscape, from which the acting forces on every particle are derived as a gradient of the potential energy with respect to the particle coordinates. ''All-atom'' force fields provide parameters for every type of atom in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
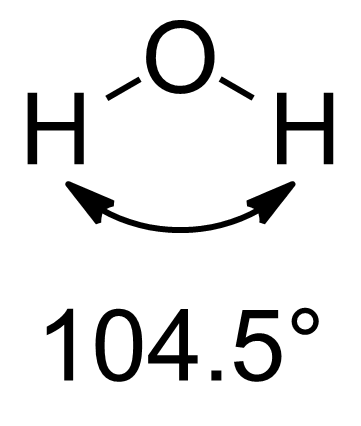
Orbital Hybridisation
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies. History and uses Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals. Pauling pointed out that a carbon atom forms four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms. All-atomistic molecular mechanics methods have the following properties: * Each atom is simulated as one particle * Each particle is assigned a radius (typically the van der Waals radius), polarizability, and a constant net charge (generally derived from quantum calculations and/or experiment) * Bonded interactions are treated as ''springs'' with an equilibrium distance equal to the experimental or calculated bond length Variants on this theme are possible. For example, many simulations have historically used a ''united-atom'' representation in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Bond Theory
In chemistry, valence bond (VB) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover the whole molecule. History Lothar Meyer in his 1864 book, ''Die modernen Theorien der Chemie'', contained an early version of the periodic table containing 28 elements, classified elements into six families by their valence—for the first time, elements had been grouped according to their valence. Works on organizing the elements by atomic weight, until then had been stymied by the widespread use of equivalent weights for the elements, rather than atomic weights. In 1916, G. N. Lewis proposed that a chemical bond forms by the interaction of two shared bonding electrons, with the repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonality
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. By extension, orthogonality is also used to refer to the separation of specific features of a system. The term also has specialized meanings in other fields including art and chemistry. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics * In optics, polarization states are said to be orthogonal when they propagate independently of each other, as in vertical and horizontal linear polarization or right- and left-handed circular polarization. * In special relativity, a time axis determined by a rapidity of motion is hyperbolic-orthogonal to a space axis of simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bent's Rule
In chemistry, Bent's rule describes and explains the relationship between the orbital hybridization of central atoms in molecules and the electronegativities of substituents. The rule was stated by Henry A. Bent as follows: The chemical structure of a molecule is intimately related to its properties and reactivity. Valence bond theory proposes that molecular structures are due to covalent bonds between the atoms and that each bond consists of two overlapping and typically hybridised atomic orbitals. Traditionally, p-block elements in molecules are assumed to hybridise strictly as sp''n'', where ''n'' is either 1, 2, or 3. In addition, the hybrid orbitals are all assumed to be equivalent (i.e. the sp''n'' orbitals have the same p character). Results from this approach are usually good, but they can be improved upon by allowing isovalent hybridization, in which the hybridised orbitals may have noninteger and unequal p character. Bent's rule provides a qualitative estimate as to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Oscillator
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the displacement ''x'': \vec F = -k \vec x, where ''k'' is a positive coefficient, constant. If ''F'' is the only force acting on the system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator, and it undergoes simple harmonic motion: sinusoidal oscillations about the equilibrium point, with a constant amplitude and a constant frequency (which does not depend on the amplitude). If a frictional force (Damping ratio, damping) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. Depending on the friction coefficient, the system can: * Oscillate with a frequency lower than in the Damping ratio, undamped case, and an amplitude decreasing with time (Damping ratio, underdamped oscillator). * Decay to the equilibrium p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervalent Molecule
In chemistry, a hypervalent molecule (the phenomenon is sometimes colloquially known as expanded octet) is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements apparently bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells. Phosphorus pentachloride (), sulfur hexafluoride (), chlorine trifluoride (), the chlorite () ion, and the triiodide () ion are examples of hypervalent molecules. Definitions and nomenclature Hypervalent molecules were first formally defined by Jeremy I. Musher in 1969 as molecules having central atoms of group 15–18 in any valence other than the lowest (i.e. 3, 2, 1, 0 for Groups 15, 16, 17, 18 respectively, based on the octet rule). Several specific classes of hypervalent molecules exist: * Hypervalent iodine compounds are useful reagents in organic chemistry (e.g. Dess–Martin periodinane) * Tetra-, penta- and hexavalent phosphorus, silicon, and sulfur compounds (e.g. PCl5, PF5, SF6, sulfuranes and persulfuranes) * Noble gas compounds (ex. xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex (chemistry)
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHARMM
Chemistry at Harvard Macromolecular Mechanics (CHARMM) is the name of a widely used set of force fields for molecular dynamics, and the name for the molecular dynamics simulation and analysis computer software package associated with them. The CHARMM Development Project involves a worldwide network of developers working with Martin Karplus and his group at Harvard to develop and maintain the CHARMM program. Licenses for this software are available, for a fee, to people and groups working in academia. Force fields The CHARMM force fields for proteins include: united-atom (sometimes termed ''extended atom'') CHARMM19, all-atom CHARMM22 and its dihedral potential corrected variant CHARMM22/CMAP, as well as later versions CHARMM27 and CHARMM36 and various modifications such as CHARMM36m and CHARMM36IDPSFF. In the CHARMM22 protein force field, the atomic partial charges were derived from quantum chemical calculations of the interactions between model compounds and water. Furthermor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-center Four-electron Bond
The 3-center 4-electron (3c–4e) bond is a model used to explain bonding in certain hypervalent molecules such as tetratomic and hexatomic interhalogen compounds, sulfur tetrafluoride, the xenon fluorides, and the bifluoride ion. It is also known as the Pimentel–Rundle three-center model after the work published by George C. Pimentel in 1951,Pimentel, G. C. The Bonding of Trihalide and Bifluoride Ions by the Molecular Orbital Method. ''J. Chem. Phys.'' 1951, ''19'', 446-448. which built on concepts developed earlier by Robert E. Rundle for electron-deficient bonding.Rundle, R. E. Electron Deficient Compounds. II. Relative Energies of "Half-Bonds". ''J. Chem. Phys.'' 1949, ''17'', 671–675. An extended version of this model is used to describe the whole class of hypervalent molecules such as phosphorus pentafluoride and sulfur hexafluoride as well as multi-center π-bonding such as ozone and sulfur trioxide. There are also molecules such as diborane (B2H6) and dialane (Al2H6) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |