|
V605 Aquilae
V605 Aquilae, in the constellation Aquila, is the variable central star of the planetary nebula Abell 58. It is a highly unusual hydrogen-deficient carbon-rich star. V605 Aquilae was first recorded as a nova in 1919, but it turned out to be a very unusual variable. It was measured to be magnitude 10.4 at its peak. Investigation of prior photographs showed that it was magnitude 15 or fainter until 1918, when it brightened to 12th magnitude. It stayed at 11th magnitude or brighter for over a year, before fading from sight. It then brightened to 12th magnitude in late 1921 and again in 1923, before disappearing. The spectral type at the time of the outbursts was R0, a cool hydrogen-deficient carbon star similar to some R Coronae Borealis (RCB) stars. V605 Aquilae was subsequently detected several times at magnitudes 18–20, but these are likely to have been detections only of a small knot of nebulosity surrounding the position of the star. Hubble images show that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
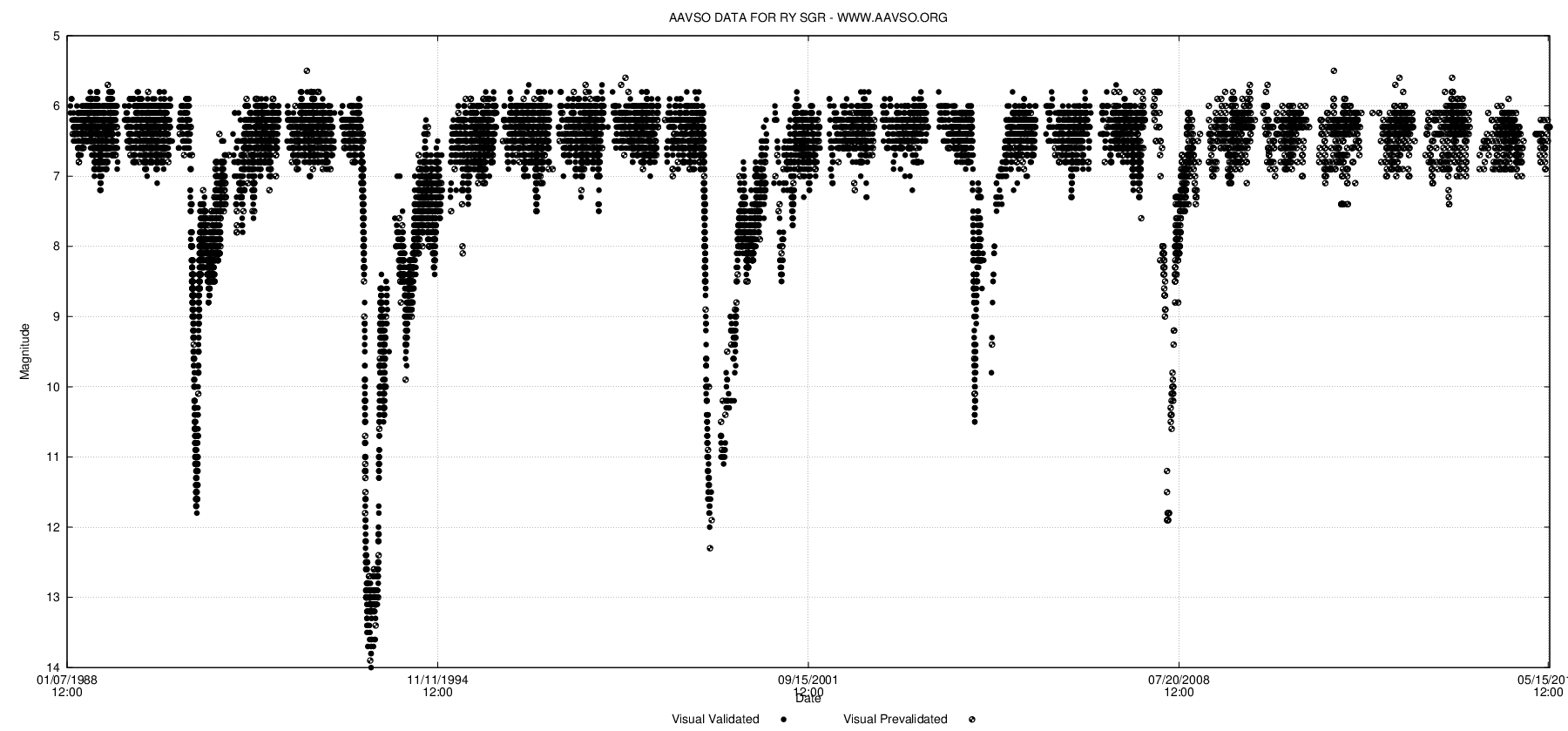
V605AqlLightCurve
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration. The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik and Delahaye. Engines built after World War II include the Lancia V6 engine in 1950 for the Lancia Aurelia, and the Buick V6 engine in 1962 for the Buick Special. The V6 layout has become the most common layout for six-cylinder automotive engines. Design Due to their short length, V6 engines are often used as the larger engine option for vehicles which are otherwise produced with inline-four engines, especially in transverse engine vehicles. A downside for luxury cars is that V6 engines produce more vibrations than straight-six engines. Some sports cars use flat-six engines instead of V6 engines, due to their lower centre of gravity (which improves the handling). The displacement of modern V6 engines is typically between , thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Coronae Borealis Star
An R Coronae Borealis variable (abbreviated RCB, R CrB) is an eruptive variable star that varies in luminosity in two modes, one low amplitude pulsation (a few tenths of a magnitude), and one irregular, unpredictably-sudden fading by 1 to 9 magnitudes. The prototype star R Coronae Borealis was discovered by the English amateur astronomer Edward Pigott in 1795, who first observed the enigmatic fadings of the star. Only about 150 RCB stars are currently known in our Galaxy while up to 1000 were expected, making this class a very rare kind of star. It is increasingly suspected that R Coronae Borealis (RCB) stars – rare hydrogen-deficient and carbon-rich supergiant stars – are the product of mergers of white-dwarfs in the intermediary mass regime (total mass between 0.6 and 1.2 ). The fading is caused by condensation of carbon to soot, making the star fade in visible light while measurements in infrared light exhibit no real luminosity decrease. R Coronae Borealis variables are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Stars
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakurai's Object
Sakurai's Object (V4334 Sagittarii) is a star in the constellation of Sagittarius. It is thought to have previously been a white dwarf that, as a result of a very late thermal pulse, swelled and became a red giant. It is located at the center of a planetary nebula and is believed to currently be in thermal instability and within its final shell helium flash phase. At the time of its discovery, astronomers believed Sakurai's Object to be a slow nova. Later spectroscopic analysis suggested that the star was not a nova, but had instead undergone a very late thermal pulse similar to that of V605 Aquilae, causing it to vastly expand. V605 Aquilae, which was discovered in 1919, is the only other star known to have been observed during the high luminosity phase of a very late thermal pulse, and models predict that Sakurai's Object, over the next few decades, will follow a similar life cycle. Sakurai's Object and other similar stars are expected to end up as helium-rich whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FG Sagittae
FG Sagittae is a supergiant star in the constellation Sagitta (constellation), Sagitta at a distance of 4000 light-years. When first noted in 1943, it was identified to be a variable star, and it was found to be a hot, blue star of stellar spectral type B-type star, B in 1955. Since then it has expanded and cooled, becoming a yellow G-type star by 1991, and then further cooling to become an orange K-type star. It started to pulsate when becoming an A-type star with a period of 15 days. This period later increased to over 100 days. Since 1992 the star has exhibited fadings and recoveries similar to that of a R Coronae Borealis variable star; this behavior is emphasized by a hydrogen deficiency typical for this class of stars. It has been proposed that this star has undergone a late thermal pulse (LTP) of helium fusion after having left the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) to move towards the hottest end of the "white dwarf cooling track". This thermal pulse is believed to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes from the emission of residual thermal energy; no fusion takes place in a white dwarf. The nearest known white dwarf is at 8.6 light years, the smaller component of the Sirius binary star. There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name ''white dwarf'' was coined by Willem Luyten in 1922. White dwarfs are thought to be the final evolutionary state of stars whose mass is not high enough to become a neutron star or black hole. This includes over 97% of the other stars in the Milky Way. After the hydrogen- fusing period of a main-sequence star of low or medium mass ends, such a star will expand to a red giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Late Thermal Pulse
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) late in their lives. Observationally, an asymptotic-giant-branch star will appear as a bright red giant with a luminosity ranging up to thousands of times greater than the Sun. Its interior structure is characterized by a central and largely inert core of carbon and oxygen, a shell where helium is undergoing fusion to form carbon (known as helium burning), another shell where hydrogen is undergoing fusion forming helium (known as hydrogen burning), and a very large envelope of material of composition similar to main-sequence stars (except in the case of carbon stars). Stellar evolution When a star exhausts the supply of hydrogen by nuclear fusion processes in its core, the core contracts and its temperature increases, causing the outer lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptotic Giant Branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) late in their lives. Observationally, an asymptotic-giant-branch star will appear as a bright red giant with a luminosity ranging up to thousands of times greater than the Sun. Its interior structure is characterized by a central and largely inert core of carbon and oxygen, a shell where helium is undergoing fusion to form carbon (known as helium burning), another shell where hydrogen is undergoing fusion forming helium (known as hydrogen burning), and a very large envelope of material of composition similar to main-sequence stars (except in the case of carbon stars). Stellar evolution When a star exhausts the supply of hydrogen by nuclear fusion processes in its core, the core contracts and its temperature increases, causing the outer l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf–Rayet Star
Wolf–Rayet stars, often abbreviated as WR stars, are a rare heterogeneous set of stars with unusual spectra showing prominent broad emission lines of ionised helium and highly ionised nitrogen or carbon. The spectra indicate very high surface enhancement of heavy elements, depletion of hydrogen, and strong stellar winds. The surface temperatures of known Wolf–Rayet stars range from 20,000 K to around 210,000 K, hotter than almost all other kinds of stars. They were previously called W-type stars referring to their spectral classification. Classic (or population I) Wolf–Rayet stars are evolved, massive stars that have completely lost their outer hydrogen and are fusing helium or heavier elements in the core. A subset of the population I WR stars show hydrogen lines in their spectra and are known as WNh stars; they are young extremely massive stars still fusing hydrogen at the core, with helium and nitrogen exposed at the surface by strong mixing and radia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives. The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The term originates from the planet-like round shape of these nebulae observed by astronomers through early telescopes. The first usage may have occurred during the 1780s with the English astronomer William Herschel who described these nebulae as resembling planets; however, as early as January 1779, the French astronomer Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix described in his observations of the Ring Nebula, "very dim but perfectly outlined; it is as large as Jupiter and resembles a fading planet". Though the modern interpretation is different, the old term is still used. All planetary nebulae form at the end of the life of a star of intermediate mass, about 1-8 solar masses. It is expected that the Sun will form a planetary nebula a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |