|
Urman, Syria
Urman ( ar, عرمان; also spelled ''Orman'' or ''Arman'') is a village in southern Syria, administratively part of the Salkhad District of the al-Suwayda Governorate. It is located south of al-Suwayda and nearby localities include Salkhad to the west, Awas to the south, Malah to the east and Sahwat al-Khudr to the north. In the 2004 census it had a population of 5,735. History Byzantine-era ruins and artifacts have been found in Urman. However, unlike other towns in the vicinity, Urman's inhabitants did not convert to Christianity by the 4th century, as indicated by an absence of Christian symbols and edifices. Paganism was practiced in the village until at least 517, as evidenced by stone inscriptions from Urman. There were Arab tribesmen in the village, but it is not clear if they formed all or part of the population. Ottoman era In 1596, Urman appeared in the Ottoman tax registers as part of the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Bani Malik as-Sadir, in the Hauran Sanjak. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorates Of Syria
Syria is a unitary state, but for administrative purposes, it is divided into fourteen governorates, also called provinces or counties in English (Arabic ''muḥāfaẓāt'', singular '' muḥāfaẓah''). The governorates are divided into sixty-five districts (''manāṭiq'', singular '' minṭaqah''), which are further divided into subdistricts (''nawāḥī'', singular '' nāḥiyah''). The ''nawāḥī'' contain villages, which are the smallest administrative units. Each governorate is headed by a governor, appointed by the president, subject to cabinet approval. The governor is responsible for administration, health, social services, education, tourism, public works, transportation, domestic trade, agriculture, industry, civil defense, and maintenance of law and order in the governorate. The minister of local administration works closely with each governor to coordinate and supervise local development projects. The governor is assisted by a provincial council, all of who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauran Sanjak
The Hauran ( ar, حَوْرَان, ''Ḥawrān''; also spelled ''Hawran'' or ''Houran'') is a region that spans parts of southern Syria and northern Jordan. It is bound in the north by the Ghouta oasis, eastwards by the al-Safa field, to the south by Jordan's desert steppe and to the west by the Golan Heights. Traditionally, the Hauran consists of three subregions: the Nuqrah and Jaydur plains, the Jabal al-Druze massif, and the Lajat volcanic field. The population of the Hauran is largely Arab, but religiously heterogeneous; most inhabitants of the plains are Sunni Muslims belonging to large agrarian clans, while Druze form the majority in the eponymous Jabal al-Druze and a significant Greek Orthodox and Greek Catholic minority inhabit the western foothills of Jabal al-Druze. The region's largest towns are Daraa, al-Ramtha and al-Suwayda. From the mid-1st century BCE, the region was governed by the Roman Empire's Herodian and Nabatean client kings until it was formally an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Syrian Revolt
The Great Syrian Revolt ( ar, الثورة السورية الكبرى) or Revolt of 1925 was a general uprising across the State of Syria and Greater Lebanon during the period of 1925 to 1927. The leading rebel forces comprised fighters of the Jabal Druze State in southern Syria, joined by Sunni, Druze, Alawite, and Christian factions. The common goal was to end French rule in the newly mandated regions, passed from Turkish to French administration following World War I. This revolution came in response to the repressive policies pursued by the French authorities under the Mandate for Syria and Lebanon, in dividing Syria into several occupied territories. The new French administration was perceived as being prejudiced against the dominant Arab culture and of intending to change the existing character of the country. In addition resentment was caused by the refusal of the French authorities to set a timetable for the independence of Syria. This revolution was an extension of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lejah
The Lajat (/ALA-LC: ''al-Lajāʾ''), also spelled ''Lejat'', ''Lajah'', ''el-Leja'' or ''Laja'', is the largest lava field in southern Syria, spanning some 900 square kilometers. Located about southeast of Damascus, the Lajat borders the Hauran plain to the west and the foothills of Jabal al-Druze to the south. The average elevation is between 600 and 700 meters above sea level, with the highest volcanic cone being 1,159 meters above sea level. Receiving little annual rainfall, the Lajat is largely barren, though there are scattered patches of arable land in some of its depressions. The region has been known by a number of names throughout its history, including "Argob" ( ''’Argōḇ'',) in the Hebrew Bible and "Trachonitis" () by the Greeks, a name under which it is mentioned in the Gospel of Luke (). Long inhabited by Arab groups, it saw development under the Romans, who built a road through the center of the region connecting it with the empire's province of Syria. The pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammiyya
The Ammiyya ( ar, الثورة العامية في جبل حوران, ', or ar, italic=yes, ʿĀmmiyya) was a revolt against Ottoman rule in Syria in 1889–1890. The tenant farmers and farmworkers sought to curb the abuses of local sheikhs, restricting them to ⅛ of the communal land. They also wanted to partition the rest of the communal land into individual plots outside the sheikh's control, ending their ability to evict poor farmers. Druze opposition was led by the Atrash family. The revolt was largely successful in its aims, restricting the sheikhs to ⅛ of the village land and establishing the system of land tenure which continued in Syria through the Assad regime. Desire to placate the locals also prompted the concessions to French and Belgian companies that led to the DHP, the area's first railway. See also * Long Depression, the economic depression at the time which caused falling prices for Hawran wheat * Abdul Hamid II Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, ع� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabal Al-Arab
Jabal al-Druze ( ar, جبل الدروز, ''jabal ad-durūz'', ''Mountain of the Druze''), officially Jabal al-Arab ( ar, جبل العرب, links=no, ''jabal al-ʿarab'', ''Mountain of the Arabs''), is an elevated volcanic region in the As-Suwayda Governorate of southern Syria. Most of the inhabitants of this region are Druze, and there are also small Muslim and significant Christian communities. Safaitic inscriptions were first found in this area. The State of Jabal Druze was an autonomous area in the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon from 1921 to 1936. In the past, the name Jabal al-Druze was used for a different area, located in Mount Lebanon. Geology The Jabal al-Druze volcanic field, the southernmost in Syria, lies in the Haurun-Druze Plateau in SW Syria near the border with Jordan. The most prominent feature of this volcanic field is 1800m-high Jabal al-Druze (also known variously as Jabal ad Duruz, Djebel Al-Arab, Jabal Druze, Djebel ed Drouz). The alkaline volc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Galilee (, ; , ). ''Galilee'' refers to all of the area that is north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and south of the east–west section of the Litani River. It extends from the Israeli coastal plain and the shores of the Mediterranean Sea with Acre in the west, to the Jordan Rift Valley to the east; and from the Litani in the north plus a piece bordering on the Golan Heights all the way to Dan at the base of Mount Hermon in the northeast, to Mount Carmel and Mount Gilboa in the south. This definition includes the plains of the Jezreel Valley north of Jenin and the Beth Shean Valley, the valley containing the Sea of Galilee, and the Hula Valley, although it usually does not include Haifa's immediate northern suburbs. By this definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
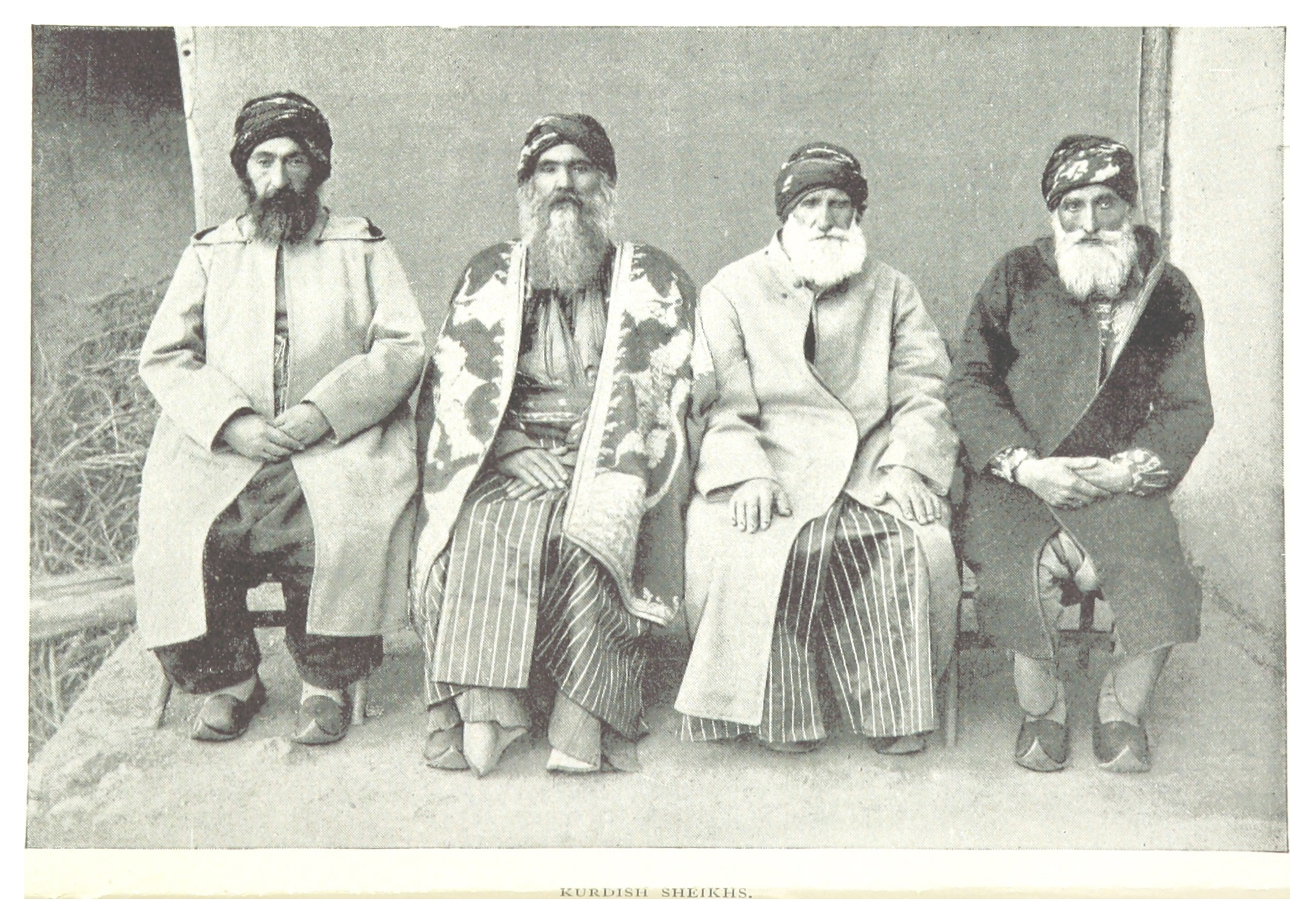
Sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a tribe or a royal family member in Arabian countries, in some countries it is also given to those of great knowledge in religious affairs as a surname by a prestige religious leader from a chain of Sufi scholars. It is also commonly used to refer to a Muslim religious scholar. It is also used as an honorary title by people claiming to be descended from Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali both patrilineal and matrilineal who are grandsons of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The term is literally translated to " Elder" (is also translated to "Lord/Master" in a monarchical context). The word 'sheikh' is mentioned in the 23rd verse of Surah Al-Qasas in the Quran. Etymology and meaning The word in Arabic stems from a triliteral root connected with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Atrash
The al-Atrash ( ar, الأطرش ), also known as Bani al-Atrash, is a Druze clan based in Jabal Hauran in southwestern Syria. The family's name ''al-atrash'' is Arabic for "the deaf" and derives from one the family's deaf patriarchs. The al-Atrash clan migrated to Jabal Hauran in the early 19th century, and under the leadership of their sheikh (chieftain) Ismail al-Atrash became the paramount ruling Druze family of Jabal Hauran in the mid-19th century, taking over from Al Hamdan. Through his battlefield reputation and his political intrigues with other Druze clans, Bedouin tribes, the Ottoman authorities and European consuls, Ismail consolidated al-Atrash power. By the early 1880s, the family controlled eighteen villages, chief among which were as-Suwayda, Salkhad, al-Qurayya, 'Ira and Urman. Ismail was succeeded by his eldest son Ibrahim and following the latter's death, by Ismail's other son Shibli. Al-Atrash sheikhs led the Druze in numerous revolts against the Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at . Geography The Mount Lebanon range extends along the entire country for about , parallel to the Mediterranean coast. Their highest peak is Qurnat as Sawda', at . The range receives a substantial amount of precipitation, including snow, which averages around deep.Jin and Krothe. ''Hydrogeology: Proceedings of the 30th International Geological Congress'', p. 170 Lebanon has historically been defined by the mountains, which provided protection for the local population. In Lebanon, changes in scenery are related less to geographical distances than to altitudes. The mountains were known for their oak and pine forests. The last remaining old growth groves of the famous Cedar of Lebanon (''Cedrus libani'' var. libanii'') are on the high slopes of Mount Lebanon, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of Hamza ibn Ali ibn Ahmad and ancient Greek philosophers like Plato, Aristotle, Pythagoras, and Zeno of Citium. Adherents of the Druze religion call themselves " the Monotheists" or "the Unitarians" (''al-Muwaḥḥidūn''). The Epistles of Wisdom is the foundational and central text of the Druze faith. The Druze faith incorporates elements of Isma'ilism, Christianity, Gnosticism, Neoplatonism, Zoroastrianism, Buddhism, Hinduism, Pythagoreanism, and other philosophies and beliefs, creating a distinct and secretive theology based on an esoteric interpretation of scripture, which emphasizes the role of the mind and truthfulness. Druze believe in theophany and reincarnation. Druze believe that at the end of the cycle of rebirth, which is achie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eli Smith
Eli Smith (born September 13, 1801, in Northford, Connecticut, to Eli and Polly (Whitney) Smith, and died January 11, 1857, in Beirut, Lebanon) was an American Protestant missionary and scholar. He graduated from Yale College in 1821 and from Andover Theological Seminary in 1826. He worked in Malta until 1829, then in company with H. G. O. Dwight traveled through Armenia and Georgia to Persia. They published their observations, ''Missionary Researches in Armenia'', in 1833 in two volumes. Eli Smith settled in Beirut in 1833. Along with Edward Robinson, he made two trips to the Holy Land in 1838 and 1852, acting as an interpreter for Robinson in his quest to identify and record biblical place names in Palestine, which was subsequently published in Robinson's ''Biblical Researches in Palestine''. He is known for bringing the first printing press with Arabic type to Syria. He went on to pursue the task which he considered to be his life's work: translation of the Bible into Arabic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |