|
Uniformity Of Process Act 1832
Uniformity may refer to: * Distribution uniformity, a measure of how uniformly water is applied to the area being watered * Religious uniformity, the promotion of one state religion, denomination, or philosophy to the exclusion of all other religious beliefs * Retention uniformity, a concept in thin layer chromatography * Tire uniformity, a concept in vehicle technology * Uniformity (chemistry), a measure of the homogeneity of a substance's composition or character * Uniformity (complexity), a concept in computational complexity theory * Uniformity (philosophy), the concept that the same natural laws and processes that operate in the universe now have always operated in the universe * Uniformity (topology), a concept in the mathematical field of topology * Uniformity of motive, a concept in astrobiology See also * Uniform (other) * Diversity (other) Diversity, diversify, or diverse may refer to: Business *Diversity (business), the inclusion of people of diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Uniformity
Distribution uniformity or DU in irrigation is a measure of how uniformly water is applied to the area being watered, normally expressed as percentage, and not to be confused with efficiency. The distribution uniformity is often calculated when performing an irrigation audit. The DU should not be confused with the coefficient of uniformity (CU) which is often preferred for describing the performance of overhead pressurized systems. The most common measure of DU is the low quarter DU expressed as DUlq, which is a measure of the average of the lowest quarter of samples, divided by the average of all samples expressed as percentage. The higher the DUlq, the more uniform the coverage of the area measured. If all samples are equal, the DUlq is 1.0 or 100%. There is no universal value of DUlq for satisfactory system performance. A value of >.80 or 80% is considered above average. Distribution uniformity may be helpful as a starting point for irrigation scheduling Irrigation schedul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Uniformity
Religious uniformity occurs when government is used to promote one state religion, denomination, or philosophy to the exclusion of all other religious beliefs. History Religious uniformity was common in many modern theocratic and atheistic governments around the world until fairly modern times. The modern concept of a separate civil government was relatively unknown until expounded upon by Roger Williams, a Christian minister, in '' The Bloudy Tenent of Persecution'' (1644) shortly after he founded the American colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations in 1636.James Emanuel Ernst, Roger Williams, ''New England Firebrand'' (Macmillan Co., Rhode Island, 1932), pg. 2/ref> In the United States, the First Amendment to the Constitution (1791) prohibits the federal government from establishing or prohibiting a religion, and in 1947 the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that states cannot create established state churches in '' Everson v. Board of Education''. See also *Act of Uniformity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retention Uniformity
Retention uniformity, or ''RU'', is a concept in thin layer chromatography. It is designed for the quantitative measurement of ''equal-spreading'' of the spots on the chromatographic plate and is one of the Chromatographic response functions. Formula Retention uniformity is calculated from the following formula: R_ = 1 - \sqrt{\frac{6(n+1)}{n(2n+1)}\sum_{i=1}^{n}{\left(R_{Fi}-\frac{i}{n+1}\right)^2 where ''n'' is the number of compounds separated, ''Rf (1...n)'' are the Retention factor In chromatography, the retardation factor (''R'') is the fraction of an analyte An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. The purest ... of the compounds sorted in non-descending order. Theoretical considerations The coefficient lies always in range and 0 indicates worst case of separation (all Rf values equal to 0 or 1), value 1 indicates ideal equal-spreading of the spot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
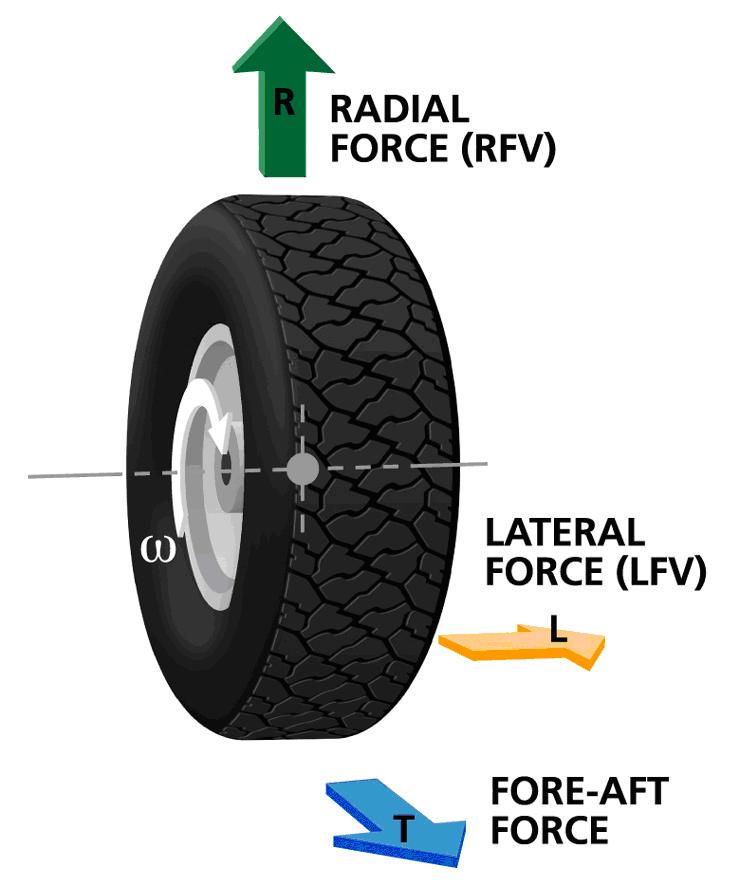
Tire Uniformity
Tire Uniformity refers to the dynamic mechanical properties of pneumatic tires as strictly defined by a set of measurement standards and test conditions accepted by global tire and car makers. These standards include the parameters of radial force variation, lateral force variation, conicity, ply steer, radial run-out, lateral run-out, and sidewall bulge. Tire makers worldwide employ tire uniformity measurement as a way to identify poorly performing tires so they are not sold to the marketplace. Both tire and vehicle manufacturers seek to improve tire uniformity in order to improve vehicle ride comfort. Force variation background The circumference of the tire can be modeled as a series of very small spring elements whose spring constants vary according to manufacturing conditions. These spring elements are compressed as they enter the road contact area, and recover as they exit the footprint. Variation in the spring constants in both radial and lateral directions cause variati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniformity (chemistry)
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which are not chemically bonded. A mixture is the physical combination of two or more substances in which the identities are retained and are mixed in the form of solutions, suspensions and colloids. Mixtures are one product of mechanically blending or mixing chemical substances such as elements and compounds, without chemical bonding or other chemical change, so that each ingredient substance retains its own chemical properties and makeup. Despite the fact that there are no chemical changes to its constituents, the physical properties of a mixture, such as its melting point, may differ from those of the components. Some mixtures can be separated into their components by using physical (mechanical or thermal) means. Azeotropes are one kind of mixture that usually poses considerable difficulties regarding the separation processes required to obtain their constituents (physical or chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniformity (complexity)
In theoretical computer science, circuit complexity is a branch of computational complexity theory in which Boolean functions are classified according to the size or depth of the Boolean circuits that compute them. A related notion is the circuit complexity of a recursive language that is decided by a uniform family of circuits C_,C_,\ldots (see below). Proving lower bounds on size of Boolean circuits computing explicit Boolean functions is a popular approach to separating complexity classes. For example, a prominent circuit class P/poly consists of Boolean functions computable by circuits of polynomial size. Proving that \mathsf\not\subseteq \mathsf would separate P and NP (see below). Complexity classes defined in terms of Boolean circuits include AC0, AC, TC0, NC1, NC, and P/poly. Size and depth A Boolean circuit with n input bits is a directed acyclic graph in which every node (usually called ''gates'' in this context) is either an input node of in-degree 0 labelle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniformity (philosophy)
Uniformitarianism, also known as the Doctrine of Uniformity or the Uniformitarian Principle, is the assumption that the same natural laws and processes that operate in our present-day scientific observations have always operated in the universe in the past and apply everywhere in the universe., "''The assumption of spatial and temporal invariance of natural laws is by no means unique to geology since it amounts to a warrant for inductive inference'' which, as Bacon showed nearly four hundred years ago, is ''the basic mode of reasoning in empirical science. Without assuming this spatial and temporal invariance, we have no basis for extrapolating from the known to the unknown'' and, therefore, no way of reaching general conclusions from a finite number of observations." It refers to Invariant (physics), invariance in the metaphysics, metaphysical principles underpinning science, such as the constancy of causality, cause and effect throughout space-time, but has also been used to desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniformity (topology)
In the mathematical field of topology, a uniform space is a set with a uniform structure. Uniform spaces are topological spaces with additional structure that is used to define uniform properties such as completeness, uniform continuity and uniform convergence. Uniform spaces generalize metric spaces and topological groups, but the concept is designed to formulate the weakest axioms needed for most proofs in analysis. In addition to the usual properties of a topological structure, in a uniform space one formalizes the notions of relative closeness and closeness of points. In other words, ideas like "''x'' is closer to ''a'' than ''y'' is to ''b''" make sense in uniform spaces. By comparison, in a general topological space, given sets ''A,B'' it is meaningful to say that a point ''x'' is ''arbitrarily close'' to ''A'' (i.e., in the closure of ''A''), or perhaps that ''A'' is a ''smaller neighborhood'' of ''x'' than ''B'', but notions of closeness of points and relative closeness a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniformity Of Motive
In astrobiology, Uniformity of Motive is an essential assumption of the Zoo hypothesis, Zoo Hypothesis explanation to Fermi paradox, Fermi’s Paradox. The Zoo Hypothesis states that alien civilizations refrain from contacting Earth, so as to not interfere in natural evolution and cultural development, or to minimize risk for themselves. Certain technological, political or ethical thresholds and standards could be implemented for other civilizations to pass, after which contact would be established. In the likely case that more than one sufficiently developed alien civilizations exist, a Uniformity of Motive with legal policy concerning the contact of newly developing civilizations would have to be established and maintained. A “Galactic Club” would be formed and maintained, possibly by an early advanced civilization. The size of a club like this would influence the likelihood of compliance by all members, since any member could break the contact rules at any point in time, maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform (other)
A uniform is a standard set of clothing identifying the wearer as a member of an organisation. Uniform may also refer to: Clothing * Baseball uniform * Military uniform, often simply "uniform", worn by members of a military organisation * School uniform, also known as "student uniform" or simply "uniform", mandated clothing for students in a particular school or school system Music and film * Uniform (band), American rock band * Uniform (film), ''Uniform'' (film) is the title of a 2003 film by director Diao Yi'nan * "Uniform", a song by Joe Beagle * "Uniform", a track on British band Bloc Party's album ''A Weekend in the City'' * "Uniform", a 1982 single by Icehouse, from the album ''Primitive Man (album), Primitive Man'' * "Uniform", a 1994 single by Inspiral Carpets, from the album ''Devil Hopping'' Mathematics and physics * Uniform circular motion, in physics * Uniform continuity of a function is a property stronger than ordinary continuity * Uniform convergence of an infin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |