|
Ungava Magmatic Event
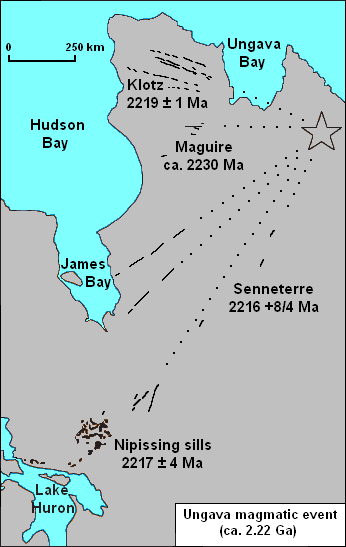
The Ungava magmatic event was a widespread magmatic event that began about 2.22 billion years ago during the Proterozoic Eon. Extent With an area of , the Ungava magmatic event caused the formation of a large igneous province. Magmatic features that were formed during the Ungava magmatic event include the Klotz, Maguire and Senneterre dikes of Quebec and the Nipissing sills of Ontario Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca .... References Igneous petrology of Quebec Igneous petrology of Ontario Paleoproterozoic magmatism {{Canada-geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungava Magmatic Event
The Ungava magmatic event was a widespread magmatic event that began about 2.22 billion years ago during the Proterozoic Eon. Extent With an area of , the Ungava magmatic event caused the formation of a large igneous province. Magmatic features that were formed during the Ungava magmatic event include the Klotz, Maguire and Senneterre dikes of Quebec and the Nipissing sills of Ontario Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca .... References Igneous petrology of Quebec Igneous petrology of Ontario Paleoproterozoic magmatism {{Canada-geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic, and Neoproterozoic. The Proterozoic covers the time from the appearance of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life (such as trilobites or corals) on the Earth. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two forms of ultimately Greek origin: meaning 'former, earlier', and , 'of life'. The well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes; several glaciations, which produced the hypothesized Snowball Earth during the Cryogenian Period in the late Neoproterozoic Era; and the Ediacaran Period (635 to 538.8 Ma) which is characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Igneous Province
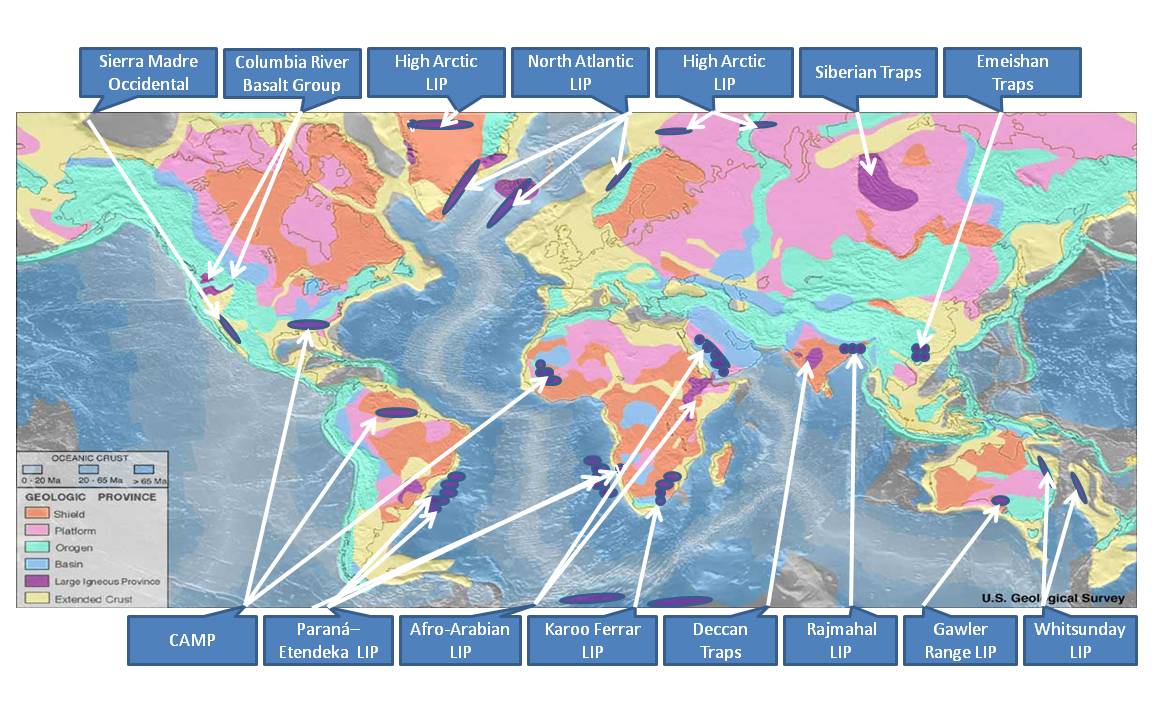
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike (geology)
A dike or dyke, in Geology, geological usage, is a sheet of rock that is formed in a Fracture (geology), fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either Intrusive rock, magmatic or Sedimentary rock, sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak Magmatic dikes A magmatic dike is a sheet of igneous rock that cuts across older rock beds. It is formed when magma fills a fracture in the older beds and then cools and solidifies. The dike rock is usually more resistant to weathering than the surrounding rock, so that erosion exposes the dike as a natural wall or ridge. It is from these natural walls that dikes get their name. Dikes preserve a record of the fissures through which most mafic magma (fluid magma low in silica) reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, Quebec was called ''Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipissing Sills
The Nipissing sills, also called the Nipissing diabase, is a large 2217– to 2210–million year old group of sills in the Superior craton of the Canadian Shield in Ontario, Canada, which intrude the Huronian Supergroup. Nipissing sills intrude all the Huronian sediments and older basement rocks in the northern margin of the Sudbury Basin; they were emplaced after the faulting and folding of Huronian rocks, and are hornblende gabbro of tholeiitic basalt composition. In the Sudbury–Elliot Lake area the Nipissing diabase is deformed; outcrops are parallel to the fold axes of the Huronian sedimentary rocks. Nipissing diabase intrusions are east-northeast trending and are no wider than . The Nipissing sills in the Southern Province of the Superior craton are thought to originate from a radiating dike swarm area to the northeast. The mantle source for the Nipissing sills did not come from the mantle beneath the Southern Province that had generated the 2500– to 2450–million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Survey Of Canada
The Geological Survey of Canada (GSC; french: Commission géologique du Canada (CGC)) is a Canadian federal government agency responsible for performing geological surveys of the country, developing Canada's natural resources and protecting the environment. A branch of the Earth Sciences Sector of Natural Resources Canada, the GSC is the country's oldest scientific agency and was one of its first government organizations. History In September 1841, the Province of Canada legislature passed a resolution that authorized the sum of £1,500 sterling be granted to the government for the estimated expense of performing a geological survey of the province. In 1842, the Geological Survey of Canada was formed to fulfill this request.Christy Vodden (1992)No Stone Unturned: The First 150 years of the Geological Survey of Canada Geological Survey of Canada Web site William Edmond Logan was in Montreal at the time and made it known that he was interested in participating in this survey. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Petrology Of Quebec
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Petrology Of Ontario
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |