|
Ubiquitin Carboxy-terminal Hydrolase L1
Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (, ''ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase'', ''UCH-L1'') is a deubiquitinating enzyme. Function UCH-L1 is a member of a gene family whose products hydrolyze small C-terminal adducts of ubiquitin to generate the ubiquitin monomer. Expression of UCH-L1 is highly specific to neurons and to cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors. It is abundantly present in all neurons (accounts for 1-2% of total brain protein), expressed specifically in neurons and testis/ovary. The catalytic triad of UCH-L1 contains a cysteine at position 90, an aspartate at position 176, and a histidine at position 161 that are responsible for its hydrolase activity. Relevance to neurodegenerative disorders A point mutation (I93M) in the gene encoding this protein is implicated as the cause of Parkinson's disease in one German family, although this finding is controversial, as no other Parkinson's disease patients with this mutation have been found. Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deubiquitinating Enzyme
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), also known as deubiquitinating peptidases, deubiquitinating isopeptidases, deubiquitinases, ubiquitin proteases, ubiquitin hydrolases, ubiquitin isopeptidases, are a large group of proteases that cleave ubiquitin from proteins. Ubiquitin is attached to proteins in order to regulate the degradation of proteins via the proteasome and lysosome; coordinate the cellular localisation of proteins; activate and inactivate proteins; and modulate protein-protein interactions. DUBs can reverse these effects by cleaving the peptide or isopeptide bond between ubiquitin and its substrate protein. In humans there are nearly 100 DUB genes, which can be classified into two main classes: cysteine proteases and metalloproteases. The cysteine proteases comprise ubiquitin-specific proteases (USPs), ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs), Machado-Josephin domain proteases (MJDs) and ovarian tumour proteases (OTU). The metalloprotease group contains only the Jab1/Mov34/M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells will undergo a programmed form of rapid cell death () when critical functions are altered and malfunctioning. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they will predisp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
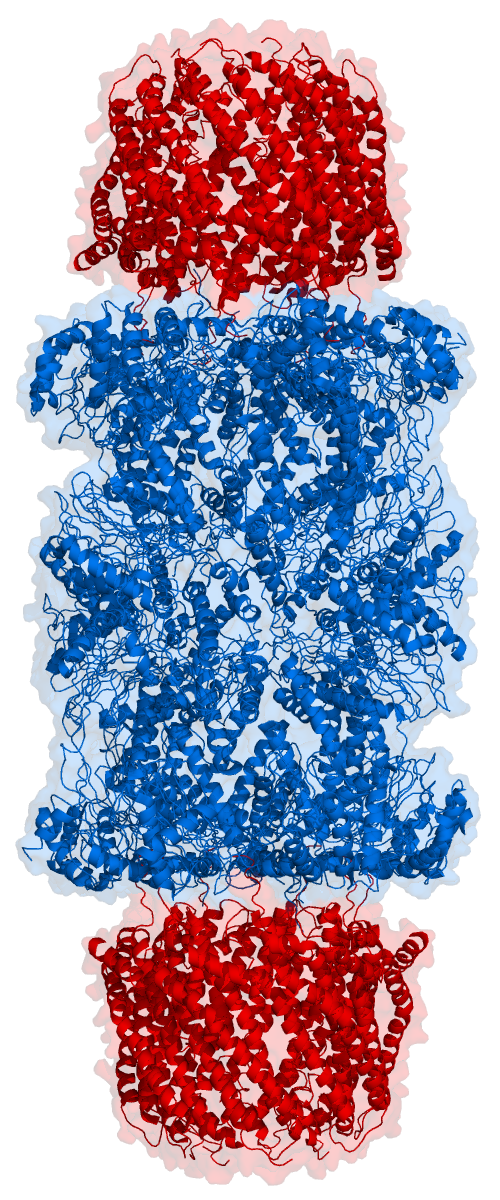
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Synuclein
Alpha-synuclein is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''SNCA'' gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release. It is abundant in the brain, while smaller amounts are found in the heart, muscle and other tissues. In the brain, alpha-synuclein is found mainly in the axon terminals of presynaptic neurons. Within these terminals, alpha-synuclein interacts with phospholipids and proteins. Presynaptic terminals release chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, from compartments known as synaptic vesicles. The release of neurotransmitters relays signals between neurons and is critical for normal brain function. The human alpha-synuclein protein is made of 140 amino acids. An alpha-synuclein fragment, known as the non-Abeta component (NAC) of Alzheimer's disease amyloid, originally found in an amyloid-enriched fraction, was shown to be a fragment of its precursor protein, NACP. It was later det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosomal Degradation
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkin (ligase)
Parkin is a 465-amino acid residue E3 ubiquitin ligase, a protein that in humans and mice is encoded by the ''PARK2'' gene. Parkin plays a critical role in ubiquitination – the process whereby molecules are covalently labelled with ubiquitin (Ub) and directed towards degradation in proteasomes or lysosomes. Ubiquitination involves the sequential action of three enzymes. First, an E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme binds to inactive Ub in eukaryotic cells via a thioester bond and mobilises it in an ATP-dependent process. Ub is then transferred to an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme before being conjugated to the target protein via an E3 ubiquitin ligase. There exists a multitude of E3 ligases, which differ in structure and substrate specificity to allow selective targeting of proteins to intracellular degradation. In particular, parkin recognises proteins on the outer membrane of mitochondria upon cellular insult and mediates the clearance of damaged mitochondria via autophagy and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson Disease
Parkinson may refer to: *Parkinson (surname) * ''Parkinson'' (TV series), British chat show, presented by Sir Michael Parkinson *Parkinson, Queensland, suburb of Brisbane, Australia *The Parkinsons (fl. early 20th century), American father-and-son architects *The Parkinsons (band), a Portuguese punk rock band * The Parkinsons, a broadcasting partnership of Sir Michael Parkinson and his wife Mary See also * Parkinson's (other) *Parkinson's disease, degenerative disorder of the central nervous system *Parkinsonism Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), rigidity, and postural instability. These are the four motor symptoms found in Parkinson's disease (PD), after which it is named, dementia with Lewy b ..., also known as Parkinson's syndrome, atypical Parkinson's, or secondary Parkinson's * Parkinson's Law, the adage "Work expands so as to fill the time available for its completion." {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-synuclein
Alpha-synuclein is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''SNCA'' gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release. It is abundant in the brain, while smaller amounts are found in the heart, muscle and other tissues. In the brain, alpha-synuclein is found mainly in the axon terminals of presynaptic neurons. Within these terminals, alpha-synuclein interacts with phospholipids and proteins. Presynaptic terminals release chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, from compartments known as synaptic vesicles. The release of neurotransmitters relays signals between neurons and is critical for normal brain function. The human alpha-synuclein protein is made of 140 amino acids. An alpha-synuclein fragment, known as the non-Abeta component (NAC) of Alzheimer's disease amyloid, originally found in an amyloid-enriched fraction, was shown to be a fragment of its precursor protein, NACP. It was later det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COP9 Constitutive Photomorphogenic Homolog Subunit 5
COP9 constitutive photomorphogenic homolog subunit 5 (Arabidopsis), also known as COPS5 or Csn5, is a gene conserved from humans to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Function The protein encoded by this gene is one of the eight subunits of COP9 signalosome, a highly conserved protein complex that functions as an important regulator in multiple signaling pathways. The structure and function of COP9 signalosome is similar to that of the 19S regulatory particle of 26S proteasome. COP9 signalosome has been shown to interact with SCF-type E3 ubiquitin ligases and act as a positive regulator of E3 ubiquitin ligases. This protein is reported to be involved in the degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CDKN1B/p27Kip1. It is also known to be a coactivator that increases the specificity of JUN/AP1 transcription factors. Interactions COP9 constitutive photomorphogenic homolog subunit 5 has been shown to interact with Macrophage migration inhibitory factor, GFER, BCL3, Ubiquitin carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Theory
In the mathematical field of topology, knot theory is the study of knot (mathematics), mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, Unknot, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3 (in topology, a circle is not bound to the classical geometric concept, but to all of its homeomorphisms). Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |