|
USS The Sullivans (DDG-68)
USS ''The Sullivans'' (DDG-68) is an (Flight I) Aegis combat system, Aegis guided missile destroyer. She is the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for the five Sullivan brothers – George, Francis, Joseph, Madison, and Albert Sullivan, aged 20 to 27 – who lost their lives when their ship, , was sunk by a Japanese submarine in November 1942 in the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal. This was the greatest military loss by any one American family during World War II. The first ship named for the brothers was the , now a museum ship in Buffalo, New York. Construction The contract to build ''The Sullivans'' was awarded to Bath Iron Works Corporation in Bath, Maine on 8 April 1992 and her keel was laid down on 27 July 1994. She was Ship naming and launching, launched on 12 August 1995 and sponsored by Kelly Ann Sullivan Loughren, granddaughter of Albert Sullivan. The ship was ship commissioning, commissioned on 19 April 1997, with Commander Gerard D. Roncolato in comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sullivan Brothers
The five Sullivan brothers were World War II sailor brothers of Irish American descent who, serving together on the light cruiser , were all killed in action during and shortly after its sinking around November 13, 1942. The five brothers, the sons of Thomas (1883–1965) and Alleta Sullivan (1895–1972) of Waterloo, Iowa, were: *George Thomas Sullivan, 27 (born December 14, 1914), Gunner's Mate Second Class (George had been previously discharged in May 1941 as Gunner's Mate Third Class.) *Francis Henry "Frank" Sullivan, 26 (born February 18, 1916), Coxswain (Frank had been previously discharged in May 1941 as Seaman First Class.) *Joseph Eugene "Joe" Sullivan, 24 (born August 28, 1918), Seaman Second Class *Madison Abel "Matt" Sullivan, 23 (born November 8, 1919), Seaman Second Class *Albert Leo "Al" Sullivan, 20 (born July 8, 1922), Seaman Second Class History The Sullivans enlisted in the US Navy on January 3, 1942, with the stipulation that they serve together. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a naval force to project air power worldwide without depending on local bases for staging aircraft operations. Carriers have evolved since their inception in the early twentieth century from wooden vessels used to deploy balloons to nuclear-powered warships that carry numerous fighters, strike aircraft, helicopters, and other types of aircraft. While heavier aircraft such as fixed-wing gunships and bombers have been launched from aircraft carriers, these aircraft have not successfully landed on a carrier. By its diplomatic and tactical power, its mobility, its autonomy and the variety of its means, the aircraft carrier is often the centerpiece of modern combat fleets. Tactically or even strategically, it replaced the battleship in the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
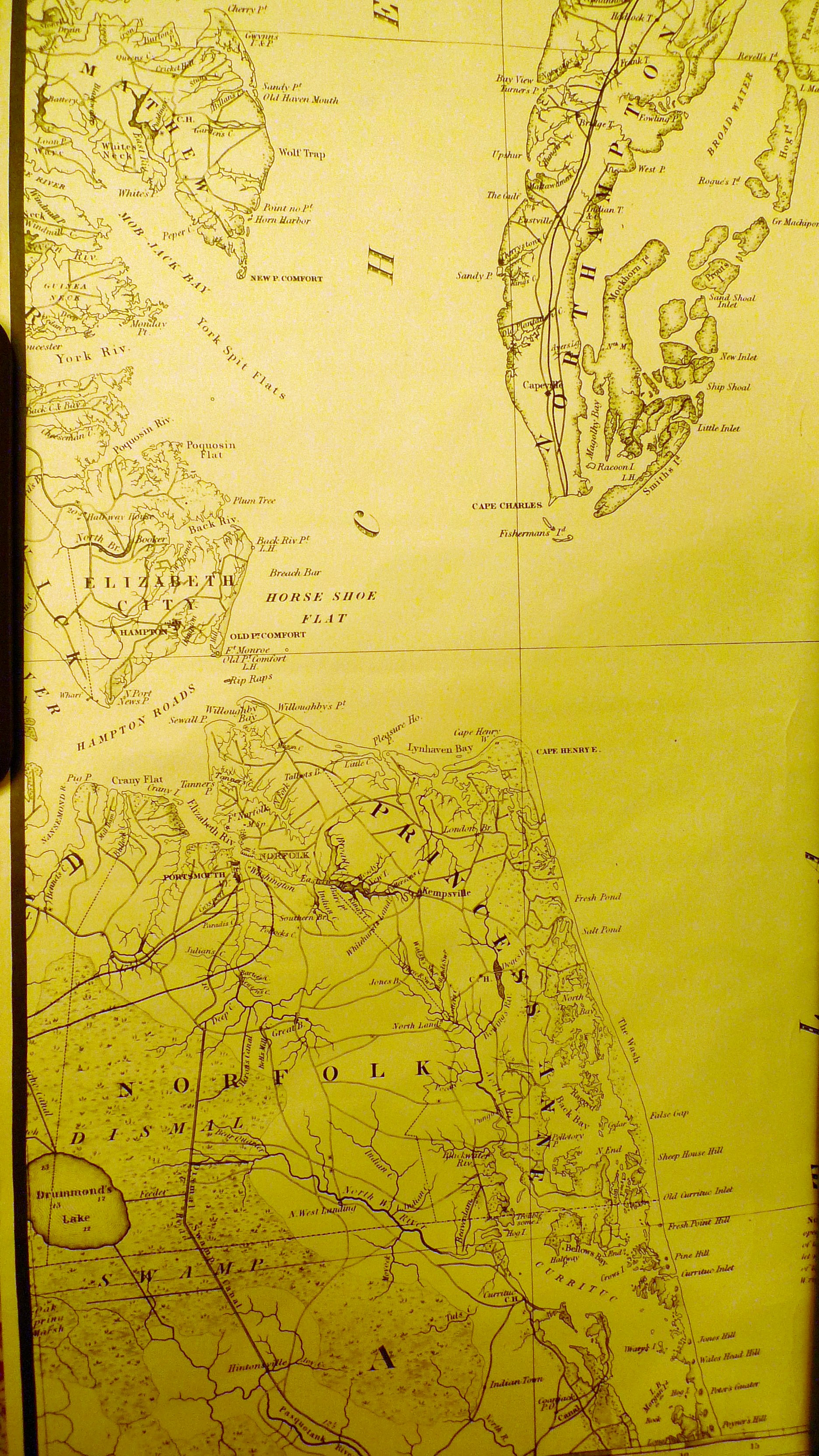
Virginia Capes
The Virginia Capes are the two capes, Cape Charles to the north and Cape Henry to the south, that define the entrance to Chesapeake Bay on the eastern coast of North America. In 1610, a supply ship learned of the famine at Jamestown when it landed at Cape Henry. "America and West Indies: June 1610." ''Calendar of State Papers Colonial, America and West Indies'': Volume 1, 1574-1660. Ed. W Noel Sainsbury. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office, 1860. 9-10British History Online.Retrieved 13 June 2019. The importance of Chesapeake Bay in American history has long made the Virginia Capes strategically significant, most notably in the naval Battle of the Chesapeake that was crucial to the American victory at the siege of Yorktown, effectively ending the American Revolutionary War. As a result, the area was heavily garrisoned, beginning with the construction of Fort Monroe and Fort Wool in 1819. During the American Civil War, a pivotal battle between the ironclad warships and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—fulfilled by frigates or sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre-dreadnought battleship. With the advent of the dreadnought battleship before World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roosevelt Roads
Roosevelt Roads Naval Station is a former United States Navy base in the town of Ceiba, Puerto Rico. The site operates today as José Aponte de la Torre Airport, a public use airport. History In 1919, future US President Franklin D. Roosevelt, then Assistant Secretary of the Navy, toured Puerto Rico, visiting Ceiba. When he returned to the White House, he expressed a liking for the terrain where the base was to be located. This was during the World War I era, and the US could benefit from an air field in Ceiba. While Puerto Rico is a Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), Commonwealth, its territorial rights belong to the US, which made it feasible for the US government to build an air base in Ceiba. It took many years for the US to become convinced of the need for an air base in Ceiba. When Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany began to invade other European countries, the US, led by then President Roosevelt, considered the idea of a naval air station in Ceiba. With war in the European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called naval mine, mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with naval artillery, large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface combatant , surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States. It is located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, and includes the eponymous main island and several smaller islands, such as Isla de Mona, Mona, Culebra, Puerto Rico, Culebra, and Vieques, Puerto Rico, Vieques. It has roughly 3.2 million residents, and its Capital city, capital and Municipalities of Puerto Rico, most populous city is San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan. Spanish language, Spanish and English language, English are the official languages of the executive branch of government, though Spanish predominates. Puerto Rico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the North Atlantic Ocean. Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some Central and South American mainland nations which have Caribbean coastlines, such as Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic island nations of Barbados, Bermuda, and Trinidad and Tobago, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Origin and use of the term In 1492, Christopher Columbus became the first European to record his arri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)



_1997.jpg)

