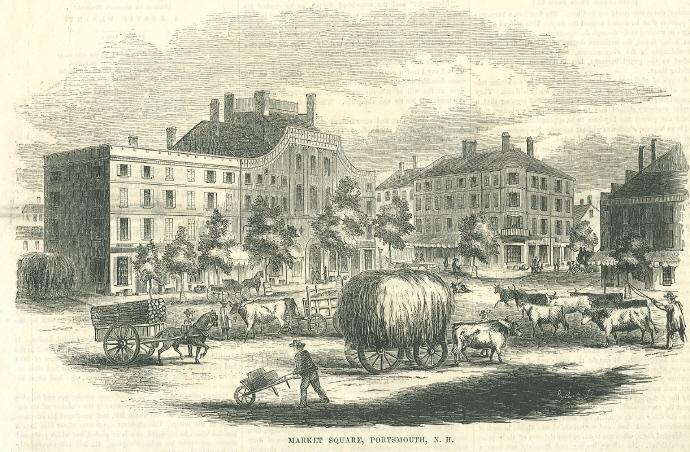|
USS Decatur (1839)
USS ''Decatur'' was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the mid-19th century. She was commissioned to protect American interests in the South Atlantic Ocean, including the interception of ships involved in the African slave trade. ''Decatur'' served in both the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War. The sloop-of-war was named in honor of Commodore Stephen Decatur (1779–1820), one of the United States Navy's greatest heroes and leaders of the first two decades of the 19th century. Launched in 1839 at the New York Navy Yard ''Decatur'', a large sloop of 566 tons, was built in 1838 and 1839 at New York Navy Yard. She was outfitted with heavy guns and manned by a crew of 150 officers and enlisted men. South Atlantic Ocean operations Commanded by Commander H. W. Ogden, she sailed from New York 16 March 1840 for duty with the Brazil Squadron, returning to Norfolk, Virginia 28 February 1843. Her second cruise, from 5 August 1843 to 3 January 1845 was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Decatur (1839)
USS ''Decatur'' was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the mid-19th century. She was commissioned to protect American interests in the South Atlantic Ocean, including the interception of ships involved in the African slave trade. ''Decatur'' served in both the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War. The sloop-of-war was named in honor of Commodore Stephen Decatur (1779–1820), one of the United States Navy's greatest heroes and leaders of the first two decades of the 19th century. Launched in 1839 at the New York Navy Yard ''Decatur'', a large sloop of 566 tons, was built in 1838 and 1839 at New York Navy Yard. She was outfitted with heavy guns and manned by a crew of 150 officers and enlisted men. South Atlantic Ocean operations Commanded by Commander H. W. Ogden, she sailed from New York 16 March 1840 for duty with the Brazil Squadron, returning to Norfolk, Virginia 28 February 1843. Her second cruise, from 5 August 1843 to 3 January 1845 was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew C
{{disambiguation ...
Matthew may refer to: * Matthew (given name) * Matthew (surname) * ''Matthew'' (ship), the replica of the ship sailed by John Cabot in 1497 * ''Matthew'' (album), a 2000 album by rapper Kool Keith * Matthew (elm cultivar), a cultivar of the Chinese Elm ''Ulmus parvifolia'' Christianity * Matthew the Apostle, one of the apostles of Jesus * Gospel of Matthew, a book of the Bible See also * Matt (given name), the diminutive form of Matthew * Mathew, alternative spelling of Matthew * Matthews (other) * Matthew effect * Tropical Storm Matthew (other) The name Matthew was used for three tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean, replacing Mitch after 1998. * Tropical Storm Matthew (2004) - Brought heavy rain to the Gulf Coast of Louisiana, causing light damage but no deaths. * Tropical Storm Matt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the portion of the Oregon Territory north of the lower Columbia River and north of the 46th parallel east of the Columbia. At its largest extent, it also included the entirety of modern Idaho and parts of Montana and Wyoming, before attaining its final boundaries in 1863. History Agitation in favor of self-government developed in the regions of the Oregon Territory north of the Columbia River in 1851–1852. A group of prominent settlers from the Cowlitz and Puget Sound regions met on November 25, 1852, at the "Monticello Convention" in present-day Longview, to draft a petition to the United States Congress calling for a separate territory north of the Columbia River. After gaining approval from the Oregon territorial government, the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions. ''Honolulu'' means "sheltered harbor" or "calm port" in Hawaiian; its old name, ''Kou'', roughly encompasses the area from Nuuanu Avenue to Alakea Street and from Hotel Street to Queen Street, which is the heart of the present downtown district. The city's desirability as a port accounts for its historical growth and importance in the Hawaiian archipelago and the broader P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valparaíso
Valparaíso (; ) is a major city, seaport, naval base, and educational centre in the commune of Valparaíso, Chile. "Greater Valparaíso" is the second largest metropolitan area in the country. Valparaíso is located about northwest of Santiago by road and is one of the Pacific Ocean's most important seaports. Valparaíso is the Capital city, capital of Chile's second most populated administrative region and has been the headquarters for the Chilean Navy since 1817 and the seat of the National Congress of Chile, Chilean National Congress since 1990. Valparaíso played an important geopolitical role in the second half of the 19th century when it served as a major stopover for ships traveling between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans by crossing the Straits of Magellan. Valparaíso experienced rapid growth during its golden age, as a magnet for European immigrants, when the city was known by international sailors as "Little San Francisco" and "The Jewel of the Pacific". Notable inhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straits Of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It was discovered and first traversed by the Spanish expedition of Ferdinand Magellan in 1520, after whom it is named. Prior to this, the strait had been navigated by canoe-faring indigenous peoples including the Kawésqar. Magellan's original name for the strait was ''Estrecho de Todos los Santos'' ("Strait of All Saints"). The King of Spain, Emperor Charles V, who sponsored the Magellan-Elcano expedition, changed the name to the Strait of Magellan in honor of Magellan. The route is difficult to navigate due to frequent narrows and unpredictable winds and currents. Maritime piloting is now compulsory. The strait is shorter and more sheltered than the Drake Passage, the often stormy open sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Squadron
The Pacific Squadron was part of the United States Navy squadron stationed in the Pacific Ocean in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially with no United States ports in the Pacific, they operated out of storeships which provided naval supplies and purchased food and obtained water from local ports of call in the Hawaiian Islands and towns on the Pacific Coast. Throughout the history of the Pacific Squadron, American ships fought against several enemies. Over one-half of the United States Navy would be sent to join the Pacific Squadron during the Mexican–American War. During the American Civil War, the squadron was reduced in size when its vessels were reassigned to Atlantic duty. When the Civil War was over, the squadron was reinforced again until being disbanded just after the turn of the 20th century. History Formation The "United States Naval Forces on Pacific Station" was established in 1818, with the HMS Macedonian#As USS Macedonian, USS ''Macedonian'' under Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Of Canso
The Strait of Canso (also Gut of Canso or Canso Strait, also called Straits of Canceau or Canseaux until the early 20th century) is a strait located in the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. It divides the Nova Scotia peninsula from Cape Breton Island. It is a long thin channel approximately 27 kilometres long and averaging 3 kilometres wide (1 km at its narrowest). The strait connects Chedabucto Bay on the Atlantic Ocean to St. George's Bay on the Northumberland Strait, a sub basin of the Gulf of St. Lawrence. The strait is extremely deep (200+ feet) with two major communities at Port Hawkesbury on the eastern side facing Mulgrave on the western side, both ports. The strait is crossed by the Canso Causeway for vehicular and rail traffic, opened in 1955. The Canso Canal allows ships to pass through the causeway, and this can accommodate any vessel capable of transiting the St. Lawrence Seaway. An account of early settlement in the area is given in the letters of loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean) and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America. Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: The Greater Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago on the north and the Lesser Antilles and the on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (the Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands), which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Squadron
The Home Squadron was part of the United States Navy in the mid-19th century. Organized as early as 1838, ships were assigned to protect coastal commerce, aid ships in distress, suppress piracy and the Atlantic slave trade, make coastal surveys, and train ships to relieve others on distant stations. It was discontinued in 1861 after the outbreak of the American Civil War, when the Union blockade forced a reassignment of ships to close off Southern ports. History Mexican–American War During the Mexican–American War the ships of the Home Squadron, commanded by Commodore David Conner, USN fought in several engagements against Mexican forces. Many of the Home Squadron vessels were attached to vice commander Commodore Matthew C. Perry's Mosquito Fleet which was involved in the battles of Tuxpan, Tabasco, Villahermosa and Veracruz. No ship-to-ship combat occurred though several merchant vessels were captured, the Home Squadron primarily operated against Mexican coastal forts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth, New Hampshire
Portsmouth is a city in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport and popular summer tourist destination on the Piscataqua River bordering the state of Maine, Portsmouth was formerly the home of the Strategic Air Command's Pease Air Force Base, since converted to Portsmouth International Airport at Pease. History American Indians of the Abenaki and other Algonquian languages-speaking nations, and their predecessors, inhabited the territory of coastal New Hampshire for thousands of years before European contact. The first known European to explore and write about the area was Martin Pring in 1603. The Piscataqua River is a tidal estuary with a swift current, but forms a good natural harbor. The west bank of the harbor was settled by European colonists in 1630 and named Strawbery Banke, after the many wild strawberries growing there. The village was protected by Fort William and Mary on what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
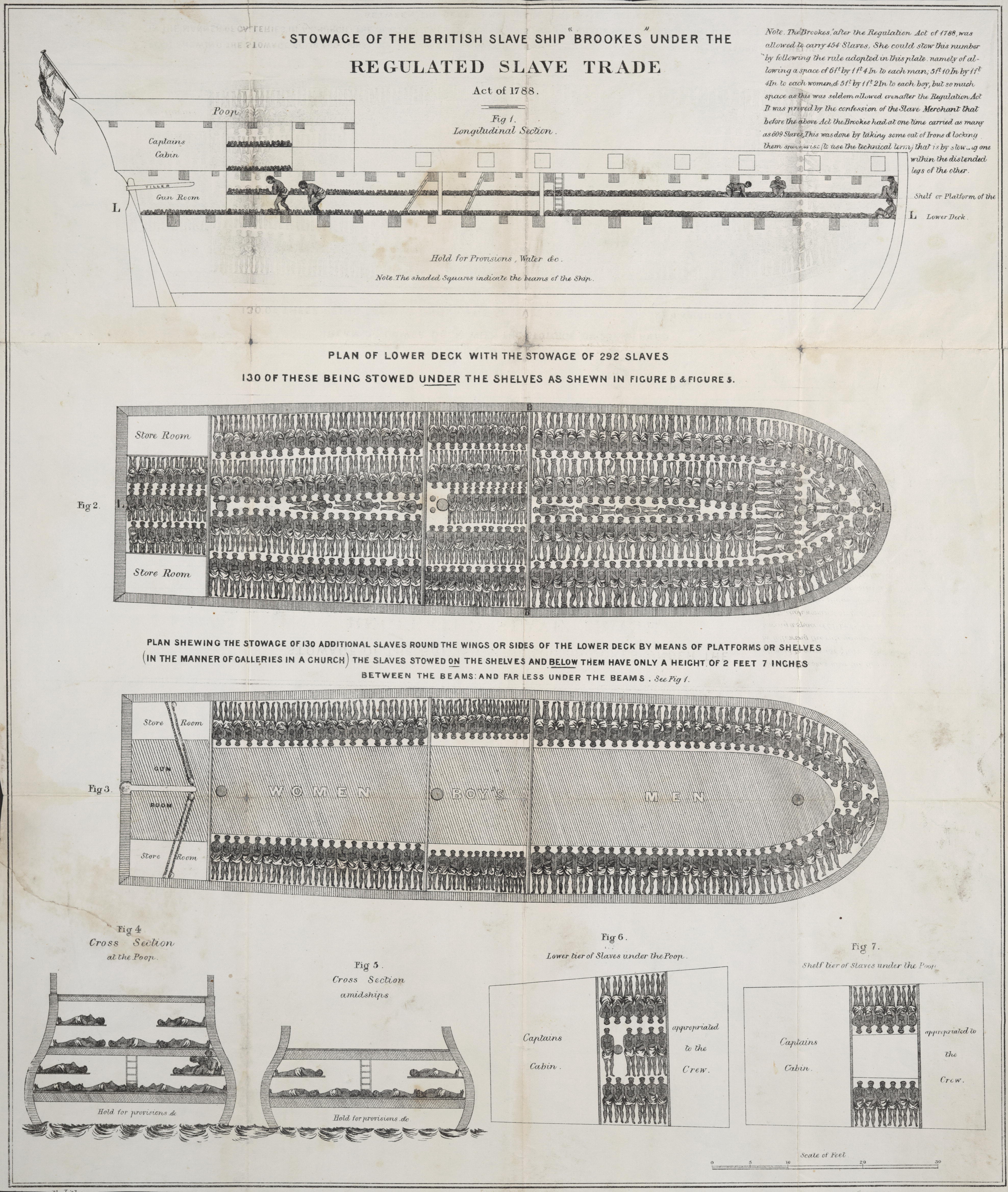
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Marie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)