|
Uterine Serous Carcinoma
Uterine serous carcinoma is a malignant form of serous tumor that originates in the uterus. It is an uncommon form of endometrial cancer that typically arises in postmenopausal women. It is typically diagnosed on endometrial biopsy, prompted by post-menopausal bleeding. Unlike the more common low-grade endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma, uterine serous carcinoma does not develop from endometrial hyperplasia and is not hormone-sensitive. It arises in the setting of endometrial atrophy and is classified as a type II endometrial cancer. Cause Initially there is a precursor lesion called serous endometrial intraepithelial carcinoma. Mutation is found in TP53 gene which is a tumor suppressor gene even in precursor lesion suggesting early involvement of this gene. Also many missense mutation and mutation in PI3K and PP2A genes are involved which also contribute to this tumor. Diagnosis The lesion is found in patients who present typically with abnormal or postmenopausal bleedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology H&E
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types (fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HER2/neu
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently referred to as ''HER2'' (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) or CD340 (cluster of differentiation 340). HER2 is a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER/EGFR/ERBB) family. But contrary to other member of the ERBB family, HER2 does not directly bind ligand. HER2 activation results from heterodimerization with another ERBB member or by homodimerization when HER2 concentration are high, for instance in cancer. Amplification or over-expression of this oncogene has been shown to play an important role in the development and progression of certain aggressive types of breast cancer. In recent years the protein has become an important biomarker and target of therapy for approximately 30% of breast cancer patients. Name ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver". Platinum is a member of the platinum group of elements and group 10 of the periodic table of elements. It has six naturally occurring isotopes. It is one of the rarer elements in Earth's crust, with an average abundance of approximately 5 μg/kg. It occurs in some nickel and copper ores along with some native deposits, mostly in South Africa, which accounts for ~80% of the world production. Because of its scarcity in Earth's crust, only a few hundred tonnes are produced annually, and given its important uses, it is highly valuable and is a major precious metal commodity. Platinum is one of the least reactive metals. It has remarkable resistance to corrosion, even at high temperatures, and is therefore considered a noble metal. Consequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
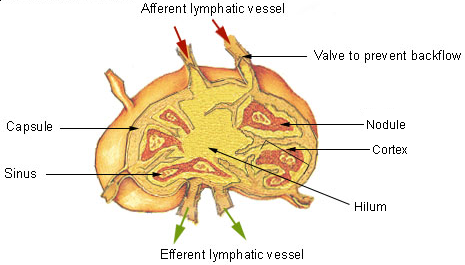
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omentectomy
The greater omentum (also the great omentum, omentum majus, gastrocolic omentum, epiploon, or, especially in animals, caul) is a large apron-like fold of Peritoneum#Layers, visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the curvatures of the stomach, greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the curvatures of the stomach, lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek ''epipleein'', meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly (from the front). Structure The greater omentum is the larger of the two peritoneal folds. It consists of a double sheet of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenectomy
Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. Indications It is usually done because many types of cancer have a marked tendency to produce lymph node metastasis early in their natural history. This is particularly true of melanoma, head and neck cancer, differentiated thyroid cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Famed British surgeon Berkeley Moynihan once remarked that "the surgery of cancer is not the surgery of organs; it is the surgery of the lymphatic system". The better-known examples of lymphadenectomy are ''axillary lymph node dissection'' for breast cancer; ''radical neck dissection'' for head and neck cancer and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
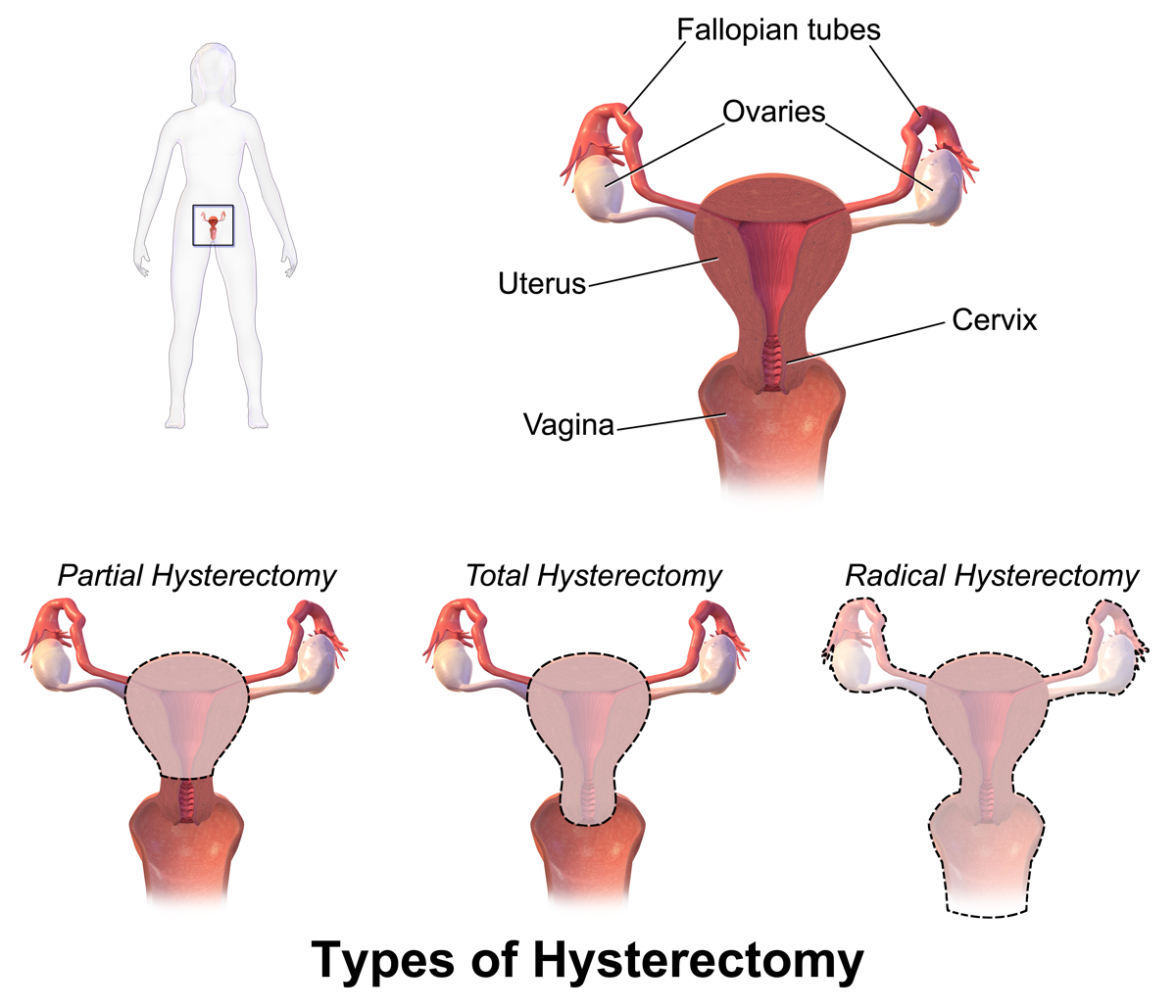
Salpingo-oophorectomy
In medicine, salpingo-oophorectomy is the removal of an ovary and its Fallopian tube. This procedure is most frequently associated with prophylactic surgery in response to the discovery of a BRCA mutation, particularly those of the normally tumor suppressing ''BRCA1'' gene (or, with a statistically lower negative impact, those of the tumour suppressing ''BRCA2'' gene), which can increase the risk of a woman developing ovarian cancer to as high as 65% (as high as 25% for a mutated ''BRCA2'' gene). See also * List of surgeries by type * Oophorectomy Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'' is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference to ... References Gynecological surgery Surgical removal procedures {{Surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), Fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. Usually performed by a gynecologist, a hysterectomy may be total (removing the body, fundus, and cervix of the uterus; often called "complete") or partial (removal of the uterine body while leaving the cervix intact; also called "supracervical"). Removal of the uterus renders the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as endometriosis, irregular bleeding, and uterine fibroids. It is expected that the frequency of hysterectom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecologic Oncology (journal)
''Gynecologic Oncology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of gynecologic oncology. The journal covers investigations relating to the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of female cancers, as well as research from any of the disciplines related to this field of interest. It is published by Elsevier and is the official journal of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Current Contents/Clinical Medicine, Index Medicus, Science Citation Index, and Scopus Scopus is Elsevier's abstract and citation database launched in 2004. Scopus covers nearly 36,377 titles (22,794 active titles and 13,583 inactive titles) from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in top-l .... References External links * Elsevier academic journals Monthly journals Oncology journals Academic journals established in 1972 English-language journals Obstetrics and gynaecology jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myometrium
The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes) but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions. Structure The myometrium is located between the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterine wall) and the serosa or perimetrium (the outer uterine layer). The inner one-third of the myometrium (termed the ''junctional'' or ''sub-endometrial'' layer) appears to be derived from the Müllerian duct, while the outer, more predominant layer of the myometrium appears to originate from non-Müllerian tissue and is the major contractile tissue during parturition and abortion. The junctional layer appears to function like a circular muscle layer, capable of peristaltic and anti-peristaltic activity, equivalent to the muscular layer of the intestines. Muscular structure The molecular structure of the smooth muscle of myometrium is very similar to tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |