|
Ushnu O Piramide Inca - Vilcashuaman, Ayacucho
An ushnu or usnu is a pyramid-shaped, terraced structure that was used by the Inca to preside at the most important ceremonies of the ''Tawantinsuyu,'' or Inca Empire. Name Little is known of the Quechua root of the term ''ushnu'', but it seemed to mean "the place of stones where the water filters". Presenting the places with characteristics of ushnu, major feasibility for the receipt of liquid offerings. They were probably used by the pre-Hispanic populations, when they had to conduct rituals in which they offered liquids, principally alcoholic maize drink, in sacrifice. Thus, a ceremonial concept formed of ushnu, that probably was referring to "the place where one offers liquids, or place of drinks ". Structure The structure is a rectangular pyramid formed by five platforms, successively built to the highest part for a perron. Everything was constructed in stone. At the top was a double armchair worked in stone, which according to the local tradition was covered with golde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cusco
Cusco, often spelled Cuzco (; qu, Qusqu ()), is a city in Southeastern Peru near the Urubamba Valley of the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cusco Region and of the Cusco Province. The city is the list of cities in Peru, seventh most populous in Peru; in 2017, it had a population of 428,450. Its elevation is around . The city was the capital of the Inca Empire from the 13th century until the 16th-century Spanish conquest of Peru, Spanish conquest. In 1983, Cusco was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO with the title "City of Cuzco". It has become a major tourist destination, hosting nearly 2 million visitors a year. The Constitution of Peru (1993) designates it as the Historical Capital of Peru. Spelling and etymology The indigenous name of this city is . Although the name was used in Southern Quechua, its origin is found in the Aymara language. The word is derived from the phrase ('rock of the owl'), related to the city's foundation myth of the Ayar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The Inca civilization arose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire in 1532 and by 1572, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru, what are now western Ecuador, western and south central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and a large portion of modern-day Chile, and into a state comparable to the historical empires of Eurasia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara Mythology
Aymara may refer to: Languages and people * Aymaran languages, the second most widespread Andean language ** Aymara language, the main language within that family ** Central Aymara, the other surviving branch of the Aymara(n) family, which today includes only the endangered Jaqaru/Kawki language * Aymara people, the native ethnic group identified with the speakers of Altiplano Aymara Culture * ''Corazón Aymara'' (English: ''Aymara Heart''), 1925 Bolivian silent feature film directed by Pedro Sambarino * Grupo Aymara, Bolivian folk troupe of traditional music of pre-Hispanic and contemporary music of the Andes * Socialist Aymara Group (Spanish: ''Grupo Aymara Socialista''), left-wing indigenous political group in Bolivia Places * Aymaraes Province, the largest of seven provinces of the Apurímac Region in Peru * Aymara Lupaca Reserved Zone, a protected area in southeastern Peru Nature * ''Aymaramyia'', genus of crane bird found in Peru * ''Aymaratherium'', genus of extinct sloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astral Deities
Astrotheology, astral mysticism, astral religion, astral or stellar theology (also referred to as astral or star worship) is the worship of the stars (individually or together as the night sky), the planets, and other heavenly bodies as deities, or the association of deities with heavenly bodies. In anthropological literature these systems of practice may be referred to as astral cults. The most common instances of this are sun gods and moon gods in polytheistic systems worldwide. Also notable is the association of the planets with deities in Babylonian, and hence in Greco-Roman religion, viz. Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Gods, goddesses, and demons may also be considered personifications of astronomical phenomena such as lunar eclipses, planetary alignments, and apparent interactions of planetary bodies with stars. The Sabians of Harran, a poorly understood pagan religion that existed in Harran during the early Islamic period (7th–10th century), were known fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Languages
Quechua (, ; ), usually called ("people's language") in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with an estimated 8–10 million speakers as of 2004.Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. Approximately 25% (7.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish encouraged its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru. History Quechua had already expanded across wide ranges of the central Andes long before the expansion of the Inca Empire. The Inca were one among many peoples in present-day Peru who already spok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
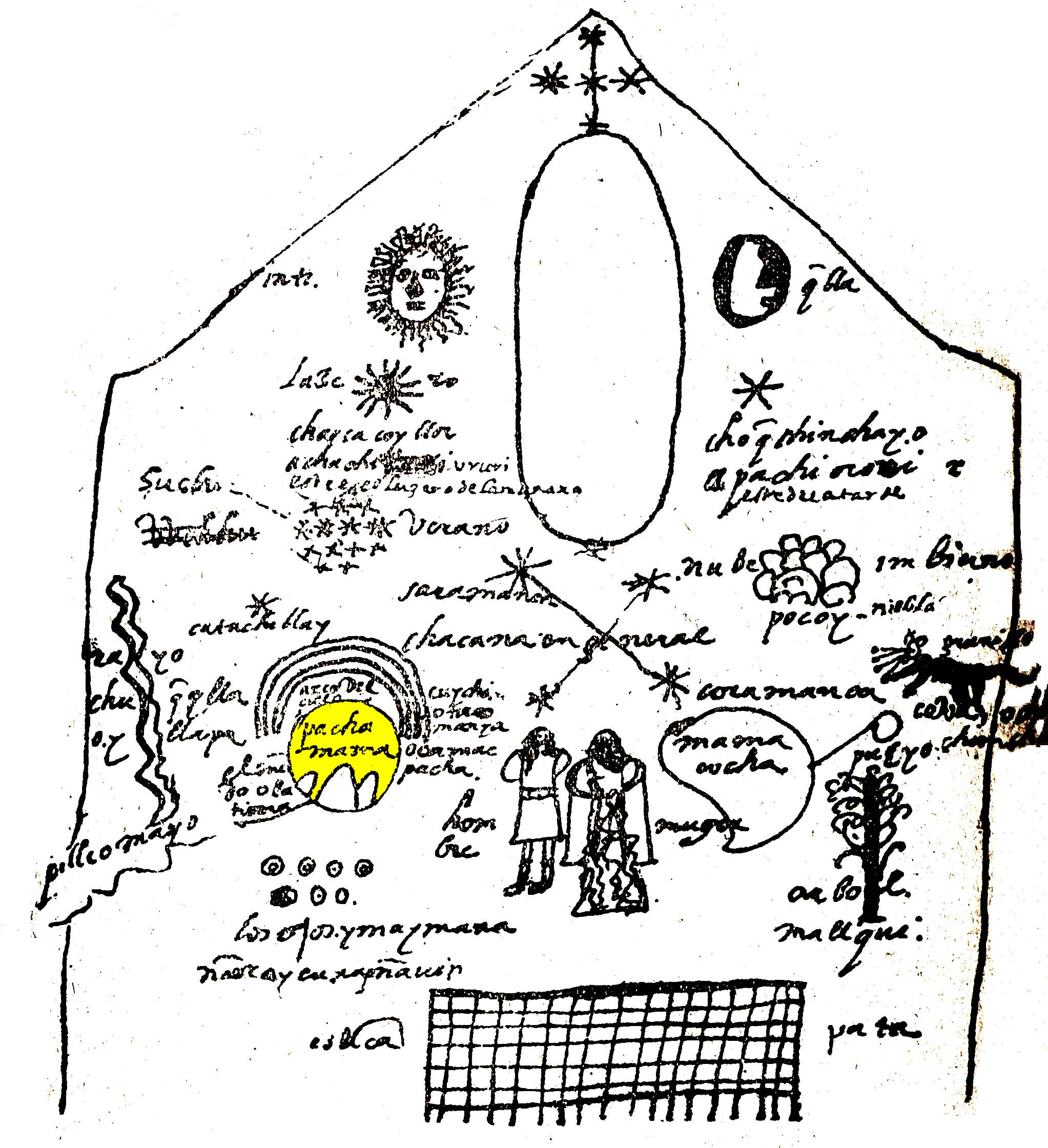
Uku Pacha
The pacha (, often translated as ''world'') was an Incan concept for dividing the different spheres of the cosmos in Incan mythology. There were three different levels of ''pacha'': the ''hana pacha'', ''hanan pacha'' or ''hanaq pacha'' (Quechua, meaning "world above"), ''ukhu pacha'' ("world below"), and ''kay pacha'' ("this world").The realms are not solely spatial, but were simultaneously spatial and temporal. Although the universe was considered a unified system within Incan cosmology, the division between the worlds was part of the dualism prominent in Incan beliefs, known as Yanantin. This dualism found that everything which existed had both features of any feature (both hot and cold, positive and negative, dark and light, etc.). Meaning of ''pacha'' ''Pacha'' is often translated as "world" in Quechua, but the concept also includes a temporal context of meaning. Catherine J. Allen writes that "The Quechua word pacha may refer to the whole cosmos or to a specific moment in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kay Pacha
The pacha (, often translated as ''world'') was an Incan concept for dividing the different spheres of the cosmos in Incan mythology. There were three different levels of ''pacha'': the ''hana pacha'', ''hanan pacha'' or ''hanaq pacha'' (Quechua, meaning "world above"), ''ukhu pacha'' ("world below"), and ''kay pacha'' ("this world").The realms are not solely spatial, but were simultaneously spatial and temporal. Although the universe was considered a unified system within Incan cosmology, the division between the worlds was part of the dualism prominent in Incan beliefs, known as Yanantin. This dualism found that everything which existed had both features of any feature (both hot and cold, positive and negative, dark and light, etc.). Meaning of ''pacha'' ''Pacha'' is often translated as "world" in Quechua, but the concept also includes a temporal context of meaning. Catherine J. Allen writes that "The Quechua word pacha may refer to the whole cosmos or to a specific moment in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanan Pacha
The pacha (, often translated as ''world'') was an Incan concept for dividing the different spheres of the cosmos in Incan mythology. There were three different levels of ''pacha'': the ''hana pacha'', ''hanan pacha'' or ''hanaq pacha'' (Quechua, meaning "world above"), ''ukhu pacha'' ("world below"), and ''kay pacha'' ("this world").The realms are not solely spatial, but were simultaneously spatial and temporal. Although the universe was considered a unified system within Incan cosmology, the division between the worlds was part of the dualism prominent in Incan beliefs, known as Yanantin. This dualism found that everything which existed had both features of any feature (both hot and cold, positive and negative, dark and light, etc.). Meaning of ''pacha'' ''Pacha'' is often translated as "world" in Quechua, but the concept also includes a temporal context of meaning. Catherine J. Allen writes that "The Quechua word pacha may refer to the whole cosmos or to a specific moment in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinchaysuyu
Chinchay Suyu or Chinchasuyu was the northwestern provincial region of the Tawantin Suyu, or Inca Empire. The most populous ''suyu'' (or Quarter, the largest division of the Inca Empire), Chinchasuyu encompassed the former lands of the Chimú Empire and much of the northern Andes. At its largest extent, the ''suyu'' extended through much of modern Ecuador and just into modern Colombia. Along with Antisuyu, it was part of the '' Hanan Suyukuna'' or "Upper Quarters" of the empire. The name is due to the Chincha culture, which was a trader kingdom in what is now the Ica Region. ''Chinchay'' in Quechua stands for the tigrillo, animal present, although not physically, in some cultures of this region due to the Amazonian influence during the Early Horizon and Early Intermediate, such as the Chavín culture or the commercial exchange between the Huarpa -civilization located in modern-day Ayacucho that had trading routes to the Amazonas- and Nazca cultures. Before the Inca Civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal De La Société Des Américanistes
The ''Journal de la Société des Américanistes'' (''Journal of the Society of Americanists'') is an academic journal covering the cultural anthropology of the Americas The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. .... External links * Société des Américanistes Anthropology journals American studies journals Publications established in 1885 Biannual journals Multilingual journals 1885 establishments in France {{anthropology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)