|
Urtijëi
Urtijëi (; german: St. Ulrich in Gröden ; it, Ortisei ) is a town of 4,637 inhabitants in South Tyrol in northern Italy. It occupies the Val Gardena within the Dolomites, a mountain chain that is part of the Alps. Geography Urtijëi borders the following municipalities: Kastelruth, Villnöß, Lajen and Santa Cristina Gherdëina. History The Ladin-language name Urtijëi derives from the Latin word and the suffix '','' with the meaning "place of nettles". From 1860 to 1914 Urtijëi experienced a relevant economic growth due to the opening of a major road connecting Val Gardena to the main railroad; as a result the local woodcarving industry flourished. International tourism developed through the discovery of the Dolomites first by English tourists, and subsequently visitors from other parts of Austria-Hungary as well as the German Empire. Currently, the town's economy is mostly based on winter skiing tourism, summer hiking tourism, and woodcarving. Coat of arms The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Val Gardena
Val Gardena (; german: Gröden ; lld, Gherdëina ) is a valley in Northern Italy, in the Dolomites of South Tyrol. It is best known as a tourist skiing, rock climbing, and woodcarving area. Geography The valley's main river is the Derjon, a tributary of the Eisack river. The mountains that surround the valley are formed by dolomite rocks, which confer on them a characteristic appearance. Most of the steep slopes are covered by pine woods. The favoured cultivations are barley, rye, potatoes, flax, buckwheat. The three municipalities in Val Gardena are Urtijëi, Sëlva, and Santa Cristina; they were served by the Val Gardena Railway from 1916 until 1960. Culture Val Gardena is one of five valleys with a majority of Ladin speakers (two of these valleys are in South Tyrol). The form of the Ladin language spoken in this valley is called ''Gardenese'' in Italian, ''Grödnerisch'' in German and ''Gherdëina'' in Ladin. Woodcarving The woodcarving industry has flourished i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Tyrol
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol , settlement_type = Autonomous province , image_skyline = , image_alt = , image_caption = , image_flag = Flag_of_South_Tyrol.svg , flag_alt = , image_shield = Suedtirol CoA.svg , shield_size = x100px , shield_alt = Coat of arms of Tyrol , anthem = , image_map = Bolzano in Italy.svg , map_alt = , map_caption = Map highlighting the location of the province of South Tyrol in Italy (in red) , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type1 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladin Language
Ladin (, also ; autonym: , it, ladino; german: Ladinisch) is a Romance language of the Rhaeto-Romance subgroup, mainly spoken in the Dolomite Mountains in Northern Italy in the provinces of South Tyrol, Trentino, and Belluno, by the Ladin people. It exhibits similarities to Swiss Romansh and Friulian. The precise extension of the Ladin language area is a subject of scholarly debate. A more narrow perspective includes only the dialects of the valleys around the Sella group, while wider definitions comprise the dialects of adjacent valleys in the Province of Belluno and even dialects spoken in the northwestern Trentino. A standard variety of Ladin () has been developed by the Office for Ladin Language Planning as a common communication tool across the whole Ladin-speaking region. Geographic distribution Ladin is recognized as a minority language in 54 Italian municipalities belonging to the provinces of South Tyrol, Trentino and Belluno. It is not possible to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villnöß
Villnöß (; it, Funes ; Ladin: ''Funès'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northeast of the city of Bolzano. Geography As of November 30, 2010, it had a population of 2,552 and an area of .All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat. The municipality of Villnöß contains the ''frazioni'' (subdivisions, mainly villages and hamlets) Koll (Colle), St. Jakob (San Giacomo), St. Magdalena (Santa Maddalena), St. Peter (San Pietro), St. Valentin (San Valentino) and Teis (Tiso). Villnöß borders the following municipalities: Brixen, Klausen, Lajen, Urtijëi, San Martin de Tor, Santa Cristina Gherdëina and Feldthurns. History Coat-of-arms The emblem represents three piles of argent on azure, the three peaks symbolize the Odle Group in the head to the Valley of Funes. The emblem was adopted in 1967. Society Linguistic distribution According to the 2011 census, 97.69% of the population speak German, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomites
The Dolomites ( it, Dolomiti ; Ladin: ''Dolomites''; german: Dolomiten ; vec, Dołomiti : fur, Dolomitis), also known as the Dolomite Mountains, Dolomite Alps or Dolomitic Alps, are a mountain range located in northeastern Italy. They form part of the Southern Limestone Alps and extend from the River Adige in the west to the Piave Valley ( Pieve di Cadore) in the east. The northern and southern borders are defined by the Puster Valley and the Sugana Valley (Italian: ''Valsugana''). The Dolomites are located in the regions of Veneto, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Friuli Venezia Giulia, covering an area shared between the provinces of Belluno, Vicenza, Verona, Trentino, South Tyrol, Udine and Pordenone. Other mountain groups of similar geological structure are spread along the River Piave to the east – ''Dolomiti d'Oltrepiave''; and far away over the Adige River to the west – ''Dolomiti di Brenta'' (Western Dolomites). A smaller group is called ''Piccole Dolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastelruth
Kastelruth (; it, Castelrotto ; Ladin: ) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, about northeast of the city of Bolzano. Geography As of 30 November 2010, it had a population of 6,456 and an area of .All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat. Kastelruth borders the following municipalities: Barbian, Campitello di Fassa, Völs am Schlern, Lajen, Urtijëi, Waidbruck, Ritten, Santa Cristina Gherdëina and Tiers. Frazioni The municipality of Kastelruth contains the '' frazioni'' (subdivisions, mainly villages and hamlets) Seiser Alm (Alpe di Siusi), Pufels (lad. Bula, it. Bulla), Runggaditsch (lad. Roncadic, it. Roncadizza), St. Michael (San Michele Siusi), St. Oswald (Sant'Osvaldo), St. Valentin (San Valentino), St. Vigil (San Vigilio), Tagusens (Tagusa), Tisens (Tisana) and Überwasser (lad. Sureghes, it. Oltretorrente). Seis am Schlern Seis am Schlern (; it, Siusi allo Sciliar ) is an Alpine village in S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lajen
Lajen (; it, Laion ; ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northeast of the city of Bolzano. Geography As of 30 November 2010, it had a population of 2,610 and an area of .All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat. Lajen borders the following municipalities: Barbian, Kastelruth, Klausen, Urtijëi, Villanders, Villnöß and Waidbruck. Frazioni The municipality of Lajen contains the ''frazioni A ''frazione'' (plural: ) is a type of subdivision of a ''comune'' (municipality) in Italy, often a small village or hamlet outside the main town. Most ''frazioni'' were created during the Fascist era (1922–1943) as a way to consolidate territ ...'' (subdivisions, mainly villages and hamlets) Albions, Freins (Fraina), Ried (Novale), St. Peter (San Pietro), Tanirz (Tanurza) and Tschöfas (Ceves). Society Linguistic distribution According to the 2011 census, 89.93% of the population speak German, 3.93% It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Cristina Gherdëina
Santa Cristina Gherdëina (; it, Santa Cristina Valgardena ; german: St. Christina in Gröden ) is a Ladin ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about east of the city of Bolzano. Its Saslong ski run is home of the Super-G and Downhill for men races in FIS Ski World Cup. Geography As of 31 December 2010, it had a population of 1,900 and an area of .All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat. The municipality of Santa Cristina borders the following municipalities: Campitello di Fassa, Kastelruth, Villnöß, Urtijëi, San Martin de Tor and Sëlva. History Coat of arms The escutcheon is argent and gules party per fess: the upper part is represented a deer. It is the family Coat of Arms of ''Primus von Dosses'', which has since 1636, near the church of St. Cristina, organized a refectory for the poor. The emblem was adopted in 1969. Society Linguistic distribution According to the 2011 census, 91.40% of the population s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
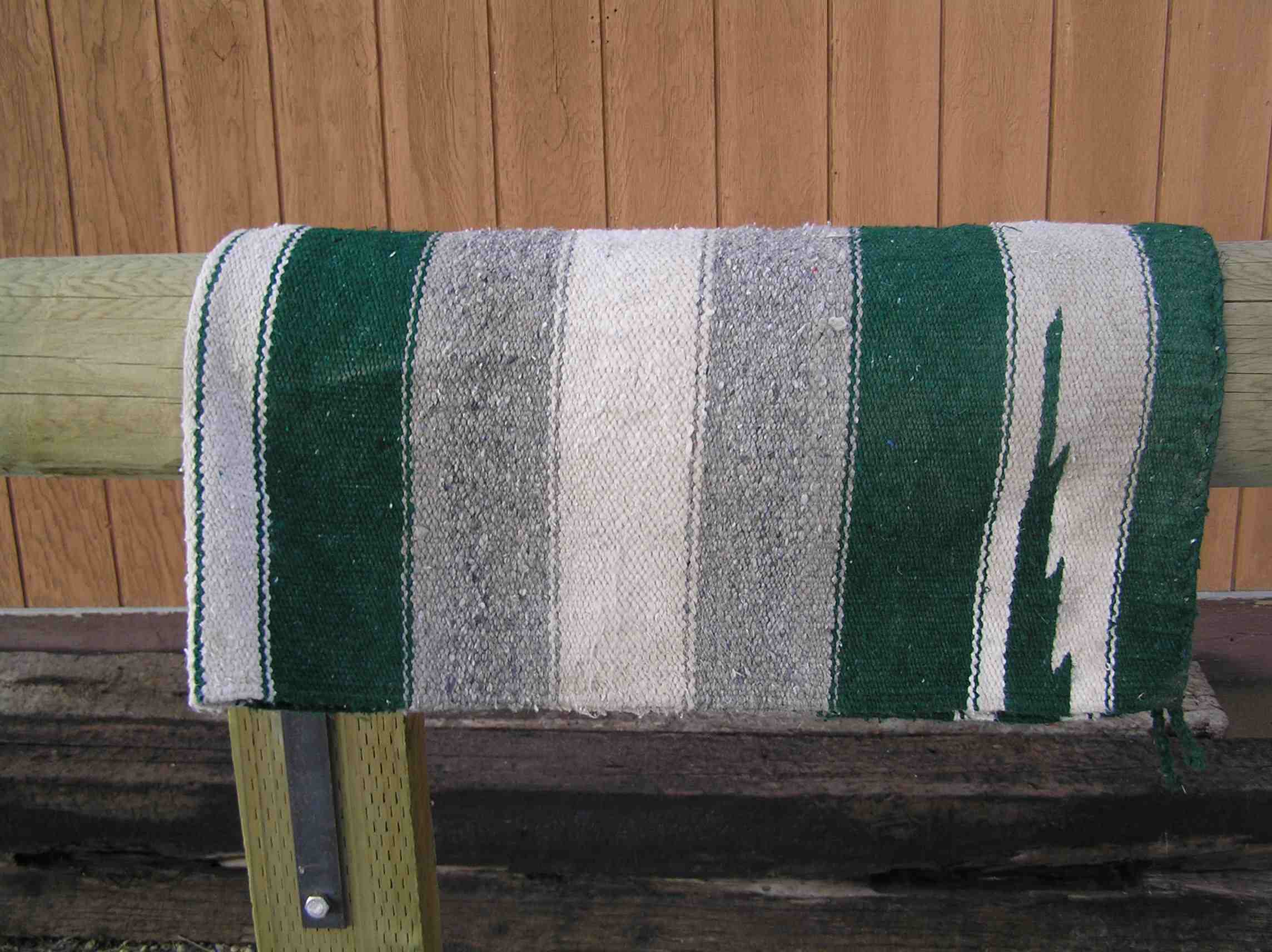
Saddle Blanket
The terms saddle blanket, saddle pad (or numnah), and saddle cloth refer to blankets, pads or fabrics inserted under a saddle. These are usually used to absorb sweat, cushion the saddle, and protect the horse's back. There are lighter types of saddle cloth, such as the shabrack, used primarily for decorative purposes, often placed over the top of a more utilitarian pad. Saddle blankets have been used for many centuries with all types of saddles. Some are a single thickness, others are made to be folded and used with a double thickness. Although a pad or blanket cannot take the place of a properly fitted saddle, pads with shims or blankets with a special design can partially compensate for minor fitting problems. The most blanket-like style is associated with the American-style western saddle. It is usually made of wool, cotton, or synthetic fabrics with similar characteristics. When fitted under the saddle, they are approximately square, although designs vary to fit ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azure (heraldry)
In heraldry, azure ( , ) is the tincture with the colour blue, and belongs to the class of tinctures called "colours". In engraving, it is sometimes depicted as a region of horizontal lines or else is marked with either az. or b. as an abbreviation. The term azure shares origin with the Spanish word "azul", which refers to the same color, deriving from hispanic Arabic ''lazawárd'' the name of the deep blue stone now called lapis lazuli. The word was adopted into Old French by the 12th century, after which the word passed into use in the blazon of coats of arms. As an heraldic colour, the word ''azure'' means "blue", and reflects the name for the colour in the language of the French-speaking Anglo-Norman nobles following the Norman Conquest of England. A wide range of colour values is used in the depiction of azure in armory and flags, and in common usage it is often referred to simply as 'blue'. In addition to the standard blue tincture called azure, there is a lighter blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimount
In heraldry, a mount (also mountain, hill, hillock) is a representation of a hill or mountain as a curved terrace in base. When the mount is included in the lower part of the shield, it may be considered an ordinary rather than a charge. A trimount, also described as ''a mount mounted'', or ''shapournet shapourned'', is a representation of a mount with three tops. For mounts with more than three tops, the number of tops is blazoned as ''coupeaux'' (e.g. ''a mount with six coupeaux''). The trimount (in German, ''Dreiberg'') can be found in all heraldic traditions (Gallo-British, German-Nordic and Latin), but it is especially common in Switzerland. A design of six hills (''Sechsberg'') can also be found in Swiss and Italian heraldry. In medieval German heraldry, mounts could have ten or more tops. Mounts with more than three tops are blazoned as a ''mount of N coupeaux'', e.g. German ''Sechsberg'' would be a ''mount of six coupeaux'', German ''Zehnberg'' as a ''mount of ten coupea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vert (heraldry)
In classical heraldry, vert () is the tincture equivalent to the colour "green". It is one of the five dark tinctures (''colours''). The word ''vert'' is simply the French for "green". It is used in English in the sense of a heraldic tincture since the early 16th century. In Modern French, ''vert'' is not used as a heraldic term. Instead, the French heraldic term for green tincture is ''sinople''. This has been the case since c. the 16th century. In medieval French heraldry, ''vert'' also meant "green" while ''sinople'' was a shade of red. Vert is portrayed by the conventions of heraldic "hatching" (in black and white engravings) by lines at a 45-degree angle from upper left to lower right, or indicated by the abbreviation vt. when a coat of arms is tricked. The colour green is commonly found in modern flags and coat of arms, and to a lesser extent also in the classical heraldry of the Late Middle Ages and the Early Modern period. Green flags were historically carried by Ottokar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |