South Tyrol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige
lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol , settlement_type =
· 5th of 21 , timezone1 = According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language ( Standard German in the written form and an
According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language ( Standard German in the written form and an
South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincial Statistics Institute of the Autonomous Province of South Tyrol
Bozen/Bolzano 2007, p. 19, Table 11 The province is granted a considerable level of self-government, consisting of a large range of exclusive legislative and executive powers and a fiscal regime that allows it to retain 90% of revenue, while remaining a net contributor to the national budget. As of 2016, South Tyrol is the wealthiest province in Italy and among the wealthiest in the
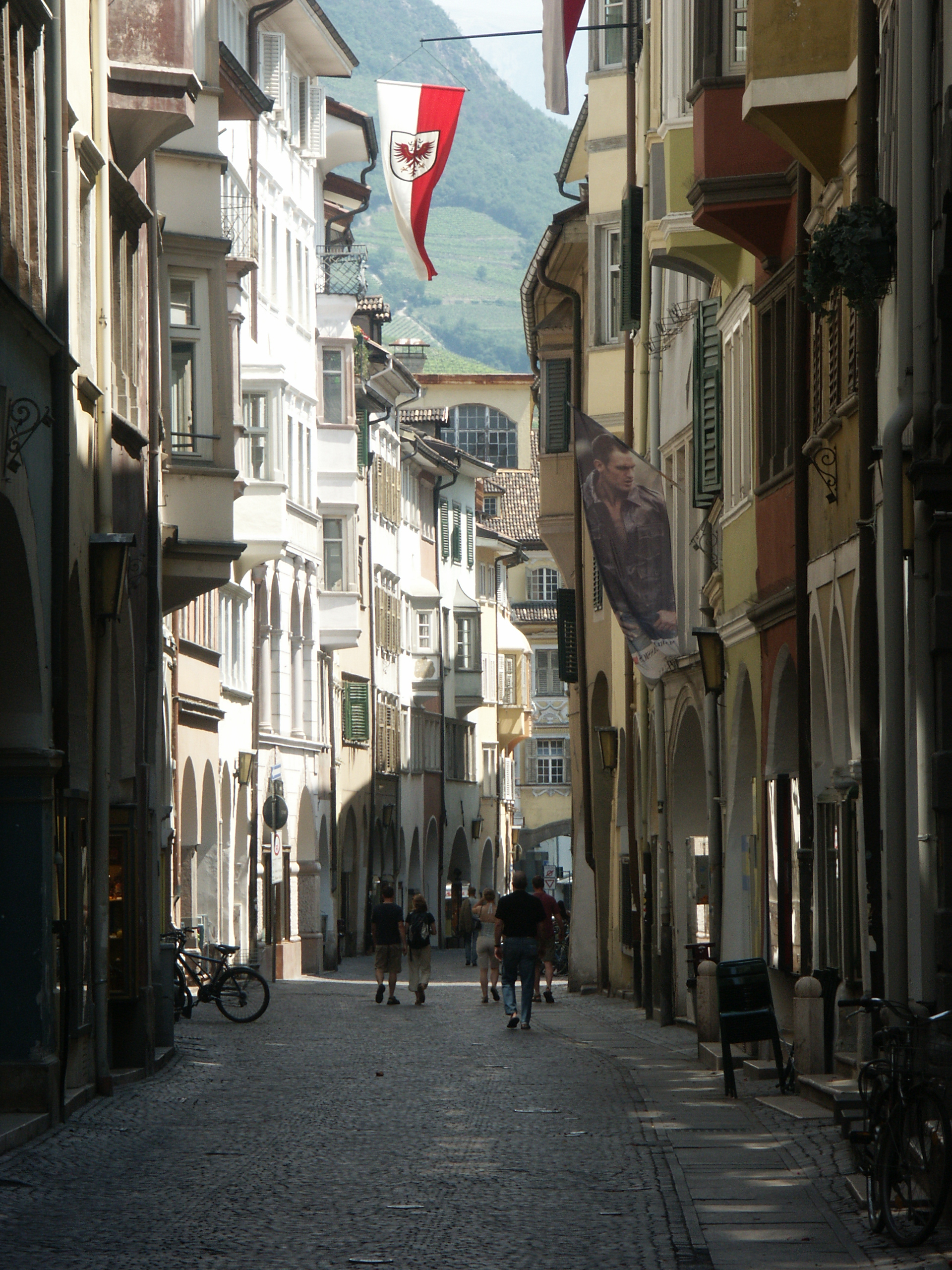
 ''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic
''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic
 South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states
South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states  Located between the mountains are many
Located between the mountains are many



 The alpine valleys between , with a typically
The alpine valleys between , with a typically
 The periadriatic seam, which separates the
The periadriatic seam, which separates the
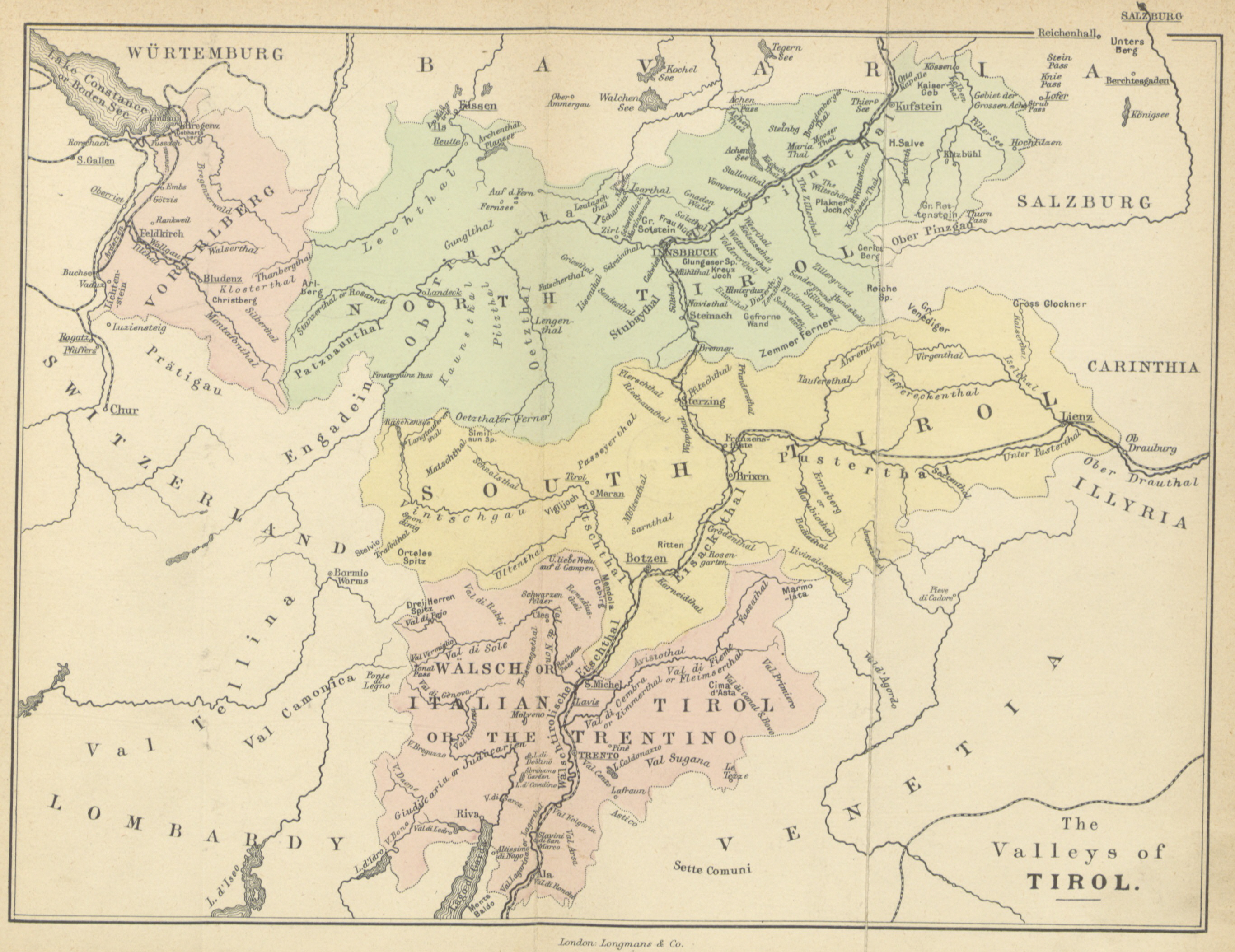
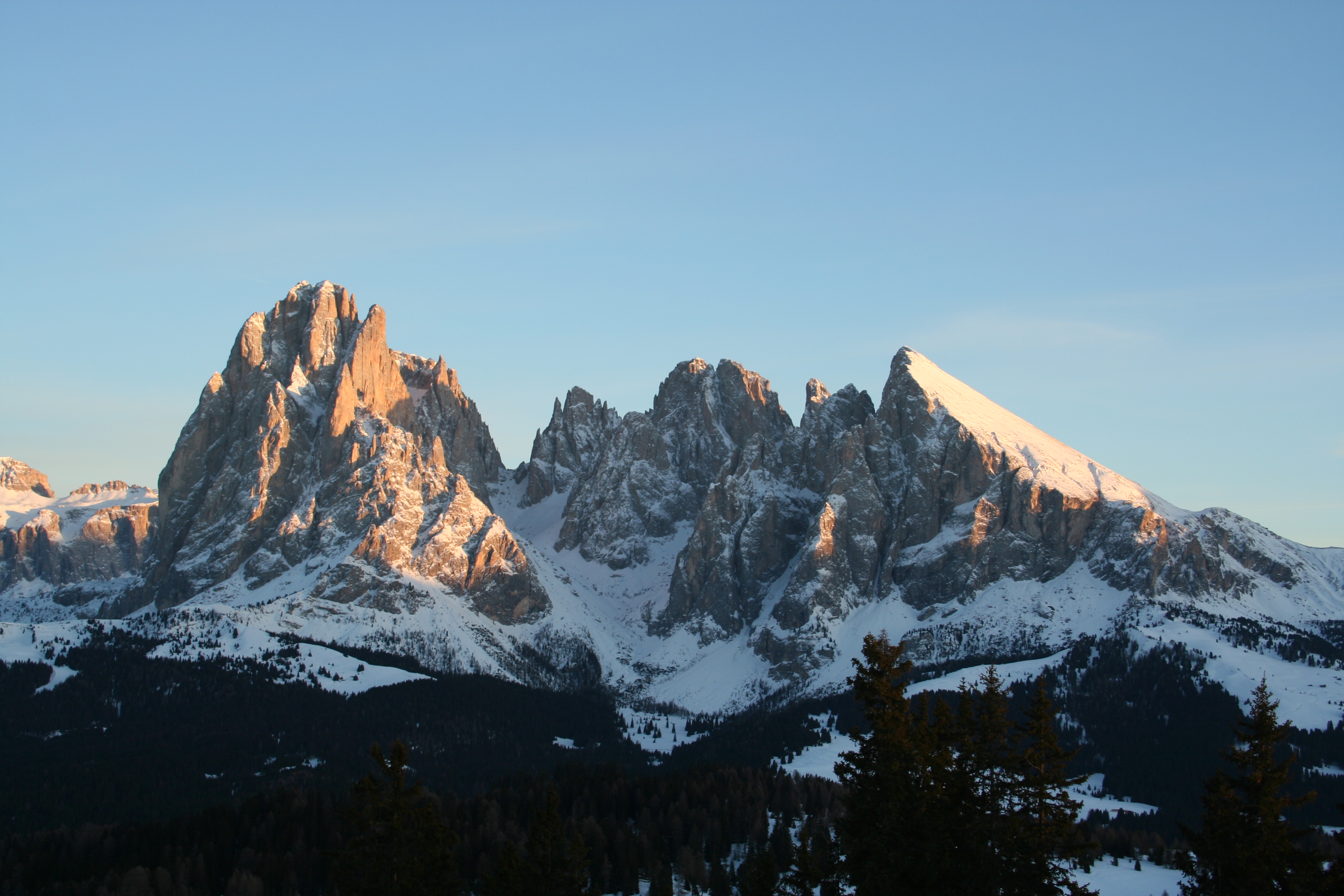
 According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by
According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by
 The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the
The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the
 The most important river in South Tyrol is the
The most important river in South Tyrol is the
 Approximately 50% of the area of South Tyrol is covered by
Approximately 50% of the area of South Tyrol is covered by

 The local government system is based upon the provisions of the
The local government system is based upon the provisions of the
 The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in
The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in
 In 2016 South Tyrol had a GDP per capita of €42,600, making it the richest province in Italy and one of the richest in the European Union.
The unemployment level in 2007 was roughly 2.4% (2.0% for men and 3.0% for women). Residents are employed in a variety of sectors, from
In 2016 South Tyrol had a GDP per capita of €42,600, making it the richest province in Italy and one of the richest in the European Union.
The unemployment level in 2007 was roughly 2.4% (2.0% for men and 3.0% for women). Residents are employed in a variety of sectors, from  The unemployment rate stood at 3.8% in 2020.
The unemployment rate stood at 3.8% in 2020.
 German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native
German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native
 The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is archaeological evidence of early Christian sites in the area as early as Late Antiquity; Säben in the Eisack Valley became an important ecclesiastical center during this period, which was only replaced by Brixen as an episcopal see in the late
The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is archaeological evidence of early Christian sites in the area as early as Late Antiquity; Säben in the Eisack Valley became an important ecclesiastical center during this period, which was only replaced by Brixen as an episcopal see in the late
 The Scheibenschlagen are the traditional "throwing of burning discs" on the first Sunday of Lent, the Herz-Jesu-Feuer are the "fires of the
The Scheibenschlagen are the traditional "throwing of burning discs" on the first Sunday of Lent, the Herz-Jesu-Feuer are the "fires of the

 The region features a large number of castles and churches. Many of the castles and
The region features a large number of castles and churches. Many of the castles and
Official website for the ''Civic Network of South Tyrol'', the Autonomous Province of Bolzano/Bozen
Special Statute for ''Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol''
Tourist information about South Tyrol
The most accurate digital map of South Tyrol
{{Authority control Regions of Europe with multiple official languages Autonomous provinces German-speaking countries and territories Provinces of Italy * Articles containing video clips
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige
lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol , settlement_type =
Autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = Flag_of_South_Tyrol.svg
, flag_alt =
, image_shield = Suedtirol CoA.svg
, shield_size = x100px
, shield_alt = Coat of arms of Tyrol
The Coat of Arms of Tyrol is the historic coat of arms of the region of Tyrol. It shows a red eagle. It was used by the Princely County of Tyrol and is today used by the states of Tyrol in Austria, South Tyrol in Italy, and numerous municipaliti ...
, anthem =
, image_map = Bolzano in Italy.svg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map highlighting the location of the province of South Tyrol in Italy (in red)
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
, subdivision_name = Italy
, subdivision_type1 = Region
, subdivision_name1 = Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol
it, Trentino (man) it, Trentina (woman) or it, Altoatesino (man) it, Altoatesina (woman) or it, Sudtirolesegerman: Südtiroler (man)german: Südtirolerin (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title = Official ...
, established_title =
, established_date =
, seat_type = Capital(s)
, seat = Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third la ...
, parts_type = Comuni
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
, parts_style = para
, p1 = 116
, government_footnotes =
, leader_party = SVP
, leader_title = Governor
, leader_name = Arno Kompatscher
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a s ...
, unit_pref = Metric
, area_footnotes =
, area_total_km2 = 7399.97
, elevation_footnotes =
, elevation_m =
, population_footnotes =
, population_total = 531178
, population_as_of = 1 January 2019
, population_density_km2 = auto
, blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal)
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
, blank_info_sec1 = €24.8 billion (2018)
, blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita
, blank1_info_sec1 = €47,100 (2018)
, blank2_name_sec1 = HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
(2019)
, blank2_info_sec1 = 0.910· 5th of 21 , timezone1 =
CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast En ...
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = CEST CEST or cest may refer to:
* Central European Summer Time (UTC+2), daylight saving time observed in the central European time zone
* Cognitive-Experiential Self-Theory
* Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer, a subset of Magnetization transfer in ...
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 39XXX
, area_code_type = Telephone prefix
, area_code = 0471, 0472, 0473, 0474
, iso_code =
, registration_plate = BZ
, blank_name_sec2 = ISTAT
The Italian National Institute of Statistics ( it, Istituto nazionale di statistica; Istat) is the main producer of official statistics in Italy. Its activities include the census of population, economic censuses and a number of social, economic ...
, blank_info_sec2 = 021
, website =
, footnotes =
, official_name =
, governing_body = Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non ...
South Tyrol (german: Südtirol; it, Alto Adige; lld, Südtirol), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano, is an autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
in northern Italy, one of the two that make up the autonomous region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol
it, Trentino (man) it, Trentina (woman) or it, Altoatesino (man) it, Altoatesina (woman) or it, Sudtirolesegerman: Südtiroler (man)german: Südtirolerin (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title = Official ...
. The province is the northernmost of Italy, the second largest, with an area of and has a total population of about 534,000 inhabitants as of 2021. Its capital and largest city is Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third la ...
(German: ''Bozen''; Ladin: ''Balsan'' or ''Bulsan'').
 According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language ( Standard German in the written form and an
According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language ( Standard German in the written form and an Austro-Bavarian dialect
Bavarian (german: Bairisch , Bavarian: ''Boarisch'') or alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a West Germanic language, part of the Upper German family, together with Alemannic and East Franconian.
Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million ...
in the spoken form); 23.4% of the population speaks Italian, mainly in and around the two largest cities (Bolzano, with an Italian-speaking majority, and Meran
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier ...
, with a slight majority German-speaking); 4.1% speaks Ladin
Ladin may refer to:
* Ladin language, a language in northern Italy, often classified as a Rhaeto-Romance language
*Ladin people, the inhabitants of the Dolomite Alps region of northern Italy
See also
*Laden (disambiguation)
* Ladino (disambigua ...
, a Rhaeto-Romance language
Rhaeto-Romance, Rheto-Romance, or Rhaetian, is a purported subfamily of the Romance languages that is spoken in south-eastern Switzerland and north-eastern Italy. The name "Rhaeto-Romance" refers to the former Roman province of Raetia. The ques ...
; 10.2% of the population (mainly recent immigrants) speaks another language natively. Of 116 South Tyrolean municipalities, 103 have a German-speaking, eight a Ladin-speaking, and five an Italian-speaking majority.
There was large-scale immigration of Italians from the rest of Italy to Bolzano and its surroundings after 1918.Oscar Benvenuto (ed.):South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincial Statistics Institute of the Autonomous Province of South Tyrol
Bozen/Bolzano 2007, p. 19, Table 11 The province is granted a considerable level of self-government, consisting of a large range of exclusive legislative and executive powers and a fiscal regime that allows it to retain 90% of revenue, while remaining a net contributor to the national budget. As of 2016, South Tyrol is the wealthiest province in Italy and among the wealthiest in the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
.
In the wider context of the European Union, the province is one of the three members of the Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion
The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion (german: Europaregion Tirol–Südtirol–Trentino; it, Euregio Tirolo–Alto Adige–Trentino) is a Euroregion formed by three different regional authorities in Austria and Italy: the Aust ...
, which corresponds almost exactly to the historical region of Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
. The other members are Tyrol state
Tyrol (; german: Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a state (''Land'') in western Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical Princely County of Tyrol. It is a constituent part of the present-day Euroregion Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino ( ...
in Austria, to the north and east, and the Italian Autonomous province of Trento
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region ...
to the south.
Name
 ''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic
''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised ...
, a former state of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
and crown land of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
of the Habsburgs. German and Ladin speakers usually refer to the area as ''Südtirol''; the Italian equivalent ''Sudtirolo'' (sometimes parsed ''Sud Tirolo'') is becoming increasingly common.
''Alto Adige'' (literally translated in English: "Upper Adige"), one of the Italian names for the province, is also used in English. The term had been the name of political subdivisions along the Adige River in the time of Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, who created the Department of Alto Adige
The Department of Alto Adige (Italian and official ''Dipartimento dell'Alto Adige'', french: link=no, département du Haut-Adige, translated into English ''Department of Upper Adige'') was a northern department of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Ital ...
, part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (1805–1814; it, Regno d'Italia; french: Royaume d'Italie) was a kingdom in Northern Italy (formerly the Italian Republic) in personal union with Napoleon I's French Empire. It was fully influenced by revolutionary Franc ...
. It was reused as the Italian name of the current province after its post-World War I creation, and was a symbol of the subsequent forced Italianization of South Tyrol.
The official name of the province today in German is ''Autonome Provinz Bozen — Südtirol''. German speakers usually refer to it not as a ''Provinz'', but as a ''Land'' (like the Länder
Länder (singular Land) or Bundesländer (singular Bundesland) is the name for (federal) states in two German-speaking countries. It may more specifically refer to:
* States of Austria, the nine federal subdivisions of Austria
* States of Germany ...
of Germany and Austria). Provincial institutions are referred to using the prefix ''Landes-'', such as ''Landesregierung'' (state government) and '' Landeshauptmann'' (governor).
The official name in Italian is ''Provincia autonoma di Bolzano — Alto Adige'', in Ladin ''Provinzia autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan — Südtirol''.
History
Annexation by Italy
South Tyrol is an administrative entity originated during theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
promised the area to Italy in the Treaty of London of 1915 as an incentive to enter the war on their side. Until 1918, it was part of the Austro-Hungarian princely County of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised ...
, but this almost completely German-speaking territory was occupied by Italy at the end of the war in November 1918 and was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy in 1919. The province as it exists today was created in 1926 after an administrative reorganization of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
, and was incorporated together with the province of Trento into the newly created region of ''Venezia Tridentina'' ("Trentine Venetia").
With the rise of Italian Fascism, the new regime made efforts to bring forward the Italianization of South Tyrol
In 1919, at the time of its annexation, the middle part of the County of Tyrol which is today called South Tyrol (in Italian ''Alto Adige'') was inhabited by almost 90% German speakers.Oscar Benvenuto (ed.):South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincia ...
. The German language was banished from public service, German teaching was officially forbidden, and German newspapers were censored (with the exception of the fascistic ''Alpenzeitung''). The regime also favoured immigration from other Italian regions.
The subsequent alliance between Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
and Benito Mussolini declared that South Tyrol would not follow the destiny of Austria, which had been annexed by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. Instead the dictators agreed that the German-speaking population be transferred to German-ruled territory or dispersed around Italy, but the outbreak of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
prevented them from fully carrying out their intention. Every single citizen had the free choice to give up his German cultural identity and stay in fascist Italy, or to leave his homeland and move to Nazi Germany to retain his cultural identity. The result was that in the difficult times of fascism, the individual South Tyrolean families were divided and separated.
In this tense relationship for the population, Walter Caldonazzi
Walter may refer to:
People
* Walter (name), both a surname and a given name
* Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Walter Jacobs (1930–1968)
* Gunther (wrestler), Austrian professional wrestler and trainer Walter Hahn (born 19 ...
from Mals was part of the resistance group around the priest Heinrich Maier
Heinrich Maier (; 16 February 1908 – 22 March 1945) was an Austrian Roman Catholic priest, pedagogue, philosopher and a member of the Austrian resistance, who was executed as the last victim of Hitler's régime in Vienna.
The resistance gr ...
, which passed plans and information about production facilities for V-1 rocket V1, V01 or V-1 can refer to version one (for anything) (e.g., see version control)
V1, V01 or V-1 may also refer to:
In aircraft
* V-1 flying bomb, a World War II German weapon
* V1 speed, V1 speed, the maximum speed at which an aircraft pilot m ...
s, V-2 rocket
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was develop ...
s, Tiger tank Tiger tank may refer to:
*Tiger I, or ''Panzerkampfwagen'' Tiger ''Ausf. E'', a German heavy tank produced from 1942 to 1944
*Tiger II, or ''Panzerkampfwagen'' Tiger ''Ausf. B'', a German heavy tank produced from 1943 to 1945, also known as ''Kön ...
s, Messerschmitt Bf 109, and Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet
The Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet is a rocket-powered interceptor aircraft primarily designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt. It is the only operational rocket-powered fighter aircraft in history as well as ...
and other aircraft to the Allies. For after the war, the group planned an independent Austria with a monarchical form of government, which would include Austria, Bavaria and South Tyrol.
In 1943, when the Italian government signed an armistice with the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, the region was occupied by Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, which reorganised it as the Operation Zone of the Alpine Foothills and put it under the administration of Gauleiter
A ''Gauleiter'' () was a regional leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as the head of a '' Gau'' or '' Reichsgau''. ''Gauleiter'' was the third-highest rank in the Nazi political leadership, subordinate only to '' Reichsleiter'' and to ...
Franz Hofer
Franz Hofer (November 27, 1902 – February 18, 1975) was, in the time of the Third Reich, the Nazi Gauleiter of the Tyrol and Vorarlberg. As the Nazi party chief for the Tirol/Vorarlberg province he was the most powerful figure in the regi ...
. The region was ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' annexed to the German Reich
German ''Reich'' (lit. German Realm, German Empire, from german: Deutsches Reich, ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty ...
(with the addition of the province of Belluno) until the end of the war. This status ended along with the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
regime, and Italian rule was restored in 1945.
Gruber–De Gasperi Agreement
After the war the Allies decided that the province would remain a part of Italy, under the condition that the German-speaking population be granted a significant level of self-government. Italy and Austria negotiated an agreement in 1946, recognizing the rights of the German minority.Alcide De Gasperi
Alcide Amedeo Francesco De Gasperi (; 3 April 1881 – 19 August 1954) was an Italian politician who founded the Christian Democracy party and served as prime minister of Italy in eight successive coalition governments from 1945 to 1953.
De Gas ...
, Italy's prime minister, a native of Trentino, wanted to extend the autonomy to his fellow citizens. This led to the creation of the region called ''Trentino-Alto Adige/Tiroler Etschland''. The Gruber–De Gasperi Agreement
The Gruber–De Gasperi Agreement was a bilateral treaty that was signed by the foreign minister of Austria, Karl Gruber, and the prime minister of Italy, Alcide De Gasperi, on 5 September 1946. Recognized by international law, it granted the Germ ...
of September 1946 was signed by the Italian and Austrian Foreign Ministers, creating the autonomous region of Trentino-South Tyrol, consisting of the autonomous provinces of Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region ...
and South Tyrol. German and Italian were both made official languages, and German-language education was permitted once more. Still Italians were the majority in the combined region.
This, together with the arrival of new Italian-speaking immigrants, led to strong dissatisfaction among South Tyroleans, which culminated in terrorist acts perpetrated by the '' Befreiungsausschuss Südtirol'' (BAS – Liberation Committee of South Tyrol). In the first phase, only public edifices and fascist monuments were targeted. The second phase was bloodier, costing 21 lives (15 members of Italian security forces, two civilians, and four terrorists).
''Südtirolfrage''
The South Tyrolean Question (''Südtirolfrage'') became an international issue. As the implementation of the post-war agreement was deemed unsatisfactory by the Austrian government, it became a cause of significant friction with Italy and was taken up by theUnited Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
in 1960. A fresh round of negotiations took place in 1961 but proved unsuccessful, partly because of the campaign of terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
.
The issue was resolved in 1971, when a new Austro-Italian treaty was signed and ratified. It stipulated that disputes in South Tyrol would be submitted for settlement to the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordanc ...
in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
, that the province would receive greater autonomy within Italy, and that Austria would not interfere in South Tyrol's internal affairs. The new agreement proved broadly satisfactory to the parties involved, and the separatist tensions soon eased.
The autonomous status granted in 1972 has resulted in a considerable level of self-government, and also allows the entity to retain almost 90% of all levied taxes.
Autonomy
In 1992, Italy and Austria officially ended their dispute over the autonomy issue on the basis of the agreement of 1972. The extensive self-government provided by the current institutional framework has been advanced as a model for settling interethnic disputes and for the successful protection of linguistic minorities. This is among the reasons why the Ladin municipalities of Cortina d'Ampezzo/Anpezo,Livinallongo del Col di Lana
Livinallongo del Col di Lana (; lld, Fodóm; german: Buchenstein) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Belluno in the Italian region Veneto, located about north of Venice and about northwest of Belluno.
Ninety percent of the ...
/Fodom and Colle Santa Lucia
Colle Santa Lucia (; Ladin language: ''Col'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Belluno in the Italian region of Veneto, located about north of Venice and about northwest of Belluno. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of ...
/Col have asked in a referendum to be detached from Veneto and reannexed to the province, from which they were separated under the fascist government.
Euroregion
In 1996, theEuroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two (or more) contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border region. ...
was formed between the Austrian state of Tyrol and the Italian provinces of South Tyrol and Trentino. The boundaries of the association correspond to the old County of Tyrol. The aim is to promote regional peace, understanding and cooperation in many areas. The region's assemblies meet together as one on various occasions, and have set up a common liaison office with the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
in Brussels.
Geography
 South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states
South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
and Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label= Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
, and by the Swiss canton of Graubünden to the west. The Italian provinces of Belluno, Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region ...
, and Sondrio border to the southeast, south, and southwest, respectively.
The landscape itself is mostly cultivated with different types of shrubs
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees ...
and forests
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
and is highly mountainous.
Entirely located in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
, the province's landscape is dominated by mountains. The highest peak is the Ortler () in the far west, which is also the highest peak in the Eastern Alps
Eastern Alps is the name given to the eastern half of the Alps, usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley up to the Splügen Pass at the Alpine divide and down the Liro River to Lake Como in t ...
outside the Bernina Range
The Bernina Range is a mountain range in the Alps of eastern Switzerland and northern Italy. It is considered to be part of the Rhaetian Alps within the Central Eastern Alps. It is one of the highest ranges of the Alps, covered with many glaciers ...
. Even more famous are the craggy peaks of the Dolomites
The Dolomites ( it, Dolomiti ; Ladin: ''Dolomites''; german: Dolomiten ; vec, Dołomiti : fur, Dolomitis), also known as the Dolomite Mountains, Dolomite Alps or Dolomitic Alps, are a mountain range located in northeastern Italy. They form pa ...
in the eastern part of the region.
The following mountain groups are (partially) in South Tyrol. All but the Sarntal Alps are on the border with Austria, Switzerland, or other Italian provinces. The ranges are clockwise from the west and for each the highest peak is given that is within the province or on its border.
 Located between the mountains are many
Located between the mountains are many valleys
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
, where the majority of the population lives.
Administrative divisions
The province is divided into eight districts (German: ''Bezirksgemeinschaften'', Italian: ), one of them being the chief city of Bolzano. Each district is headed by a president and two bodies called the district committee and the district council. The districts are responsible for resolving intermunicipal disputes and providing roads, schools, and social services such as retirement homes. The province is further divided into 116 '' Gemeinden'' or ''comuni
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
''.
Districts
Largest municipalities


Climate
Climatically, South Tyrol may be divided into five distinct groups: TheAdige
The Adige (; german: Etsch ; vec, Àdexe ; rm, Adisch ; lld, Adesc; la, Athesis; grc, Ἄθεσις, Áthesis, or , ''Átagis'') is the second-longest river in Italy, after the Po. It rises near the Reschen Pass in the Vinschgau in the pro ...
valley area, with cold winters (24-hour averages in January of about ) and warm summers (24-hour averages in July of about ), usually classified as humid subtropical climate — Cfa. It has the driest and sunniest climate of the province. The main city in this area is Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third la ...
.
The midlands, between , with cold winters (24-hour averages in January between ) and mild summers (24-hour averages in July between ). This is a typical oceanic climate, classified as Cfb. It is usually wetter than the subtropical climate, and very snowy during the winters. During the spring and autumn, there is a large foggy season, but fog may occur even on summer mornings. Main towns in this area are Meran
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier ...
, Bruneck
Bruneck (; it, Brunico or Ladin: ''Bornech'' or ''Burnech''; la, Branecium or ''Brunopolis'' is the largest town in the Puster Valley in the Italian province of South Tyrol.
Geography
Bruneck rises up in the middle of a wide valley (perhaps ...
, Sterzing
Sterzing (; it, Vipiteno ) is a comune in South Tyrol in northern Italy. It is the main town of the southern Wipptal, and the Eisack River flows through the medieval town.
History
Origin
The town traces its roots to 14 B.C., when Nero Claudius ...
, and Brixen
Brixen (, ; it, Bressanone ; lld, Porsenù or ) is a town in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about north of Bolzano.
Geography
First mentioned in 901, Brixen is the third largest city and oldest town in the province, and the artistic an ...
. Near the lakes in higher lands (between ) the humidity may make the climate in these regions milder during winter, but also cooler in summer, then, a subpolar oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
, Cfc, may occur.
 The alpine valleys between , with a typically
The alpine valleys between , with a typically humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
— Dfb, covering the largest part of the province. The winters are usually very cold (24-hour averages in January between ), and the summers, mild with averages between . It is a very snowy climate; snow may occur from early October to April or even May. Main municipalities in this area are Urtijëi
Urtijëi (; german: St. Ulrich in Gröden ; it, Ortisei ) is a town of 4,637 inhabitants in South Tyrol in northern Italy. It occupies the Val Gardena within the Dolomites, a mountain chain that is part of the Alps.
Geography
Urtijëi borders th ...
, Badia, Sexten, Toblach
Toblach (; it, Dobbiaco ) is a ''comune''/''Gemeinde'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located in the Puster Valley about northeast of the city of Bolzano, on the border with Austria.
Geography
As of November 30, 2010, it had ...
, Stilfs, Vöran
Vöran (; it, Verano ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northwest of the city of Bolzano.
Geography
As of November 30, 2010, it had a population of 927 and an area of .All demographics and other sta ...
, and Mühlwald
Mühlwald (; it, Selva dei Molini ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol, a province in northern Italy, located about northeast of Bolzano, on the border with Austria.
Geography
As of 31 December 2015, it had a population of 1,442 and a ...
.
The alpine valleys between , with a subarctic climate — Dfc, with harsh winters (24-hour averages in January between ) and cool, short, rainy and foggy summers (24-hour averages in July of about ). These areas usually have five months below the freezing point, and snow sometimes occurs even during the summer, in September. This climate is the wettest of the province, with large rainfalls during the summer, heavy snowfalls during spring and fall. The winter is usually a little drier, marked by freezing and dry weeks, although not sufficiently dry to be classified as a Dwc climate. Main municipalities in this area are Corvara, Sëlva
Sëlva (; it, Selva di Val Gardena ; german: Wolkenstein in Gröden ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Val Gardena in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about east of the city of Bolzano. The Ladin place name derives from the Latin word ...
, Santa Cristina Gherdëina
Santa Cristina Gherdëina (; it, Santa Cristina Valgardena ; german: St. Christina in Gröden ) is a Ladin ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about east of the city of Bolzano. Its Saslong ski run is home of the ...
.
The highlands above , with an alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
tundra climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. undra climate https://www.britannica.com/science/tundra-climateThe Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2019 It is classified as ET according to Köppen ...
, ET, which becomes an ice cap climate
An ice cap climate is a polar climate where no mean monthly temperature exceeds . The climate covers areas in or near the high latitudes (65° latitude) to polar regions (70–90° north and south latitude), such as Antarctica, some of the northe ...
, EF, above . The winters are cold, but sometimes not as cold as the higher valleys' winters. In January, most of the areas at have an average temperature of about , while in the valleys at about , the mean temperature may be as low as . The higher lands, above are usually extremely cold, with averages of about during the coldest month, January.
Geology
 The periadriatic seam, which separates the
The periadriatic seam, which separates the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern ...
from the Central Alps
The Alps form a large mountain range dominating Central Europe, including parts of Italy, France, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Slovenia, Germany and possibly Hungary (if one includes the Kőszeg Mountains).
This article describes the d ...
, runs through South Tyrol in a southwest-northeast direction. In South Tyrol at least three of the four main structural elements of the Alps come to light: the Southern Alpine comes to light south of the periadriatic suture, the Eastern Alpine north of it, and in the northern part of the country, east of the Brenner Pass, the Tauern window, in which the Peninsular and, according to some authors, the Helvetic are visible.
In South Tyrol, the following structure can be roughly recognized: The lowest floor forms the crystalline basement. About 280 million years ago, in the Lower Permian, multiple magmatic events occurred. At that time the Brixen granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
was formed at the northern boundary of the Southern Alps, and at about the same time, further south in the Bolzano area, there was strong volcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
that formed the Adige Valley volcanic complex. In the Upper Permian a period began in which sedimentary rocks were formed. At first, these were partly clastic sediments, among which the Gröden sandstone is found. In the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
, massive carbonate platforms of dolomitic rocks then formed; this process was interrupted in the Middle Triassic by a brief but violent phase of volcanic activity.
In South Tyrol, the Eastern Alps
Eastern Alps is the name given to the eastern half of the Alps, usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley up to the Splügen Pass at the Alpine divide and down the Liro River to Lake Como in t ...
consist mainly of metamorphic rocks, such as gneisses or mica schists, with occasional intercalations of marble and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
sedimentary rocks with metamorphic overprint (e.g., in the Ortler or southwest of the Brenner). Various metamorphic rocks are found in the Tauern Window, such as Hochstegen marble (as in Wolfendorn), Grünschiefer (as in Hochfeiler), or rocks of the Zentralgneiss (predominantly in the area of the Zillertal Main Ridge).
The province of South Tyrol has placed numerous geological natural monuments under protection. Among the best known are the Bletterbach Gorge, a 12 km (7½ mile) long canyon in the municipality of Aldein, and the Ritten Earth Pyramids, which are the largest in Europe with a height of up to .
Mountains
 According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by
According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
in 2009 as a "Dolomite World Heritage Site".
Although some isolated massifs approach and show strong glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate be ...
(especially in the Ortler Alps and on the main ridge of the Alps), South Tyrol is by far dominated by mountains with altitudes of between . Among the multitude of peaks, the Dolomites
The Dolomites ( it, Dolomiti ; Ladin: ''Dolomites''; german: Dolomiten ; vec, Dołomiti : fur, Dolomitis), also known as the Dolomite Mountains, Dolomite Alps or Dolomitic Alps, are a mountain range located in northeastern Italy. They form pa ...
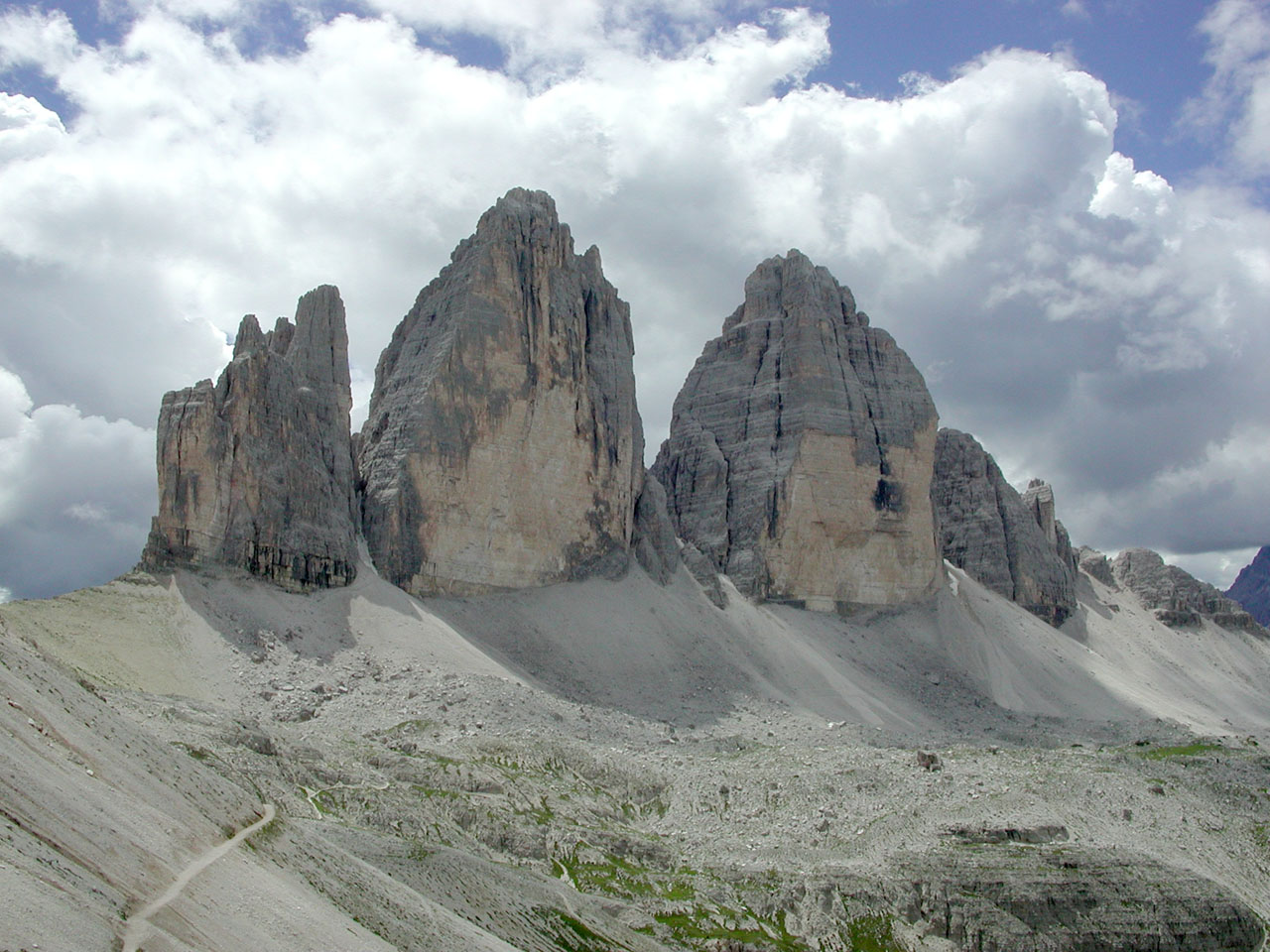
are the highest in the Alps. Among the large number of peaks, three stand out for their alpine or cultural importance: the Ortler () as the highest mountain in South Tyrol, the Schlern
The Schlern (; it, Sciliar ; lld, Sciliër; 2,563 m) is a mountain of the Dolomites in South Tyrol, Italy.
The peak at the north west end of the mountain (left, in the image at right) was first ascended in July 1880 by Johann Santner. It i ...
() as the country's "landmark" and the Drei Zinnen
The Tre Cime di Lavaredo (; ), also called the Drei Zinnen (; ), are three distinctive battlement-like peaks, in the Sexten Dolomites of northeastern Italy. They are probably one of the best-known mountain groups in the Alps. The three peaks, f ...
() as the center of alpine climbing. Other well-known mountains are the Königspitze
The Königspitze (german: Königspitze; it, Gran Zebrù) is a mountain of the Ortler Alps on the border between South Tyrol and the Province of Sondrio ( Lombardy), Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the ...
(), the Weißkugel
Weißkugel (; ) or Weißkogel is the second highest mountain in the Ötztal Alps and the third highest mountain in Austria. Featuring many glaciers, it lies on the border between Austria and Italy. The easiest way to climb it is over its south ...
(), the Similaun
The Similaun () is a mountain in the Schnalskamm group of the Ötztal Alps. It is on the Austrian- Italian border. At 3,606 m, it is Austria's sixth highest summit. It was first ascended in 1834 by Josef Raffeiner and Theodor Kaserer. It ...
(), the Hochwilde
The Hochwilde or Hohe Wilde ( it, Altissima) is a mountain in the Ötztal Alps on the border between Tyrol, Austria, and South Tyrol, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in ...
(), the Sarner Weißhorn (), the Hochfeiler (), the Dreiherrnspitze (), the Hochgall (), the Peitlerkofel (), the Langkofel () and the Rosengartenspitze ().
The extensive mountain landscapes
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the p ...
, about 34% of the total area of South Tyrol, are alpine pastures (including the of the great Alpe di Siusi). Along the main valleys, the mountain ranges descend in many places to valley bottoms over gently terraced landscapes, which are geological remains of former valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
systems; situated between inhospitable high mountains and formerly boggy or deeply incised valley bottoms, these areas known as the "Mittelgebirge" (including, for example, the Schlern area) are of particular importance in terms of settlement history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
.
Valleys
 The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the
The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the Adige Valley
The Adige (; german: Etsch ; vec, Àdexe ; rm, Adisch ; lld, Adesc; la, Athesis; grc, Ἄθεσις, Áthesis, or , ''Átagis'') is the second-longest river in Italy, after the Po. It rises near the Reschen Pass in the Vinschgau in the pro ...
, the Eisack Valley and the Puster Valley
The Puster Valley ( it, Val Pusteria ; german: Pustertal, ) is one of the largest longitudinal valleys in the Alps that runs in an east-west direction between Lienz in East Tyrol, Austria, and Mühlbach near Brixen in South Tyrol, Italy. The S ...
, formed by the Ice Age Adige glacier and its tributaries. The highest part of the Adige valley in western South Tyrol, from Reschen () to Töll (approx. ) near Merano, is called Vinschgau; the southernmost section, from Bolzano to Salurner Klause (), is divided into Überetsch and Unterland. From there, the Adige Valley continues in a southerly direction until it merges with the Po plain at Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
.
At Bolzano, the Eisack Valley merges into the Adige Valley. The Eisack Valley runs from Bolzano northeastward to Franzensfeste, where it merges with the Wipp Valley, which runs first northwestward and then northward over the Brenner Pass to Innsbruck. In the town of Brixen, the Eisack Valley meets the Puster Valley, which passes through Bruneck and reaches Lienz via the Toblacher Sattel (). In addition to the three main valleys, South Tyrol has a large number of side valleys. The most important and populated side valleys are (from west to east) Sulden, Schnals, Ulten, Passeier, Ridnaun, the Sarntal, Pfitsch, Gröden, the Gadertal, the Tauferer Ahrntal and Antholz.
In mountainous South Tyrol, about 64.5% of the total land area
This is a list of the world's countries and their dependent territories by land, water and total area, ranked by total area.
Entries in this list include, but are not limited to, those in the ISO 3166-1 standard, which includes sovereign ...
is above above sea level and only 14% below . Therefore, a large part of the population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
is concentrated in relatively small areas in the valleys at an altitude of between , mainly in the area of the extensive alluvial cones and broad basins. The most densely populated areas are in the Adige valley, where three of the four largest cities, Bolzano, Merano and Laives, are located. The flat valley bottoms are mainly used for agriculture.
Hydrography
 The most important river in South Tyrol is the
The most important river in South Tyrol is the Adige
The Adige (; german: Etsch ; vec, Àdexe ; rm, Adisch ; lld, Adesc; la, Athesis; grc, Ἄθεσις, Áthesis, or , ''Átagis'') is the second-longest river in Italy, after the Po. It rises near the Reschen Pass in the Vinschgau in the pro ...
, which rises at the Reschen Pass, flows for a distance of about to the border at the Salurner Klause, and then flows into the Po Valley and the Adriatic Sea. The Adige, whose total length of in Italy is exceeded only by the Po, drains 97% of the territory's surface area. Its river system also includes the Eisack, about long, and the Rienz, about long, the next two largest rivers in South Tyrol. They are fed by numerous rivers and streams in the tributary valleys. The most important tributaries are the Plima, the Passer, the Falschauer, the Talfer, the Ahr and the Gader. The remaining 3% of the area is drained by the Drava and Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
river systems to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
and by the Piave river
The Piave ( la, Plavis, German: ''Ploden'') is a river in northern Italy. It begins in the Alps and flows southeast for into the Adriatic Sea near the city of Venice. One of its tributaries is the Boite.
In 1809 it was the scene of a battle du ...
system to the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, respectively.
In South Tyrol there are 176 natural lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s with an area of more than half a hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100- metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is ...
(1¼ acre), most of which are located above altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
. Only 13 natural lakes are larger than 5 ha, and only three of them are situated below altitude: the Kalterer See (), the Großer () and the Kleiner Montiggler See (). Fourteen South Tyrolean reservoirs used for energy production include the Reschensee (), which with an area of forms the largest standing body of water in South Tyrol, the Zufrittsee () and the Arzkarsee ().
The natural monument
A natural monument is a natural or natural/cultural feature of outstanding or unique value because of its inherent rarity, representative of aesthetic qualities or cultural significance.
Under World Commission on Protected Areas guidelines, na ...
s designated by the province of South Tyrol include numerous hydrological objects, such as streams, waterfalls, moors, glaciers and mountain lakes like the Pragser Wildsee (), the Karersee () or the Spronser Seen ().
Vegetation
forests
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, another 40% is above and thus largely beyond the forest demarcation line, which varies between . In each case, more than half of the total forest area is located on land with a slope steeper than 20° and at altitudes
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
between . Approximately 24% of the forest area can be classified as protective forest preserving settlements, traffic routes and other human infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
. A 1997 study classified about 35% of South Tyrol's forests as near-natural or natural, about 41% as moderately modified and about 24% as heavily modified or artificial. The forests are found in the valley bottoms.
The flat valley bottoms were originally completely covered with riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...
forests, of which only very small remnants remain along the river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
s. The remaining areas have given way to settlements and agricultural land
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with ...
. On the valley slopes, sub-Mediterranean mixed deciduous forests are found up to altitude, characterized mainly by manna ash, hop hornbeam, hackberry, sweet chestnut and downy oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
. From about of altitude, red beech or pine forests can appear instead, colonizing difficult and arid sites (more rarely). At altitudes between , spruce forests are found; between , montane and subalpine spruce forests predominate. The latter are often mixed with tree species such as larch, rowan, white pine and stone pine. The larch and stone pine forests at the upper edge of the forest belt occupy relatively small areas. Beyond the forest edge, subalpine dwarf shrub communities, alpine grasslands and, lately, alpine tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
dominate the landscape as vegetation types.
Politics

 The local government system is based upon the provisions of the
The local government system is based upon the provisions of the Italian Constitution
The Constitution of the Italian Republic ( it, Costituzione della Repubblica Italiana) was enacted by the Constituent Assembly on 22 December 1947, with 453 votes in favour and 62 against. The text, which has since been amended sixteen times, ...
and the Autonomy Statute of the Region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol
it, Trentino (man) it, Trentina (woman) or it, Altoatesino (man) it, Altoatesina (woman) or it, Sudtirolesegerman: Südtiroler (man)german: Südtirolerin (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title = Official ...
. The 1972 second Statute of Autonomy for Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol devolved
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
most legislative and executive competences from the regional level to the provincial level, creating ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' two separate regions.
The considerable legislative power
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known a ...
of the province is vested in an assembly, the Landtag of South Tyrol
The Council of South Tyrol is the provincial council (german: Südtiroler Landtag; it, Consiglio della Provincia autonoma di Bolzano; lld, Cunsëi dla Provinzia autonoma de Bulsan) of the autonomous province of South Tyrol (Bolzano) in northe ...
(German: ''Südtiroler Landtag''; Italian: ''Consiglio della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano''; Ladin: ''Cunsëi dla Provinzia Autonoma de Bulsan'').
The legislative powers of the assembly are defined by the second Statute of Autonomy.
The executive powers are attributed to the government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
(German: ''Landesregierung''; Italian: ''Giunta Provinciale'') headed by the '' Landeshauptmann'' Arno Kompatscher
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a s ...
. He belongs to the ''South Tyrolean People's Party
The South Tyrolean People's Party (german: Südtiroler Volkspartei, SVP) is a regionalist and autonomist political party in South Tyrol, an autonomous province with a German-speaking majority in northern Italy.
Founded on 8 May 1945, the SVP h ...
'', which has been governing with a parliamentary majority since 1948. South Tyrol is characterized by long sitting presidents, having only had two presidents between 1960 and 2014 (Silvius Magnago
Silvius Magnago (5 February 1914 – 25 May 2010) was a South Tyrolean politician.
Biography
Magnago was born in Merano, which was then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, on 5 February 1914. In 1936 he graduated from the grammar school of ...
1960–1989, Luis Durnwalder
Luis Durnwalder (born 23 September 1941) is an Italian politician, former governor of the autonomous province of South Tyrol from 1989 until 2014, and former president and vice-president of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, in Northern Italy.
Bi ...
1989–2014).
A fiscal regime allows the province to retain a large part of most levied taxes, in order to execute and administer its competences. Nevertheless, South Tyrol remains a net contributor to the Italian national budget.
Last provincial elections
List of governors
Provincial Government
 The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in
The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Junta provinziala in Ladin
Ladin may refer to:
* Ladin language, a language in northern Italy, often classified as a Rhaeto-Romance language
*Ladin people, the inhabitants of the Dolomite Alps region of northern Italy
See also
*Laden (disambiguation)
* Ladino (disambigua ...
) consists of a provincial governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
and a variable number of provincial councilors
A councillor is an elected representative for a local government council in some countries.
Canada
Due to the control that the provinces have over their municipal governments, terms that councillors serve vary from province to province. Unl ...
. Currently (2021), the provincial government consists of eight provincial councilors and the provincial governor. The deputies of the provincial governor are appointed from among the provincial councilors. The current governor is Arno Kompatscher (SVP), his deputies are the provincial councilors Arnold Schuler (SVP), Giuliano Vettorato (LN) and Daniel Alfreider (SVP).
The Governor and the Provincial Councilors are elected by Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
by secret ballot with an absolute majority
A supermajority, supra-majority, qualified majority, or special majority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority r ...
of votes. The composition of the provincial government must in any case reflect the proportional distribution of the German and Italian language groups in the provincial parliament. In the past, this provision prevented the German-dominated South Tyrol People's Party (SVP) from governing alone and allowed Italian parties to participate in the provincial government. Since the Ladin language group, with just under 4% of South Tyrol's resident population, has little electoral potential, a separate provision in the autonomy statute allows Ladin representation in the provincial government regardless of their proportional representation in the provincial parliament.
Secessionist movement
Given the region's historical and cultural association with neighboring Austria, calls for the secession of South Tyrol and its reunification with Austria do surface from time to time among German- and Ladin-speakers, although falling short of an absolute majority in the province when considering also the Italian-speaking population, the majority does support a separation. Among the political parties that support South Tyrol's reunification into Austria areSouth Tyrolean Freedom
South Tyrolean Freedom (german: Süd-Tiroler Freiheit, STF) is a regionalist, separatist and national-conservative political party in South Tyrol, Italy. The party, which is part of the South Tyrolean independence movement, seeks to represent th ...
, Die Freiheitlichen
''Die Freiheitlichen'' (), abbreviated dF, is a regionalist, separatist and national-conservative political party in South Tyrol, Italy. The party, which is part of the South Tyrolean independence movement, seeks to represent the German-sp ...
and Citizens' Union for South Tyrol
The Citizens' Union for South Tyrol (german: BürgerUnion für Südtirol, BUfS), formerly Union for South Tyrol (''Union für Südtirol'', UfS), was a national-conservative political party active in South Tyrol, Italy.
The party was committed t ...
.
Economy
 In 2016 South Tyrol had a GDP per capita of €42,600, making it the richest province in Italy and one of the richest in the European Union.
The unemployment level in 2007 was roughly 2.4% (2.0% for men and 3.0% for women). Residents are employed in a variety of sectors, from
In 2016 South Tyrol had a GDP per capita of €42,600, making it the richest province in Italy and one of the richest in the European Union.
The unemployment level in 2007 was roughly 2.4% (2.0% for men and 3.0% for women). Residents are employed in a variety of sectors, from agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
— the province is a large producer of apples, and its South Tyrol wine are also renowned — to industry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
to services
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a p ...
, especially tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
. Spas located on the Italian Alps have become a favorite for tourists seeking wellness.
South Tyrol is home to numerous mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, an ...
companies, some of which are the global market leaders in their sectors: the Leitner Group that specializes in cable cars and wind energy
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
, TechnoAlpin AG, which is the global market leader in snow-making technology and the snow groomer
Snow grooming is the process of manipulating snow for recreational uses with a tractor, snowmobile, piste caterpillar, truck or snowcat towing specialized equipment. The process is used to maintain ski hills, cross-country ski
Cross-countr ...
company Prinoth.
Transport
The region is, together with northern and eastern Tyrol, an important transit point between southern Germany and Northern Italy. Freights by road and rail pass through here. One of the most important highways is the A22, also called the ''Autostrada del Brennero''. It connects to the Brenner Autobahn in Austria. Thevehicle registration plate
A vehicle registration plate, also known as a number plate (British English), license plate (American English), or licence plate ( Canadian English), is a metal or plastic plate attached to a motor vehicle or trailer for official identific ...
of South Tyrol is the two-letter provincial code Bz for the capital city, Bolzano. Along with the autonomous Trentino (Tn) and Aosta Valley
, Valdostan or Valdotainian it, Valdostano (man) it, Valdostana (woman)french: Valdôtain (man)french: Valdôtaine (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title = Official languages
, population_blank1 = Italian French
...
(Ao), South Tyrol is allowed to surmount its license plates with its coat of arms.
Rail transport goes over the Brenner Pass. The Brenner Railway is a major line connecting the Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
and Italian railways
The Italian railway system is one of the most important parts of the infrastructure of Italy, with a total length of of which active lines are 16,723 km. The network has recently grown with the construction of the new high-speed rail netw ...
from Innsbruck and Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
climbing the Wipptal
The Wipp Valley (german: Wipptal) is an Alpine valley in Tyrol, Austria and in South Tyrol, Italy, running between Innsbruck and Franzensfeste. The Brenner Pass (1,374 m) at the Austro-Italian border divides it into the northern, Austrian Lower ...
, passing over the Brenner Pass and descending down the Eisack Valley to Bolzano and then down the Adige Valley from Bolzano to Rovereto and to Verona. The line is part of the Line 1 of Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T).
Other railways are the Pustertalbahn, Ritten Railway
The Ritten Railway (german: Rittnerbahn or ''Rittner Bahn'', it, Ferrovia del Renon) is an electric light railway which originally connected Bolzano with the Ritten plateau and today continues to operate on the plateau, connecting the villages l ...
and Vinschgaubahn. Due to the steep slopes of the mountains, a number of funicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite e ...
s exist, such as the Gardena Ronda Express funicular and Mendel Funicular.
The Brenner Base Tunnel
The Brenner Base Tunnel (german: Brennerbasistunnel; it, Galleria di base del Brennero) is a railway tunnel under construction through the base of the Eastern Alps beneath the Brenner Pass. Upon completion, it will be the second or third longe ...
is under construction and scheduled to be completed by 2025. With a planned length of , this tunnel will increase freight train average speed to and reduce transit time by over an hour.
Larger cities used to have their own tramway system, such as the Meran Tramway
The Merano Tramway was built and opened in 1908 to satisfy the urban transport requirement in the town of Merano, at that time an important town in the Austrian monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the ...
and Bolzano Tramway. These were replaced after the Second World War with buses. Many other cities and municipalities have their own bus system or are connected with each other by it.
The Bolzano Airport
Bolzano Airport ( it, Aeroporto di Bolzano — Dolomiti, german: Flughafen Bozen — Dolomiten) is a small regional airport near Bolzano in the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy.
History
The airport was created in October 1926 with a 130 ...
is the only airport serving the region.
Demographics
Languages
 German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native
German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native Austro-Bavarian
Bavarian (german: Bairisch , Bavarian: ''Boarisch'') or alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a West Germanic language, part of the Upper German family, together with Alemannic and East Franconian.
Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million pe ...
dialects of the German language. Standard German plays a dominant role in education and media. All citizens have the right to use their own mother tongue, even at court. Schools are separated for each language group. All traffic signs are officially bi- or trilingual. Most Italian toponyms are translations performed by Italian nationalist Ettore Tolomei
Ettore Tolomei (16 August 1865, in Rovereto – 25 May 1952, in Rome) was an Italian nationalist and fascist. He was designated a Member of the Italian Senate in 1923, and ennobled as Conte della Vetta in 1937.
Pre-World War I activism
Born int ...
, the author of the ''Prontuario dei nomi locali dell'Alto Adige
The Prontuario dei nomi locali dell'Alto Adige (Italian for ''Reference Work of Place Names of Alto Adige'') is a list of Italianized toponyms for mostly German place names in South Tyrol (''Alto Adige'' in Italian) which was published in 1916 by ...
''.
To reach a fair allocation of jobs in public service a system called ethnic proportion ( it, proporzionale etnica, german: ethnischer Proporz) has been established. Every ten years, when the general census of population takes place, each citizen has to declare the linguistic group to which they belong or want to be aggregated to. According to the results they decide how many people of which group are going to be employed in public service.
At the time of the annexation of the southern part of Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
by Italy in 1919, the overwhelming majority of the population spoke German and identified with the Austrian or German nationality: in 1910, according to the last population census before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the German-speaking population numbered 224,000, the Ladin 9,000 and the Italian 7,000.
As a result of the Italianization of South Tyrol about 23% of the population are Italian-speakers (they were 33%, 138,000 of 414,000 inhabitants in the 1971 census) according to the census of 2011. 103 out of 116 comuni
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
have a majority of German native speakers — with Martell reaching 100% — eight have a Ladin-speaking majority, and five a majority of Italian speakers. The Italian-speaking population lives mainly around the provincial capital Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third la ...
, where they are the majority (73.8% of the inhabitants), and partially a result of Benito Mussolini's policy of Italianisation after he took power in 1922, when he encouraged immigration from the rest of Italy.
The other four comuni
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
where the Italian-speaking population is the majority are Laives, Salorno
Salorno sulla Strada del Vino (; german: Salurn ) is the southernmost '' comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about southwest of the city of Bolzano. It is one of only five mainly Italian-speaking municipalities in ...
, Bronzolo
Bronzolo (; german: Branzoll ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about south of the city of Bolzano. It is one of only five mainly Italian speaking municipalities in South Tyrol.
Geography
As of 30 November ...
and Vadena
Vadena (; german: Pfatten ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about southwest of the city of Bolzano. It is one of only five mainly Italian speaking municipalities in South Tyrol.
Geography
As of November 3 ...
. The eight comuni
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
with Ladin
Ladin may refer to:
* Ladin language, a language in northern Italy, often classified as a Rhaeto-Romance language
*Ladin people, the inhabitants of the Dolomite Alps region of northern Italy
See also
*Laden (disambiguation)
* Ladino (disambigua ...
majorities are: La Val
La Val ( it, La Valle ; german: Wengen ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northeast of the city of Bolzano.
Geography
As of 30 November 2010, it had a population of 1,307 and an area ...
, Badia, Corvara, Mareo
Mareo ( it, Marebbe ; german: Enneberg ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northeast of Bolzano.
Geography
As of 30 November 2010, it had a population of 2,911 and an area of .All demographics and ot ...
, San Martin de Tor
San Martin de Tor ( it, San Martino in Badia ; german: St. Martin in Thurn ) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northeast of the city of Bolzano.
Geography
As of 30 November 2010, it had a population ...
, Santa Cristina Gherdëina
Santa Cristina Gherdëina (; it, Santa Cristina Valgardena ; german: St. Christina in Gröden ) is a Ladin ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about east of the city of Bolzano. Its Saslong ski run is home of the ...
, Sëlva
Sëlva (; it, Selva di Val Gardena ; german: Wolkenstein in Gröden ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Val Gardena in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about east of the city of Bolzano. The Ladin place name derives from the Latin word ...
, Urtijëi
Urtijëi (; german: St. Ulrich in Gröden ; it, Ortisei ) is a town of 4,637 inhabitants in South Tyrol in northern Italy. It occupies the Val Gardena within the Dolomites, a mountain chain that is part of the Alps.
Geography
Urtijëi borders th ...
. Most of the immigrants from South Tyrol to the United States identify themselves as being of German rather than Austrian identity. According to the United States Census Bureau, in 2015, there were 365 individuals living in the U.S. born in Italy who identified themselves as being of Austrian ancestry. By contrast, in the same year, there were 1040 individuals living in the U.S. born in Italy who identified themselves as being of German ancestry.
The linguistic breakdown according to the census of 2011:
Religion
The majority of the population is Christian, mostly in the Catholic tradition. TheRoman Catholic Diocese of Bolzano-Brixen
The Diocese of Bolzano-Brixen (german: Diözese Bozen-Brixen, it, Diocesi di Bolzano-Bressanone, la, Dioecesis Bauzanensis-Brixinensis) is a Catholic diocese in northern Italy, with its seat in the city of Bolzano. Its territory corresponds wit ...
corresponds to the territory of the province of South Tyrol. Since July 27, 2011 the bishop of Bolzano-Brixen is Ivo Muser.
Catholic Church
 The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is archaeological evidence of early Christian sites in the area as early as Late Antiquity; Säben in the Eisack Valley became an important ecclesiastical center during this period, which was only replaced by Brixen as an episcopal see in the late
The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is archaeological evidence of early Christian sites in the area as early as Late Antiquity; Säben in the Eisack Valley became an important ecclesiastical center during this period, which was only replaced by Brixen as an episcopal see in the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. The territory of present-day South Tyrol was divided for centuries
A century is a period of 100 years. Centuries are numbered ordinally in English and many other languages. The word ''century'' comes from the Latin ''centum'', meaning ''one hundred''. ''Century'' is sometimes abbreviated as c.
A centennial or ...
between the dioceses of Brixen, Chur (until 1808/1816) and Trent (until 1964).
The most famous bishop of Brixen was the polymath Nicholas of Cusa. Important figures of the regional ecclesiastical life in the 19th century were the beatified bishop of Trent Johann Nepomuk von Tschiderer and the mystic Maria von Mörl.
In 1964, with reference to modern political boundaries, the Bishopric of Brixen, which had lost its extensive territories of North and East Tyrol after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, was enlarged to form the Diocese of Bolzano-Brixen, whose extension is now identical to that of the province of South Tyrol. Since then, the faithful have been led by Bishops Joseph Gargitter (1964-1986), Wilhelm Egger (1986-2008), Karl Golser (2008-2011) and Ivo Muser (since 2011). The diocese comprises 28 deaneries and 281 parishes (in 2014), 23 its episcopal churches are the Cathedral of Brixen
The Cathedral of Brixen (german: Brixner Dom, it, Duomo di Bressanone) is a cathedral in the city of Brixen, South Tyrol, Italy. It is dedicated to the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary and to Cassian of Imola. Since the foundation it has bee ...
and the Cathedral of Bolzano
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral ...
. Cassian and Vigilius are venerated as diocesan patrons. Important references in the current discourses of the local Catholic Church are St. Joseph Freinademetz and Blessed Joseph Mayr-Nusser.
Other communities
There is aLutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
community in Merano
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier ...
(founded 1861) and another one in Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third la ...
(founded 1889). Since the Middle Ages the Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
presence has been documented in South Tyrol. In 1901 the Synagogue of Merano was built. As of 2015, South Tyrol was home to about 14,000 Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
.
Culture
Traditions
South Tyrol has long-standing traditions, mainly inherited from its membership in the historical Tyrol. The Schützen associations are particularly fond of Tyrolean traditions. The Scheibenschlagen are the traditional "throwing of burning discs" on the first Sunday of Lent, the Herz-Jesu-Feuer are the "fires of the
The Scheibenschlagen are the traditional "throwing of burning discs" on the first Sunday of Lent, the Herz-Jesu-Feuer are the "fires of the Sacred Heart of Jesus
The Most Sacred Heart of Jesus ( la, Cor Jesu Sacratissimum) is one of the most widely practised and well-known Catholic devotions, wherein the heart of Jesus is viewed as a symbol of "God's boundless and passionate love for mankind". This dev ...
" that are lit on the third Sunday after Pentecost. The Krampus
Krampus is a horned, anthropomorphic figure in the Central and Eastern Alpine folklore of Europe who, during the Advent season, scares children who have misbehaved. Assisting Saint Nicholas, or Santa Claus, the pair visit children on the nigh ...
are disguised demons who accompany St Nicholas.
There are also several legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived, both by teller and listeners, to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess ...
s and sagas linked to the peoples of the Dolomites; among the best known are the legend of King Laurin The South Tyrolean saga of King Laurin (German: ''König Laurin'', Ladin: ''Re Laurin'', Italian: ''Re Laurino'') is part of a popular tradition in the Dolomites. It is a popular explanation of the optical phenomenon of Alpenglow (Ladin: ''Enrosadi ...
and that of the Kingdom of Fanes
The Kingdom of Fanes ( lld, Rëgn de Fanes) is the national epic of the Ladin people in the Dolomites and the most important part of the Ladin literature. Originally an epic cycle, today it is known through the work of Karl Felix Wolff in 1932 ...
, which belongs to the Ladin
Ladin may refer to:
* Ladin language, a language in northern Italy, often classified as a Rhaeto-Romance language
*Ladin people, the inhabitants of the Dolomite Alps region of northern Italy
See also
*Laden (disambiguation)
* Ladino (disambigua ...
mythological heritage.
Alpine Transhumance
Alpine transhumance is transhumance as practiced in the Alps, that is, a seasonal droving of grazing livestock between the valleys in winter and the high mountain pastures in summer (German ' from the term for "seasonal mountain pasture", '). T ...
(from German "''Almabtrieb''"), is a farm practice: every year, between September and October, the livestock that stayed on the high pastures is brought back to the valley, with traditional music and dances. Especially, the transhumance between the Ötztal
The Ötztal is an alpine valley located in Tyrol, Austria. The Ötztaler Ache river flows through the valley in a northern direction. The Ötztal separates the Stubai Alps in the east from the Ötztal Alps in the west. The valley is long. The no ...
(in Austria) and Schnals Valley and Passeier Valley
The Passeier Valley (german: Passeier or ; it, Passiria or Val Passiria ) is the valley of the Passer river, in the mountains of South Tyrol, northern Italy. The Passer river is a left-bank tributary to the Adige. At the mouth of the valley, whe ...
was recognised by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
as universal intangible heritage in 2019.
Education
Architecture
 The region features a large number of castles and churches. Many of the castles and
The region features a large number of castles and churches. Many of the castles and Ansitz
An ''Ansitz'' is a small residence designed for the lower nobility of the Germanic Alpine region.
History
The concept of ''Ansitz'' dates back to the end of the Middle Ages up to the 19th century. Unlike castles, they were hardly fortified. T ...
e were built by the local nobility and the Habsburg rulers. See List of castles in South Tyrol
{{unreferenced, date=November 2011
This is a list of castles in South Tyrol in Italy.
# Castle Aichberg, Eppan an der Weinstraße
# Altenburg bei St. Pauls, Eppan an der Weinstraße
# Annaberg, Goldrain
# Castle Auer, Tirol
# Castleruine B ...
.
Museums
Among the major museums of South Tyrol are: * theSouth Tyrol Museum of Archaeology
South Tyrol Museum of Archaeology (german: Südtiroler Archäologiemuseum; it, Museo archeologico dell'Alto Adige) is an archaeological museum in the city of Bolzano, South Tyrol, Italy. It is the home of the preserved body of Ötzi the Iceman.
...
, which has the mummy of Ötzi the Iceman
Ötzi, also called the Iceman, is the natural mummy of a man who lived some time between 3350 and 3105 BC, discovered in September 1991 in the Ötztal Alps (hence the nickname "Ötzi") on the border between Austria and Italy.
Ötzi is believed to ...
* the Museion
The Musaeum or Mouseion of Alexandria ( grc, Μουσεῖον τῆς Ἀλεξανδρείας; ), which arguably included the Great Library of Alexandria, was an institution said to have been founded by Ptolemy I Soter and his son Ptolemy II ...
, Museum of modern and contemporary art of Bolzano
* the Messner Mountain Museum
The Messner Mountain Museum (MMM) is a museum project created in 2006 by Italian mountaineer and extreme climber Reinhold Messner in South Tyrol in northern Italy. Messner's museum project is designed to educate visitors on "man's encounter with m ...
of Reinhold Messner
Reinhold Andreas Messner (; born 17 September 1944) is an Italian mountaineer, explorer, and author from South Tyrol. He made the first solo ascent of Mount Everest and, along with Peter Habeler, the first ascent of Everest without supplemental ...
* the White Tower (Brixen)
The "White Tower" (in German ''Weißer Turm'' ) is located in Brixen (; it, Bressanone ; lld, Porsenù or ), a small town in South Tyrol, Italy. It dates back to the 15th century.
The Gothic architecture tower stands 72m tall and the cathedral ...
museum
Media
German-language TV channels in South Tyrol: * RAS *Rai Südtirol Rai Südtirol is a German-language radio and television service provided by the Italian public-service broadcaster RAI to South Tyrol from its studios in Bozen.
Services
* Rai Südtirol (TV channel)
Rai Südtirol ( ''Rai South Tyrol'') is an ...
* Südtirol Digital Fernsehen
Südtirol Digital Fernsehen (SDF) is an Italian private television channel based in Bolzano (german: Bozen), in the autonomous province of South Tyrol ( it, Alto Adige, german: Südtirol). It is the province's only private channel broadcast in Germ ...
* Südtirol Heute
Music
TheBozner Bergsteigerlied
The Bozner Bergsteigerlied ( en, Bozen mountaineer song) is one of the two unofficial hymns of the South Tyroleans, the other being the '' Andreas-Hofer-Lied''. Its lyrics were composed in 1926 by Karl Felderer in Moos am Ritten to the melody o ...
and the Andreas-Hofer-Lied are considered to be the unofficial anthems of South Tyrol.Rainer Seberich (1979). "Singen unter dem Faschismus: Ein Untersuchungsbericht zur politischen und kulturellen Bedeutung der Volksliedpflege". ''Der Schlern
''Der Schlern'' (full German title: ''Der Schlern – Zeitschrift für Südtiroler Landeskunde''; en, The Schlern – Magazine for South Tyrolean Regional Studies) is a German-language monthly for the study of science, research, art and culture r ...
'', 50,4, 1976, pp. 209–218, here p. 212.
The folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has b ...
al group Kastelruther Spatzen
The Kastelruther Spatzen (German for Kastelruth sparrows) are a musical group from South Tyrol, northern Italy, who have won many honours and awards for their schlager in folk music style.
Members
The Kastelruther Spatzen were formed in 1976 by ...
from Kastelruth
Kastelruth (; it, Castelrotto ; Ladin: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, about northeast of the city of Bolzano.
Geography
As of 30 November 2010, it had a population of 6,456 and an area of .All demographics an ...
and the rock band Frei.Wild
Frei.Wild (pronounced FRY-vilt, the word ''Frei'' translates to "free" and the word ''Wild'' translates to "wild") is a German rock band from Brixen, South Tyrol, Italy. Its members belong to the German-speaking population of South Tyrol and the ...
from Brixen
Brixen (, ; it, Bressanone ; lld, Porsenù or ) is a town in South Tyrol, northern Italy, located about north of Bolzano.
Geography
First mentioned in 901, Brixen is the third largest city and oldest town in the province, and the artistic an ...
have received high recognition in the German-speaking part of the world.
Award-winning electronic music
Electronic music is a genre of music that employs electronic musical instruments, digital instruments, or circuitry-based music technology in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means ( electroa ...
producer Giorgio Moroder was born and raised in South Tyrol in a mixed Italian, German and Ladin-speaking environment.
Sports
South Tyroleans have been successful atwinter sports
Winter sports or winter activities are competitive sports or non-competitive recreational activities which are played on snow or ice. Most are variations of skiing, ice skating and sledding. Traditionally, such games were only played in cold are ...
and they regularly form a large part of Italy's contingent at the Winter Olympics
The Winter Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'hiver) is a major international multi-sport event held once every four years for sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympic Games, the 1924 Winter Olympics, were h ...
. Famed mountain climber Reinhold Messner
Reinhold Andreas Messner (; born 17 September 1944) is an Italian mountaineer, explorer, and author from South Tyrol. He made the first solo ascent of Mount Everest and, along with Peter Habeler, the first ascent of Everest without supplemental ...
, the first climber to climb Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetic languages, Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is List of highest mountains on Earth, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border ru ...
without the use of oxygen tanks
An oxygen tank is an oxygen storage vessel, which is either held under pressure in gas cylinders, or as liquid oxygen in a cryogenic storage tank.
Uses
Oxygen tanks are used to store gas for:
* medical breathing at medical facilities and at home ...
, was born and raised in the region. Other successful South Tyroleans include luger Armin Zöggeler
Armin Zöggeler OMRI (born 4 January 1974) is a retired Italian luger and double Olympic champion. He is one of the most successful men in the sport, nicknamed ''Il Cannibale'' ("The Cannibal"), for his notable series of victories, or ''The Iceb ...
, figure skater Carolina Kostner
Carolina Kostner (born 8 February 1987) is an Italian figure skater. She is the 2014 Olympic bronze medalist, the 2012 World champion, a five-time European champion (2007–2008, 2010, 2012–2013), and the 2011 Grand Prix Final champion. She ...
, skier Isolde Kostner
Isolde Kostner (born 20 March 1975) is an Italian former Alpine skier who won two bronze medals at the 1994 Winter Olympics and a silver medal at the 2002 Winter Olympics. She was the Italian flag bearer at the opening ceremony of the 2002 Olym ...
, luge and bobsleigh
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Feder ...
medallist Gerda Weissensteiner
Gerda Weissensteiner OMRI (born 3 January 1969) is an Italian luger and bobsleigh pilot who competed from the late 1980s to 2006. Competing in six Winter Olympics, she won the gold medal in the women's singles luge event at the 1994 Winter Olym ...
, tennis players Andreas Seppi
Andreas Seppi (born 21 February 1984) is an Italian former professional tennis player.
He reached a career-high singles ranking of world No. 18 on 28 January 2013. He became the first Italian to win a title on all three surfaces.
Tennis ca ...
and Jannik Sinner
Jannik Sinner (; ; born 16 August 2001) is an Italian professional tennis player. He has been ranked as high as world No. 9 by the Association of Tennis Professionals (ATP), achieved on 1 November 2021, and world No. 124 in doubles, achieved on 2 ...
, and team principal of Haas F1 Team in the FIA Formula One World Championship Guenther Steiner
Guenther Steiner (born 7 April 1965) is a motorsport engineer and team manager who holds dual Italian and American citizenship. He is the current team principal of the Haas Formula One Team (since 2014), and the previous managing director of Ja ...
.
HC Interspar Bolzano-Bozen Foxes are one of Italy's most successful ice hockey teams, while the most important football club in South Tyrol is F.C. Südtirol
Fußball Club Südtirol is an Italian association football club, based in the city of Bolzano, in the autonomous province South Tyrol. The club was formerly known as its bilingual name F.C. Südtirol – Alto Adige. They will play in Serie B f ...
, which won its first-ever promotion to Serie B
The Serie B (), currently named Serie BKT for sponsorship reasons, is the second-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie A. It has been operating for over ninety years since the 1929–30 season. It had been ...
in 2022.
The province is famous worldwide for its mountain climbing opportunities, while in winter it is home to a number of popular ski resorts including Val Gardena
Val Gardena (; german: Gröden ; lld, Gherdëina ) is a valley in Northern Italy, in the Dolomites of South Tyrol. It is best known as a tourist skiing, rock climbing, and woodcarving area.
Geography
The valley's main river is the Derjon, a ...
, Alta Badia and Seiser Alm.
See also
*History of South Tyrol
Modern-day South Tyrol, an autonomous Italian province created in 1948, was part of the Austro-Hungarian County of Tyrol until 1918 (then known as ''Deutschsüdtirol'' and occasionally ''Mitteltirol''). It was annexed by Italy following the def ...
* Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
* Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion
The Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion (german: Europaregion Tirol–Südtirol–Trentino; it, Euregio Tirolo–Alto Adige–Trentino) is a Euroregion formed by three different regional authorities in Austria and Italy: the Aust ...
References
Bibliography
* Gottfried Solderer (ed) (1999–2004). ''Das 20. Jahrhundert in Südtirol''. 6 Vol., Bozen: Raetia Verlag. * Antony E. Alcock (2003). ''The History of the South Tyrol Question''. London: Michael Joseph. 535 pp. *Rolf Steininger
Rolf Steininger (August 2, 1942, Plettenberg) is a German historian and former university professor for contemporary history.
Steininger studied English language and literature and history at the universities of Marburg, Göttingen, Munich, Lanc ...
(2003). ''South Tyrol: A Minority Conflict of the Twentieth Century''. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers.
* Georg Grote (2012). ''The South Tyrol Question 1866–2010. From National Rage to Regional State''. Oxford: Peter Lang.
* Georg Grote, Hannes Obermair (2017). ''A Land on the Threshold. South Tyrolean Transformations, 1915–2015.'' Oxford/Bern/New York: Peter Lang.
External links
Official website for the ''Civic Network of South Tyrol'', the Autonomous Province of Bolzano/Bozen
Special Statute for ''Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol''
Tourist information about South Tyrol
The most accurate digital map of South Tyrol
{{Authority control Regions of Europe with multiple official languages Autonomous provinces German-speaking countries and territories Provinces of Italy * Articles containing video clips