|
Urological
Urology (from Greek οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and ''-logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary-tract system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs (testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis). The urinary and reproductive tracts are closely linked, and disorders of one often affect the other. Thus a major spectrum of the conditions managed in urology exists under the domain of genitourinary disorders. Urology combines the management of medical (i.e., non-surgical) conditions, such as urinary-tract infections and benign prostatic hyperplasia, with the management of surgical conditions such as bladder or prostate cancer, kidney stones, congenital abnormalities, traumatic injury, and stress incontinence. Urological t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TURP
Transurethral resection of the prostate (commonly known as a TURP, plural TURPs, and rarely as a transurethral prostatic resection, TUPR) is a urology, urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, it is performed by visualising the prostate through the urethra and removing tissue by electrocautery or sharp dissection. It has been the standard treatment for BPH for many years, but recently alternative, minimally invasive techniques have become available. This procedure is done with spinal or general anaesthetic. A triple lumen catheter is inserted through the urethra to irrigate and drain the bladder after the surgical procedure is complete. Outcome is considered excellent for 80–90% of BPH patients. The procedure carries minimal risk for erectile dysfunction, moderate risk for bleeding, and a large risk for retrograde ejaculation. Indications BPH is normally initially treated medically. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
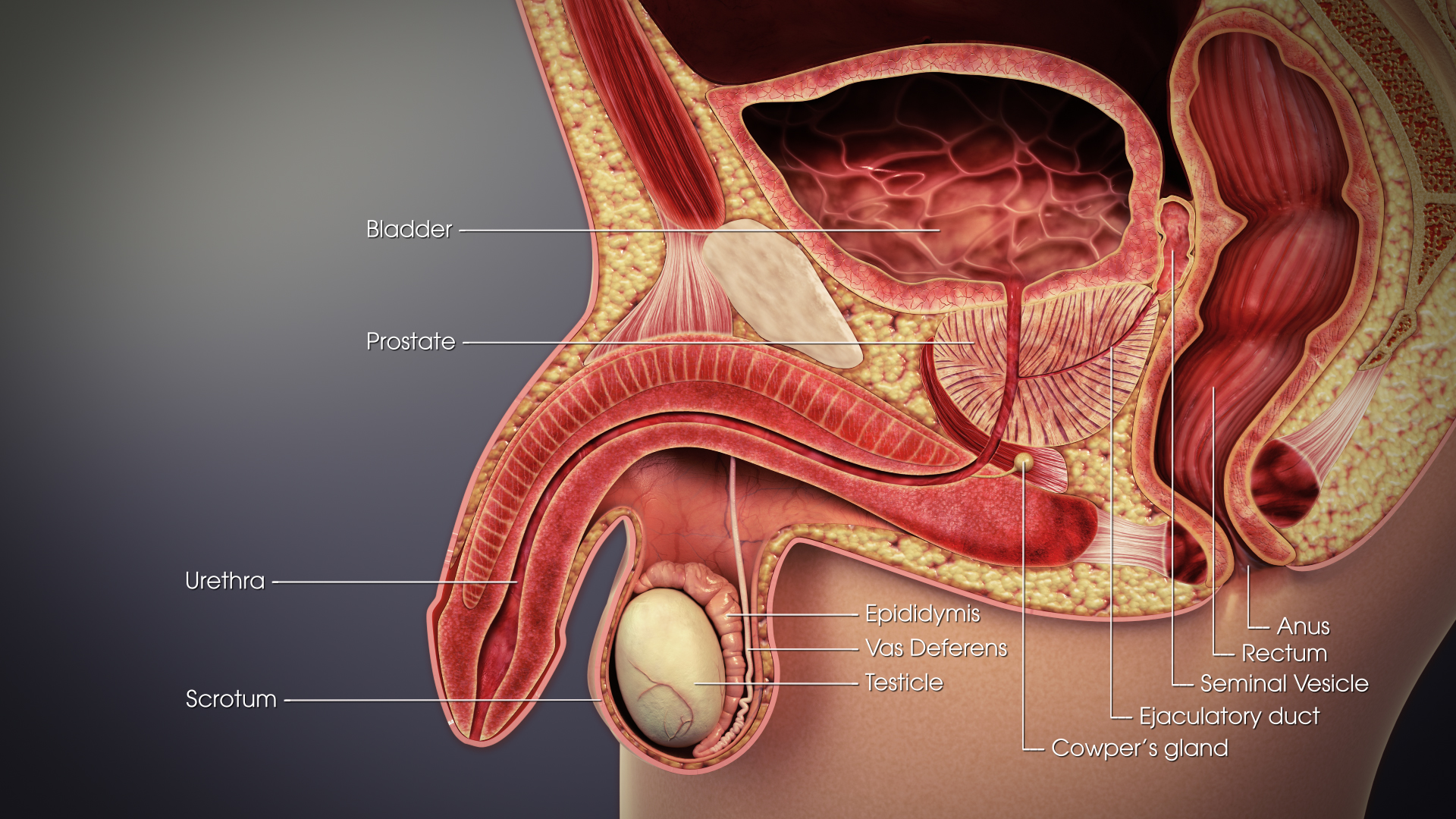
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that surrounds the urethra just below the bladder. It is located in the hypogastric region of the abdomen. To give an idea of where it is located, the bladder is superior to the prostate gland as shown in the image The rectum is posterior in perspective to the prostate gland and the ischial tuberosity of the pelvic bone is inferior. Only those who have male reproductive organs are able to get prostate cancer. Most prostate cancers are slow growing. Cancerous cells may spread to other areas of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes. It may initially cause no symptoms. In later stages, symptoms include pain or difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or pain in the pelvis or back. Benign prostatic hyperplasia may produce similar symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymis
The epididymis (; plural: epididymides or ) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, in length. It serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Anatomy The epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head ( la, caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinium of the testis at the superior pole of the testis. The head is characterized histologically by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia (described below) and a little smooth muscle. It is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentrated. The concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes (in the form of urine) exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination (voiding). The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra. Urine is formed in the kidneys through a filtrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel"; the plural version is ''vasa deferentia''. ''Ductus deferens'' is also Latin, meaning "carrying-away duct"; the plural version is ''ducti deferentes''. Structure There are two vasa deferentia, connecting the left and right epididymis with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct in order to move sperm. The (human) vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. The vas deferens is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis. The vas deferens exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitourinary Disorders
The genitourinary system, or urogenital system, are the organs of the reproductive system and the urinary system. These are grouped together because of their proximity to each other, their common embryological origin and the use of common pathways, like the male urethra. Also, because of their proximity, the systems are sometimes imaged together. The term "apparatus urogenitalis" was used in ''Nomina Anatomica'' (under Splanchnologia) but is not used in the current ''Terminologia Anatomica''. Development The urinary and reproductive organs are developed from the intermediate mesoderm. The permanent organs of the adult are preceded by a set of structures that are purely embryonic and that, with the exception of the ducts, disappear almost entirely before the end of fetal life. These embryonic structures are on either side: the pronephros, the mesonephros and the metanephros of the kidney, and the Wolffian and Müllerian ducts of the sex organ. The pronephros disappears very ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)