|
Uranium Mining In The United States
Uranium mining in the United States produced of U3O8 in 2023, 15% of the 2018 production of of U3O8. The 2023 production represents 0.4% of the uranium fuel requirements of the US's nuclear power reactors for the year. Production came from five In situ leach, in-situ leaching plants, four in Wyoming (Nichols Ranch ISR Project, Lance Project, Lost Creek Project, and Smith Ranch-Highland Operation) and one in Nebraska (Crowe Butte Operation); and from the White Mesa conventional mill in Utah. From 1949 to 2019, total US production of uranium oxide (U3O8) was 979.9 million pounds (444,500 tonnes). History While uranium is used primarily for nuclear power, uranium mining had its roots in the production of radium-bearing ore from 1898 from the mining of uranium-vanadium sandstone deposits in western Colorado. The 1950s saw a boom in uranium mining in the western U.S., spurred by the fortunes made by prospectors such as Charlie Steen. The United States was the world's leading prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
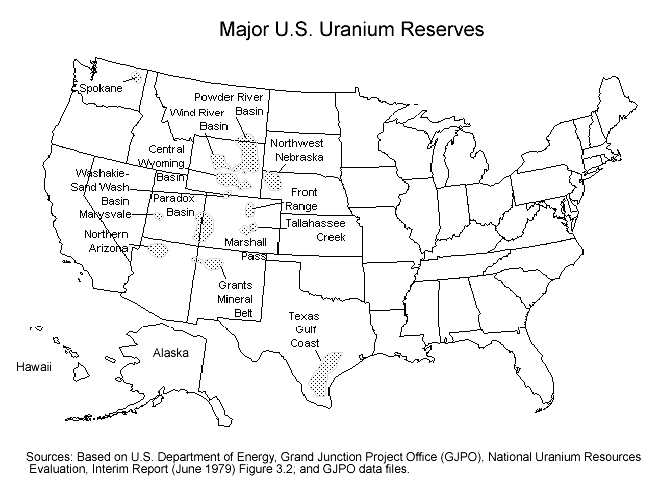
Map Of US Uranium Reserves
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the south. With an estimated population of 587,618 as of 2024, Wyoming is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, least populous state despite being the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 10th largest by area, and it has the List of U.S. states by population density, second-lowest population density after Alaska. The List of capitals in the United States, state capital and List of municipalities in Wyoming, most populous city is Cheyenne, Wyoming, Cheyenne, which had a population of 65,132 in 2020. Wyoming's western half consists mostly of the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains; its eastern half consists of high-elevation prairie, and is referred to as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives, and an Upper house, upper body, the United States Senate, U.S. Senate. They both meet in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. Members of Congress are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a Governor (United States), governor's appointment. Congress has a total of 535 voting members, a figure which includes 100 United States senators, senators and 435 List of current members of the United States House of Representatives, representatives; the House of Representatives has 6 additional Non-voting members of the United States House of Representatives, non-voting members. The vice president of the United States, as President of the Senate, has a vote in the Senate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radon
Radon is a chemical element; it has symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon isotopes, only Rn has a sufficiently long half-life (3.825 days) for it to be released from the soil and rock where it is generated. Radon isotopes are the immediate decay products of radium isotopes. The instability of Rn, its most stable isotope, makes radon one of the rarest elements. Radon will be present on Earth for several billion more years despite its short half-life, because it is constantly being produced as a step in the decay chains of U and Th, both of which are abundant radioactive nuclides with half-lives of at least several billion years. The decay of radon produces many other short-lived nuclides, known as "radon daughters", ending at stable isotopes of lead. Rn occurs in significant quantities as a step in the normal radioactive decay chain of U, also known as the uranium series, which slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to the China–Kazakhstan border, east, Kyrgyzstan to the Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, southeast, Uzbekistan to the Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, south, and Turkmenistan to the Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, while the largest city and leading cultural and commercial hub is Almaty. Kazakhstan is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, ninth-largest country by land area and the largest landlocked country. Steppe, Hilly plateaus and plains account for nearly half its vast territory, with Upland and lowland, lowlands composing another third; its southern and eastern frontiers are composed of low mountainous regions. Kazakhstan has a population of 20 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Resource Classification
There are several classification systems for the economic evaluation of mineral deposits worldwide. The most commonly used schemes base on the International Reporting Template, developed by the CRIRSCO – Committee for Mineral Reserves International Reporting Standards, like the Australian Joint Ore Reserves Committee – JORC Code 2012, the Pan-European Reserves & Resources Reporting Committee' – PERC Reporting Standard from 2021, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum – CIM classification and the South African Code for the Reporting of Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (SAMREC). A more detailed description of the historical development concerning reporting about mineral deposits can be found on the PERC web site. In 1997, the United Nations Framework Classification for Resources (UNFC) was development by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). The Pan African Resource Reporting Code (PARC) is based on UNFC. Mineral resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEU Purchase Agreement
HEU may refer to: * Harbin Engineering University, in Harbin, China * Highly enriched uranium Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (23 ..., uranium that is 20% or more U235 * Hospital Employees' Union, trade union in British Columbia, Canada {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound (mass)
The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in both the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. Various definitions have been used; the most common today is the international avoirdupois pound, which is legally defined as exactly , and which is divided into 16 avoirdupois ounces. The international standard symbol for the avoirdupois pound is lb; an alternative symbol (when there might otherwise be a risk of confusion with the pound-force) is lbm (for most pound definitions), # ( chiefly in the U.S.), and or ̶ (specifically for the apothecaries' pound). The unit is descended from the Roman (hence the symbol ''lb'', descended from the scribal abbreviation, '). The English word ''pound'' comes from the Roman ('the weight measured in '), and is cognate with, among others, German , Dutch , and Swedish . These units are now designated as historical and are no longer in common usage, being replaced by the metric system. Usage of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spot Price
In finance, a spot contract, spot transaction, or simply spot, is a contract of buying or selling a commodity, security or currency for immediate settlement (payment and delivery) on the spot date, which is normally two business days after the trade date. The settlement price (or rate) is called spot price (or spot rate). A spot contract is in contrast with a forward contract or futures contract where contract terms are agreed now but delivery and payment will occur at a future date. Spot prices and future price expectations Depending on the item being traded, spot prices can indicate market expectations of future price movements in different ways. For a security or non-perishable commodity (e.g. silver), the spot price reflects market expectations of future price movements. In theory, the difference in spot and forward prices should be equal to the finance charges, plus any earnings due to the holder of the security, according to the cost of carry model. For example, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and its interaction with the economy and the environment. EIA programs cover data on coal, petroleum, natural gas, electric, renewable and nuclear energy. EIA is part of the U.S. Department of Energy. Background The Department of Energy Organization Act of 1977 established EIA as the primary federal government authority on energy statistics and analysis, building upon systems and organizations first established in 1974 following the oil market disruption of 1973. EIA conducts a comprehensive data collection program that covers the full spectrum of energy sources, end uses, and energy flows; generates short- and long-term domestic and international energy projections; and performs informative energy analyses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |