|
Upper Weser Valley
The Upper Weser Valley (german: Oberes Wesertal) in central Germany has been formed by the Upper Weser river cutting through the Weser Uplands for around between the towns of Hann. Münden and Minden. It lies in the German federal states of Lower Saxony, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia. Course The Upper Weser Valley begins near Hann. Münden, where the rivers Werra and Fulda join to form the Weser and follows the course of the Upper Weser northwards through the Weser Uplands to Bodenwerder, then continues in a northwestern direction, south of the Süntel hills and the Weser Hills, and ends finally at the great gap of Porta Westfalica, where the Weser breaks through the Wiehen and Weser Hills out into the North German Plain. In the south the Upper Weser Valley crosses the Solling-Vogler Nature Park and, in the north, the Weser Uplands Schaumburg-Hamelin Nature Park. At its northern end, the Upper Weser Valley is followed by the Middle Weser Valley, part of the Middle Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Weser Valley With The Grohnde Nuclear Power Plant
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage ''The Upper Footage'' (also known as ''Upper'') is a 2013 found footage film written and directed by Justin Cole. First released on January 31, 2013 to a limited run of midnight theatrical screenings at Landmark’s Sunshine Cinema in New York Cit ...'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North German Plain
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland (german: Norddeutsches Tiefland) is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands (''die Mittelgebirge'') to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east. In the west, the southern boundary of the North German Plain is formed by the Lower Saxon Hills: specifically the ridge of the Teutoburg Forest, the Wiehen Hills, the Weser Hills and the Lower Saxon Börde, which partly separate it from that area of the Plain known as the Westphalian Lowland. Elements of the Rhenish Massif also act a part of the southern boundary of the plain: the Eifel, Bergisches Land and the Sauerland. In the east the North German Plain spreads out beyond the Harz Mountains and Kyffhäuser further to the south as far as the Central Saxon hill country and the foothills of the Ore M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
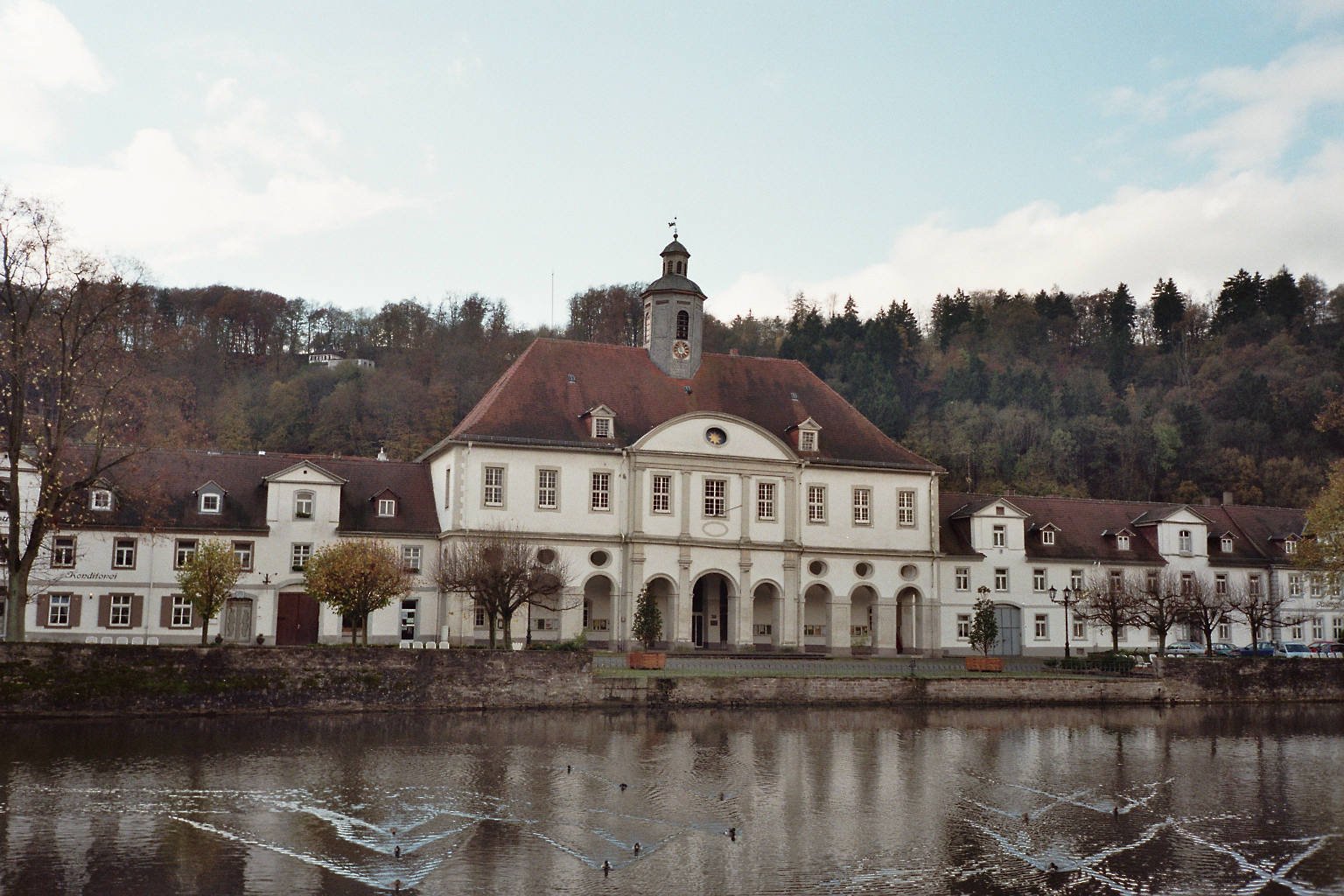
Bad Karlshafen
Bad Karlshafen () is a baroque, thermal salt spa town in the district of Kassel, in Hesse, Germany. It has 2300 inhabitants in the main ward of Bad Karlshafen, and a further 1900 in the medieval village of Helmarshausen. It is situated at the confluence of the Diemel and Weser rivers, 15 km south of Höxter, and 37 km north of Kassel. History The town was founded in 1699 by French Huguenots fleeing persecution in France. Though initially named Sieburg, the town was later named after Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, who granted them refuge. ThGerman Huguenot Museumlocated here contains a picture archive, library, and family histories of the Huguenots in Germany. Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, had ambitious plans for town-planning and developing new water trade channels in the region; including a 'haven' in Karlshafen. Together with his engineer and architect Friedrich Conradi he developed plans for a Landgrave-Carl-Canal in order to avoid customs duty at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogler (mountain Range)
The Vogler is a range of hills, up to 460.4 m high, in the Weser Uplands in southern Lower Saxony (Germany). Together with the Solling, the Vogler forms the Solling-Vogler Nature Park which lies a couple of kilometres further south. Geography The Vogler is located in the district of Holzminden between the hills of the Ith to the north, the Hils to the northeast, the Homburg Forest to the east, the Amtsberge to the southeast, the Solling to the south and the Burgberg to the south-southwest. It also lies in the triangle formed by the towns of Bevern, Bodenwerder and Eschershausen. The River Weser flows by the Vogler to the west heading north to the North Sea. To the north the Lenne, a western tributary of the Weser runs past in a northwesterly direction. The Vogler drops steeply to the Weser through a height of 220 m. Nestling in its northern foothills is the village of Heinrichshagen, where Henry the Fowler was supposed to have trapped birds. Geology The unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgberg (ridge)
The Burgberg (also called the Burgberge) is a ridge of hills up to high in the German federal state of Lower Saxony. Geography The Burgberg, which belongs to the Solling-Vogler Nature Park, is located in the district of Holzminden in the Weser Uplands between the hill ranges of the Vogler to the north, the Homburgwald to the northeast, and the Solling to the south. It lies between the towns of Bevern in the southwest and Golmbach and Stadtoldendorf in the east. To the west flows the River Weser. A section of the B 64 federal road runs along the southern part of the Burgberg, linking Holzminden with Negenborn. Sights The ruined walls of the former castle of Everstein may be seen on the twin peaks of the Großer (Higher) Everstein () and Kleiner (Lower) Everstein. Since 1116, the noble lords and Counts of Everstein (also Eberstein) have been named after their castles on the Großer and Kleiner Everstein on the Burgberg. As followers and relatives of the Imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solling
The Solling () is a range of hills up to high in the Weser Uplands in the German state of Lower Saxony, whose extreme southerly foothills extend into Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia. Inside Lower Saxony it is the second largest range of hills and the third highest after the Harz (Wurmberg; 971 m) and the Kaufungen Forest ( Haferberg; 581 m). The Solling is a cultural landscape consisting mainly of spruce and beech forests. Oak also grows in some areas. The Solling forest is home of a number of animals and birds, for example red deer or chaffinch. They can best be observed in the ''Neuhaus wildlife park''. Together with the smaller and lower Vogler range and the little Burgberg to the north, the Solling is part of the Solling-Vogler Nature Park. Hills The main hills in the Solling include the following (heights given in m above Normalnull): * Große Blöße (527.8 m) * Großer Ahrensberg (524.9 m) * Moosberg (513.0 m) – with Hochsolling observation tower * Vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bramwald
The Bramwald is a range of hills up to in the Weser Uplands in Lower Saxony (Germany). It is a unique, natural, wild, hill and forest landscape. This is particularly so in the north around the Totenberg. Geography The Bramwald in the northwest of the Münden Nature Park lies in South Lower Saxony some 20 km (as the crow flies) west of Göttingen and 5 km north of the town of Hann. Münden. It lies east of the upper, southern course of the Weser, whose western banks are dominated by the vast Reinhardswald forest in North Hesse. North of the Bramwald are the Kiffing hills, which lie south of the Schwülme valley and north of the Bramwald's north-northwestern foothills. The long ridge of the Bramwald is part of the state forest of Bramwald and is bordered in the north by the state forest of Bad Karlshafen and in the south by the Hann. Münden state forest. Its highest hill is the Totenberg (408 m), which lies in the north of the forested region and is surround ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lippe Uplands
The Lippe Uplands (german: Lipper Bergland, , or ''Lippisches Bergland'') is a range of hills in Ostwestfalen-Lippe within the administrative district of Detmold in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Geography The Lippe Uplands are part of the Weser Uplands and are delineated by the river Werre in the west and the Weser in the north and east. To the south the Lippe Uplands merge into the Egge Hills and the Oberwälder Land. The landscape has sharp variations in relief: rounded peaks (''Kuppen'') alternate with steep ridges, and flat depressions with hills dissected by valleys. Three larger rivers - the Weser, Werre and Bega, cut deeply into the terrain, the Lippe Uplands dropping away down into their valleys. The highest elevation is the Köterberg at . Flora and fauna The woods are dominated by stands of beech and oak. The agricultural land is almost exclusively used for arable farming. Rare and protected animals and plants are found along the partly, almost natural r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrmont Uplands
The Pyrmont Uplands (german: Pyrmonter Bergland) are a muschelkalk region within the Lower Saxon Hills and covers an area of 180 km2. Their maximum elevation is about 350 metres above sea level (NN). The valley of the Emmer divides the uplands into the Ottenstein Plateau in the east and Pyrmont Heights (''Pyrmonter Höhen'') in the west. In these muschelkalk hills lies the Pyrmont Basin (''Pyrmonter Talkessel'') on the fault lines of which mineral and brine springs rise, and to which the town of Bad Pyrmont owes its status as a spa town. The Ottenstein Plateau is used for agriculture. On the hill of ''Pyrmonter Berg'' is the only large area of deciduous forest. In spite of its poor soils, agriculture dominates: grasslands follow the rivers in the valleys. Forestry is carried out on the Pyrmont Heights. The valley of the Emmer stream has been declared as a Special Area of Conservation; part of it also has nature reserve A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhardswald
The Reinhardswald () is a range of hills up to and covering an area of over 200 km² in the in the district of , (). Of this, 183 km² are part of the known as ''Gutsbezirk Reinhard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland (geography)
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is usually reserved for ranges of low mountains. However, the two terms are sometimes interchangeable. Highlands internationally Probably the best-known area officially or unofficially referred to as ''highlands'' in the Anglosphere is the Scottish Highlands in northern Scotland, the mountainous region north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault. The Highland council area is a local government area in the Scottish Highlands and Britain's largest local government area. Other highland or upland areas reaching 400-500 m or higher in the United Kingdom include the Southern Uplands in Scotland, the Pennines, North York Moors, Dartmoor and Exmoor in England, and the Cambrian Mountains in Wales. Many countries and regions also have areas referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Weser Region
The Middle Weser Region (german: Mittelweserregion) includes, in its fullest sense, the land along the Middle Weser between Minden and Bremen. It lies within the federal states of North Rhine-Westphalia, Lower Saxony and Bremen. However, the term is often used just to refer to the Lower Saxon part, because of the different political development of the three states and the cooperative associations formed in Lower Saxony some years ago (see below). The Lower Saxon part of the Middle Weser Region forms the geographical heart of this state. In the centre of the Middle Weser Region are the towns of Minden, Nienburg/Weser and Verden (Aller). In the extreme north, the city of Bremen, which is not part of Lower Saxony, has a very important influence on that area of Lower Saxony surrounding it. ''For information about the Westphalian part of the Middle Weser Region see also Ostwestfalen-Lippe and Minden Land'' Landscape The Middle Weser Region is part of the North German Plain. On either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |