|
Upagraha (astrology)
In Jyoti·π£a or Indian astrology, the term UpagrƒÅha (Sanskrit: ý§âý§™ý§óý•çý§∞ý§π) refers to the so-called "shadow planets" (Sanskrit: ý§õý§æý§Øý§æý§óý•çý§∞ý§æý§π, ''chƒÅyƒÅgrƒÅha'') that are actually mathematical points, that are used for astrological evaluation. UpagrƒÅha is a generic term used for two distinct and different calculations. One type of UpagrƒÅha called AprakƒÅ≈õa (ý§Öý§™ý•çý§∞ý§ïý§æý§∂) is calculated from the degree of the Sun. Another type is more generally called UpagrƒÅha or KƒÅlavelƒÅ (ý§ïý§æý§≤ý§µý•áý§≤ý§æ) is calculated by dividing duration of diurnal sky (from sunrise to sunset) or the duration of the nocturnal sky (from sunset to sunrise) into eight parts. The classic writers like ParƒÅ≈õara, VarƒÅhamihira and later writers like Vankatesa ≈öarma, author of Sarvartha Chintamani, all classify the UpagrƒÅhas in various ways. Overview The Vedic astrology is primarily based on the calculation of mathematical points. For instance, the ''Yoga'', also referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Astrology
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is rooted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daridra Yogas (Hindu Astrology)
Daridra yogas or ''Nirdhanta yogas'' along with Kemadruma yoga and Shakat yoga, are certain exceptional ava-yogas or unfavourable planetary combinations that indicate poverty. The word, Daridra (Sanskrit: ý§¶ý§∞ý§øý§¶ý•çý§∞) means poor, needy or deprived, and the word, Nirdhanta (Sanskrit: ý§®ý§øý§∞ý•çý§ßý§®ý§§ý§æ) means poverty, poorness or indigence. Overview Ava-yogas, indicating poverty, basically involve an affliction to the 2nd house or bhava and/or its lord, and to Jupiter and the lord of the 11th. Kemadruma yoga is also caused when the Moon is in the 2nd or in the 12th house, and no planet occupies the bhavas either sides of the Moon. The Shakat yoga is caused when Jupiter occupies the 6th or the 8th house from the Moon. In both events, there will be lack of wealth and much difficulty in making a living or gaining in prosperity. The good and bad effects of Daridra yogas are felt during the adverse dashas or planetary periods of the afflicted lords of wealth and gains, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navagraha
Navagraha are nine heavenly bodies and deities that influence human life on Earth according to Hinduism and Hindu astrology. The term is derived from ''nava'' ( sa, ý§®ý§µ "nine") and ''graha'' ( sa, ý§óý•çý§∞ý§π "planet, seizing, laying hold of, holding"). Note that the Earth, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto are excluded from the Navagraha,. However, the Sun is part of the Navagraha. In astrology, the term ''planet'' originally applied only to the five planets visible to the naked eye and excluded Earth. The term was later broadened, particularly in the Middle Ages, to include the sun and the moon (sometimes referred to as "lights"), making a total of seven planets. The seven days of the week in the Hindu calendar also correspond with the seven classical planets, and are named accordingly in most languages of the Indian subcontinent. Most Hindu temples around the world have a designated place dedicated to Navagraha worship. Planets, celestial bodies and lunar nodes Carnatic music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
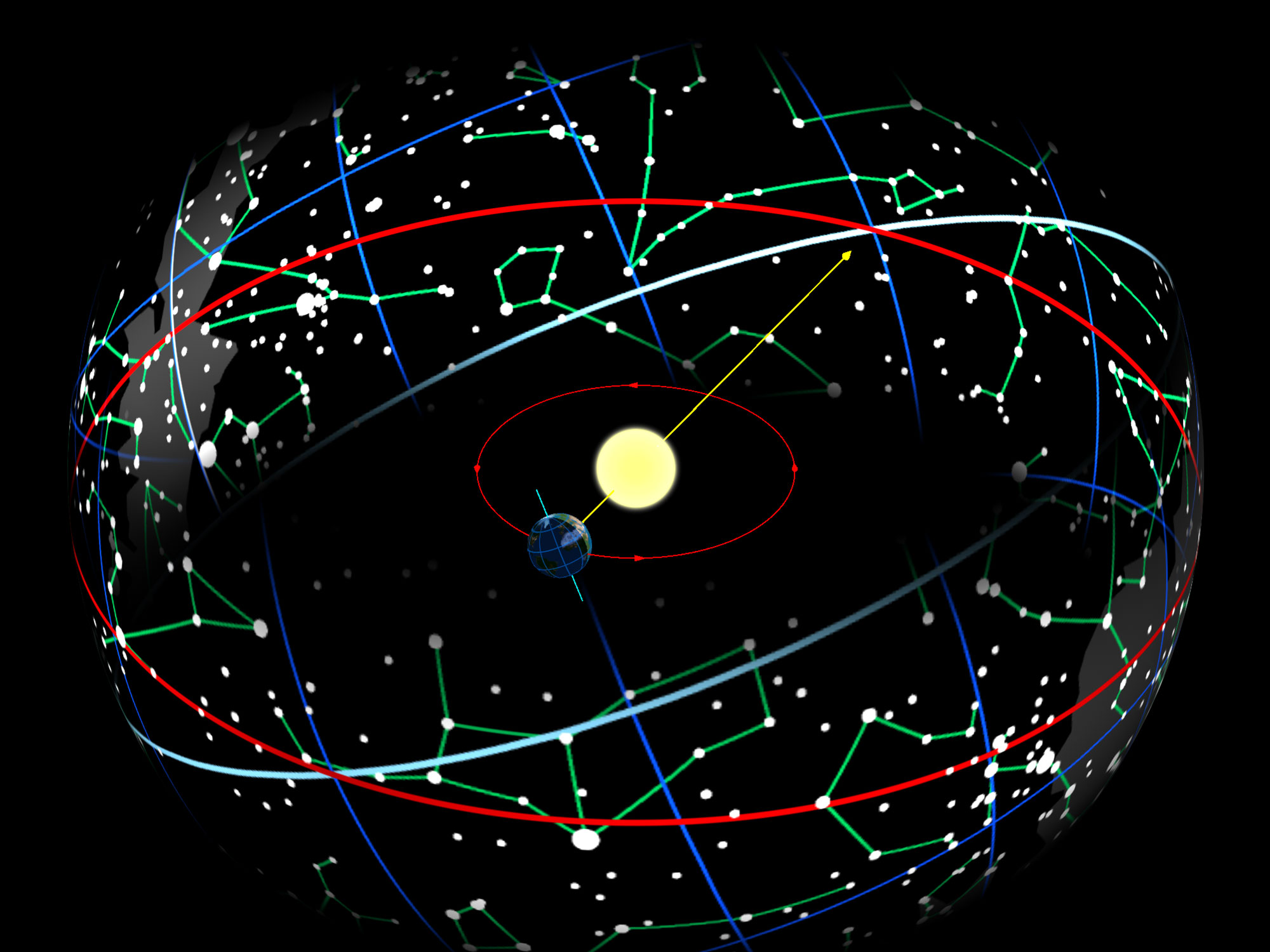
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into astrological sign, twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagna
In Vedic Astrology Jyotiṣa, the Lagna (') or Hour Marker, is the first moment of contact between the soul and its new life on earth in Jyotiṣa.''The Essentials of Vedic and thantrik Astrology'', by Komilla Sutton, The Wessex Astrologer Ltd, England, 1999, p.96. Lagna's Rashi and Nakshatra represents the "Atman" (Soul) of an Individual Person while the Lagna Lord represents the Ruler of the Horoscope and therefore the Rashi & Nakshatra where the Lagna Lord is positioned is equally very important as the Lagna Lord also absorbs the traits and qualities of that specific Rashi & Nakshatra. Beliefs and functions One's Hour Marker, or Lagna, is the degree of the rāśi (or sign) and nakshatra (or constellation) specifically the nakshatra pada (also known as the division of a constellation into 4 different parts) which is either rising on the eastern horizon (''Udaya Lagna'') or setting in the western horizon (''Godhuli Lagna'') depending on the sunrise or sunset astrological traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttara Kalamrita
Uttara Kalamrita is a reference work on Vedic astrology or Jyotisa. It is also termed as sidereal astrology, written by Kalidasa. However, it is unknown whether the Kalidasa who wrote this work is the same Kalidasa who wrote Raghuvamsha and Abhijñānaśākuntalam. The manuscript is available in various libraries in India, including the Government Oriental Manuscript Library in Chennai. History The text was first printed in the Telugu script. The reference to Andhra Bhasha, Urdu or Persian, Turushka, Sukkani, Rahu Kala, and other things show that he came after the sixteenth century. His use of the words Udyoga, got job, mud-cleaning, Smarta, Nadi and Vinadi, Sarasa-sallapa (a peculiar Telugu expression), Tyajya Kala and others prove that he is South Indian. His opposition to the marriage with the daughter of the maternal uncle references to the usages in the South in the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. These and other factors convince us that the author belongs to a tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalidasa
Kālidāsa (''fl.'' 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on the Vedas, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata and the Purāṇas. His surviving works consist of three plays, two epic poems and two shorter poems. Much about his life is unknown except what can be inferred from his poetry and plays. His works cannot be dated with precision, but they were most likely authored before the 5th century CE. Early life Scholars have speculated that Kālidāsa may have lived near the Himalayas, in the vicinity of Ujjain, and in Kalinga. This hypothesis is based on Kālidāsa's detailed description of the Himalayas in his ''Kumārasambhava'', the display of his love for Ujjain in ''Meghadūta'', and his highly eulogistic descriptions of Kalingan emperor Hemāngada in '' Raghuvaṃśa'' (sixth ''sarga''). Lakshmi Dhar Kalla (1891–1953), a Sanskrit scholar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Yoga (Hindu Astrology)
Raja yogas are ''Shubha'' ('auspicious') ''yogas'' that are superstitiously believed to give success and a grand rise in career or business, and a greater degree of financial prosperity particularly during the '' dasha'' of the planets that give rise to ''Raja yogas''. However, these results get adversely modified by the presence of other ''Ashubha'' ('inauspicious') ''Arista yogas''. Basically, the Yoga or Raja yoga-causing planets during the course of their respective dashas confer their most auspicious results if they happen to own the lagna-bhava (the Ascendant) or the Suta-bhava (the 5th house) or the Bhagyasthana (the 9th house); the person remains healthy, wealthy, happy and successful enjoying yoga and Raja yoga results in case the lagna, the 3rd, the 6th, the 8th, the 9th and the 12th houses counted from the lagna are also not occupied by any planet, and the kendras (quadrants) are occupied only by benefic planets. The most powerful yogas are included in the raja yogas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Dispositors (Hindu Astrology)
Planetary dispositors play an important role in Astrology. A dispositor is a planet that rules the sign that another planet is located in. For example, if Venus is in Gemini, then Mercury is the dispositor of Venus. Dispositor The dispositor is the planet which is the ruler of the sign or house that is occupied by another sign or house lord. Western astrology looks upon planetary dispositors as the final response to the meaning of an aspect in a horoscope, and it prefers drawing up of ''Dispositor trees'' that assist in determining in the Natal Chart the temporal status and the active nature of all planets. The concept of Planetary dispositors is not new to Hindu astrology, the ancient Hindu texts on Hindu predictive astrology have described numerous yogas based on this principle. In fact, most yogas are dependent upon the benefic placement of the dispositors of the planets giving rise to those yogas. In Hindu astrology the Planetary dispositor is also known as the ''Poshaka'', m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasha (astrology)
Dasha (Devanagari: ý§¶ý§∂ý§æ, Sanskrit, ', 'condition', 'state', 'circumstances', 'period of life', 'planetary period'.) The dasha pattern shows which planets according to Jyotish will be ruling at particular times. Overview The Sanskrit term "dasha" in Hindu astrology is used to indicate planetary periods. The planetary periods indicate when the good or bad effects are produced according to their placement by sign (Rasi), house (Bhava), combinations (Yogas or Raja Yogas) or aspects ( Drishti). The Dasha Paddhati (system) of Directional Astrology is unique to the Hindus; it is found nowhere else. There are many kinds of Dasha systems, Parashara mentions forty-two of them, but of these only two are in vogue, namely, "Vimshottari" and "Ashtottari".V.G. Rele (1970). Directional Astrology of the Hindus as propounded in Vimshottari Dasa, D.B. Taraporevala Sons & Co., Private Ltd, Mumbai, India ''Dashas'' provide a system to judge the effects of the planets throughout a person's life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varga (astrology)
The term Varga (Sanskrit ', 'set, division') in Indian astrology (Jyotisha) refers to the division of a zodiacal sign (''rāśi'') into parts. Each such fractional part of a sign, known as an , has a source of influence associated with it, so that these sources of influence come to be associated with collections of regions around the zodiac. There are sixteen varga, or divisional, charts used in Jyotisha. These vargas form the basis of a unique system of finding the auspiciousness or inauspiciousness of planets. Overview Hindu astrology divides the zodiac into several types of segments; these subtle divisions or divisional charts are called Vargas and are said to be the various micro-zodiacs created within the natural macro-zodiac, the Horoscope. The particular location of planets in the Varga charts materially influences the results of planets constituting a yoga. The two sets of vargas that are commonly used are – a) the Shadvarga i.e. the six-fold division of sign namely, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navamsa (astrology)
In Vedic astrology a constant reference is made to the Navamsa occupied by planets and the Lagna-point. Both, the Rasi-chart and the Navamsa-chart are deemed equally important and therefore, consulted together. Whereas the Rasi-chart provides overall information regarding the location of planets and sensitive-points such as the Lagna, the latter provides vital information regarding their active quality and strength. A planet may be well-placed in the natal-chart Rasi-wise but its full effects may not materialise if its situation in the navamsa-chart is not supportive. Definition In Vedic astrology, Navamsa means one-ninth part of a Zodiac Sign. Navamsa literally means the "Ninth Division". Thus, each navamsa measures 3 degrees and 20 minutes in longitude or one-quarter of a Nakshatra (Constellation), and the Zodiac of Signs comprises 108 navamsas. There are 3 important ways of reckoning a Navamsa Chart: 1. Parasara Navamsa 2. Krishna Mishra Navamsa 3. Somanatha Navamsa Parasar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |