|
United States Army South
United States Army South is an Army service component command of United States Southern Command whose area of responsibility includes 31 countries and 15 areas of special sovereignty in Central and South America and the Caribbean. It is headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas. U.S. Army South's currently officially stated mission is to conduct and support multinational operations and security cooperation in the United States Southern Command area of responsibility in order to counter transnational threats and strengthen regional security in defense of the homeland. It may be still required to serve as a Joint Task Force Land Component Command or Joint Task Force, as directed. Panama Canal Department The Isthmian Canal Commission of 1904–1914 and the Panama Canal Guard both played a pivotal role in the construction and early defense of the Canal. The Panama Canal Guard was active from 1907 to 1917. On 1 July 1917, the Panama Canal Department was established as a separate geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Service Component Command
Army Service Component Commands (ASCCs) are U.S. Army commands responsible for recommendations to the Joint Force Commander on the allocation and employment of U.S. Army forces within a combatant command or further assigned to subordinate unified command. In the event that a combatant commander created a subordinate unified command the Department of the Army will form a matching Army component headquarters. In matching, the Secretary of the Army also has the authority to redirect service responsibilities outside of Army Service Command Component channels. The Command itself may also redirect administrative responsibility outside Army forces. ASCCs also server administrative control for some of its functions, this is also typically true among Reserve Component forces. Shared administrative control also applies to direct reporting units of the Army that typically perform single or unique functions. Four types of command authority can be distinguished: #Unified combatant command, COC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Engineers
11 (eleven) is the natural number following 10 and preceding 12. It is the first repdigit. In English, it is the smallest positive integer whose name has three syllables. Name "Eleven" derives from the Old English ', which is first attested in Bede's late 9th-century ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People''. It has cognates in every Germanic language (for example, German ), whose Proto-Germanic ancestor has been reconstructed as , from the prefix (adjectival " one") and suffix , of uncertain meaning. It is sometimes compared with the Lithuanian ', though ' is used as the suffix for all numbers from 11 to 19 (analogously to "-teen"). The Old English form has closer cognates in Old Frisian, Saxon, and Norse, whose ancestor has been reconstructed as . This was formerly thought to be derived from Proto-Germanic (" ten"); it is now sometimes connected with or ("left; remaining"), with the implicit meaning that "one is left" after counting to ten.''Oxford English Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
193rd Infantry Brigade (United States)
The 193rd Infantry Brigade is a United States Army infantry brigade, which was originally constituted in the Army's organized reserves on 24 June 1922 as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, 193rd Infantry Brigade and assigned to the 97th Division. The brigade was converted and redesignated in February 1942 as the 97th Reconnaissance Troop, 97th Division. In February 1943, the Troop was ordered into active military service and organized at Camp Swift, Texas. It was reorganized and redesignated in October 1945 as the 97th Mechanized Cavalry Reconnaissance Troop. World War II The 97th Reconnaissance Troop landed at Le Havre, France, 2 March 1945 as part of the 97th Infantry Division. The Division crossed the German border west of Aachen and took up a defensive position along the west bank of the Rhine River opposite Düsseldorf, engaging in patrolling. The division then entered the battle of the Ruhr pocket, crossing the Rhine near Bonn and taking up a position on the southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20th Infantry Regiment (United States)
The 20th Infantry Regiment ("Sykes' Regulars") is a United States Army infantry regiment. Currently only the 5th Battalion of the 20th Infantry still exists. Stationed at Joint Base Lewis-McChord and part of the 1st Stryker Brigade Combat Team, 2nd Infantry Division, 5-20 Infantry was one of the original battalions selected to take part in the testing and fielding of the Army's new Stryker vehicle. History Creation The regiment was organized on 6 June 1862 at Fort Independence (Massachusetts), as the 2nd Battalion of the 11th Infantry, one of the nine "three-battalion" regiments of regulars, each battalion containing eight companies of infantry, in contrast to the original ten regular regiments of infantry, which were organized on the traditional ten-company line. The 20th Infantry was first led by General George Sykes in the Battle of Bull Run. Following the US Civil War, the Army was reorganized by Congress in July 1866, and the 11th was divided into three regiments, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
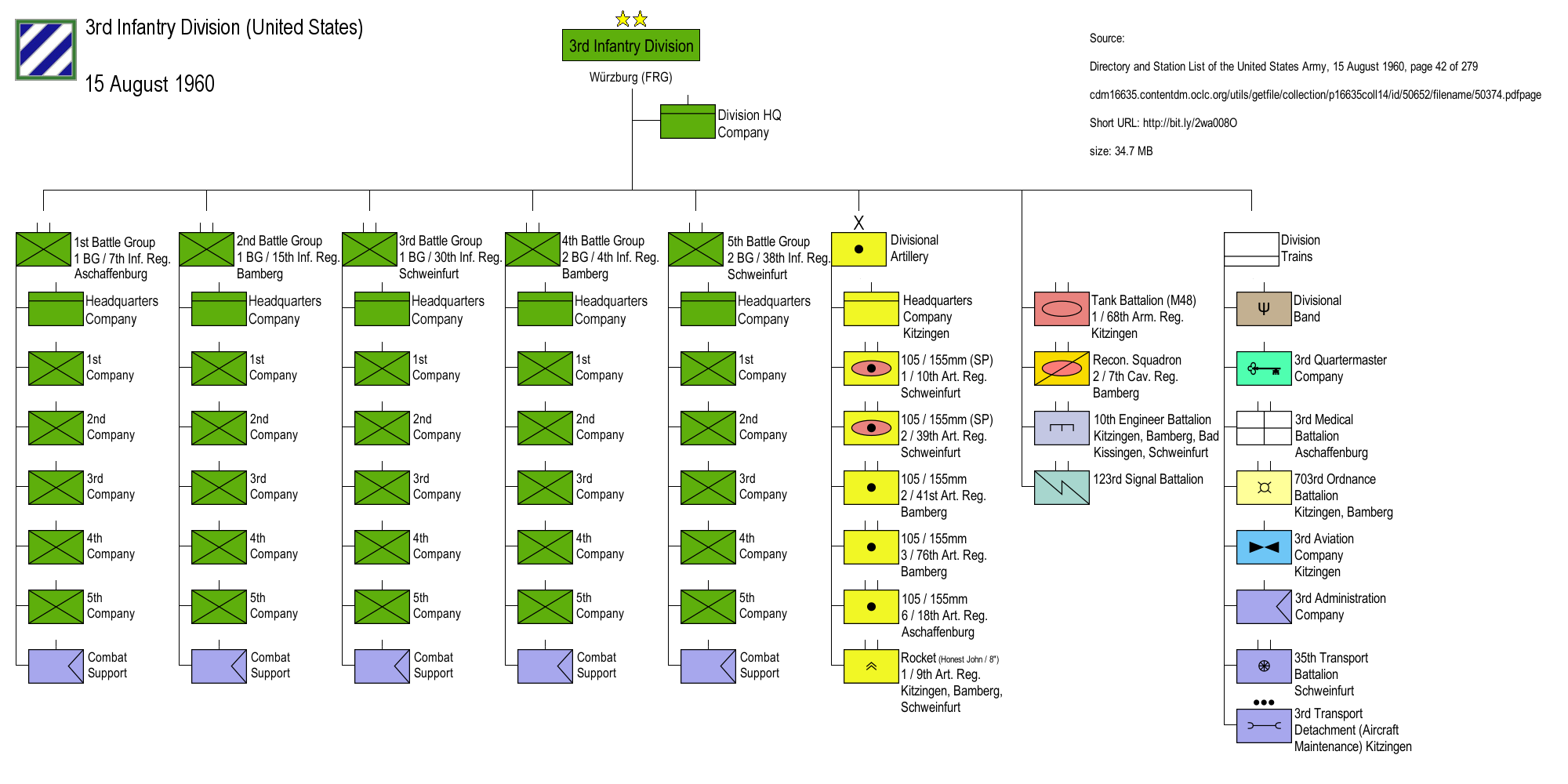
Pentomic
Pentomic (cf. ''Greek pent(e)-'' +''-tome'' "of five parts") was a structure for infantry and airborne divisions adopted by the US Army between 1957 and 1963, in response to the potential use of tactical nuclear weapons, on future battlefields. It was intended that the five subordinate units, which were often referred to as battle groups (to distinguish them from traditional units), would be able to deploy and engage in operations more rapidly than conventional brigades, whilst also having greater offensive capabilities than conventional battalions. One US Army publication defines the pentomic division as "a public relations term designed to combine the concept of five subordinate units ('penta') with the idea of a division that could function on itheran atomic or nonatomic battlefield". Several other countries also temporarily adopted similar structures in their armed forces, at around the same time as the US example, including France (from 1955), Australia, Turkey and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuba–Soviet Union Relations
After the establishment of diplomatic ties with the Soviet Union after the Cuban Revolution of 1959, Cuba became increasingly dependent on Soviet markets and military aid and was an ally of the Soviet Union during the Cold War. In 1972 Cuba joined the COMECON, an economic organization of states designed to create co-operation among the communist planned economies, which was dominated by its largest economy, the Soviet Union. Moscow kept in regular contact with Havana and shared varying close relations until the end of the Soviet Union in 1991. Cuba then entered an era of serious economic hardship, the Special Period. History Relations before Cuban Revolution The first diplomatic relations between the Soviet Union and Cuba developed during World War II. Maxim Litvinov, the Soviet ambassador to the United States, set up the first Soviet embassy in Havana in 1943, and Cuban diplomats under the auspices of President Fulgencio Batista visited Moscow the same year. The Soviets then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion (, sometimes called ''Invasión de Playa Girón'' or ''Batalla de Playa Girón'' after the Playa Girón) was a failed military landing operation on the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly financed and directed by the United States. It was aimed at overthrowing Fidel Castro's communist government. The operation took place at the height of the Cold War, and its failure influenced relations between Cuba, the United States, and the Soviet Union. In December 1958, American ally General Fulgencio Batista was deposed by Castro's 26th of July Movement during the Cuban Revolution. Castro nationalized American businesses—including banks, oil refineries, and sugar and coffee plantations—then severed Cuba's formerly close relations with the United States and reached out to its Cold War rival, the Soviet Union. The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) began planning the overthrow of Castro, which U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara (; June 9, 1916 – July 6, 2009) was an American business executive and the eighth United States Secretary of Defense, serving from 1961 to 1968 under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. He remains the List of United States Secretaries of Defense by time in office, longest serving Secretary of Defense, having remained in office over seven years. He played a major role in promoting the United States' involvement in the Vietnam War. McNamara was responsible for the institution of systems analysis in public policy, which developed into the discipline known today as policy analysis. He was born in San Francisco, California, graduated from University of California, Berkeley, UC Berkeley and Harvard Business School and served in the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. After the war, Henry Ford II hired McNamara and a group of other Army Air Force veterans to work for Ford Motor Company. These "Whiz Kids (Ford), Whiz Kids" helped re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jungle Warfare Training Center
Camp Gonsalves is a United States Marine Corps, U.S. Marine Corps jungle warfare training area located in northern Okinawa, Japan, across the villages of Kunigami, Okinawa, Kunigami and Higashi, Okinawa, Higashi. Established in 1958, it is the largest U.S training facility in Okinawa. The camp is located in the Yanbaru forest protected area, raising long time ecological concerns enhanced by the 2016 plan to built new helipads. Terrain Also known as the NTA (Northern Training Area), and since 1998 as the JWTC (Jungle Warfare Training Center) it occupies of jungle in Northern Okinawa Prefecture, Okinawa. The hilly and rugged terrain is topped with single and double canopy forests. The region supplies the densely populated south of the island with drinking water. As part of the Ryukyu Islands subtropical evergreen forests, most of the area surrounding JWTC is designated as a national forest by the Government of Japan. The area is home to 24 endangered species including the Okinawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Caribbean Command
United may refer to: Places * United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Films * ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film * ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two film Literature * ''United!'' (novel), a 1973 children's novel by Michael Hardcastle Music * United (band), Japanese thrash metal band formed in 1981 Albums * ''United'' (Commodores album), 1986 * ''United'' (Dream Evil album), 2006 * ''United'' (Marvin Gaye and Tammi Terrell album), 1967 * ''United'' (Marian Gold album), 1996 * ''United'' (Phoenix album), 2000 * ''United'' (Woody Shaw album), 1981 Songs * "United" (Judas Priest song), 1980 * "United" (Prince Ital Joe and Marky Mark song), 1994 * "United" (Robbie Williams song), 2000 * "United", a song by Danish duo Nik & Jay featuring Lisa Rowe Television * ''United'' (TV series), a 1990 BBC Two documentary series * ''United!'', a soap opera that aired on BBC One from 1965-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)