|
United Shipyards, Inc.
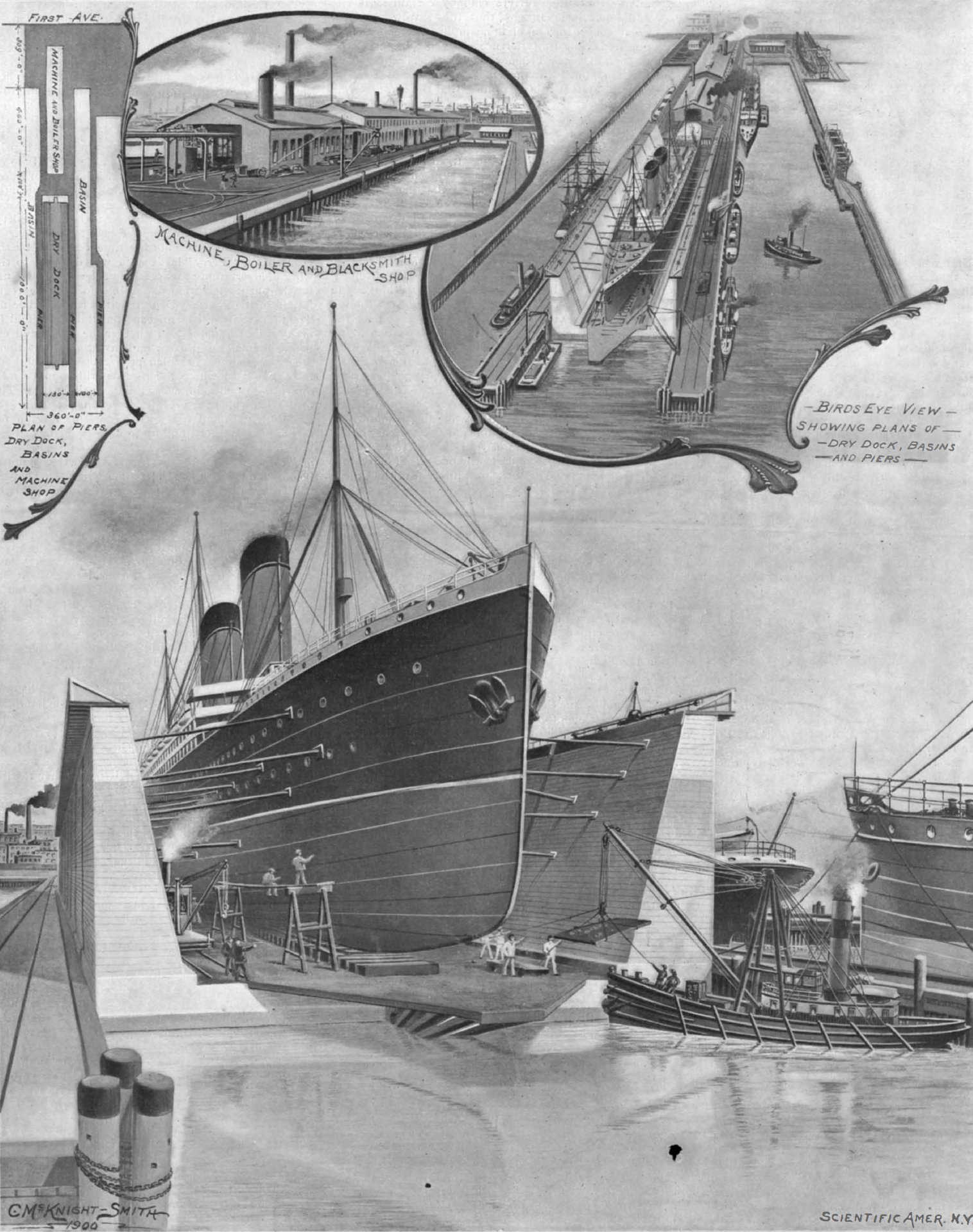
The Morse Dry Dock and Repair Company was a major late 19th/early 20th century ship repair and conversion facility located in New York City. Begun in the 1880s as a small shipsmithing business known as the Morse Iron Works, the company grew to be one of America's largest ship repair and refit facilities, at one time owning the world's largest floating dry dock. In addition to servicing some of the finest steamships of the era, the company maintained many of the yachts of New York's elite business community, and also occasionally built small watercraft such as tugboats. During World War I, the company was heavily engaged in work for the U.S. government and military. In 1929, the company merged with five other major New York ship repair facilities to become United Dry Docks, Inc.—the largest company of its type in the world—with the former head of Morse Dry Dock, Edward P. Morse, as chairman of the board. United Dry Docks later changed its name to United Shipyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward P
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy and Ned. Peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelius Vanderbilt III
Brigadier General Cornelius "Neily" Vanderbilt III (September 5, 1873 – March 1, 1942) was an American military officer, inventor, engineer, and yachtsman. He was a member of the Vanderbilt family. Early life Born in New York City to Cornelius Vanderbilt II and Alice Claypoole Gwynne, he was educated by private tutors at St. Paul's School in Concord, New Hampshire, then attended Yale University and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree in 1895. Against his father's wishes, in August 1896 he married Grace Graham Wilson, the youngest child of New York banker Richard Thornton Wilson Sr., and Melissa Clementine Johnston. As a consequence, his father disinherited him. Remaining at Yale until 1899, he earned a Bachelor of Philosophy degree and, having a great deal of interest in the technical aspects of his family's railroad business, he also earned a Master of Engineering degree in mechanical engineering. Inheritance Upon his father's death in 1899 Vanderbilt received $500,000 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Crane
An overhead crane, commonly called a bridge crane, is a type of crane found in industrial environments. An overhead crane consists of two parallel rails seated on longitudinal I-beams attached to opposite steel columns by means of brackets. The traveling bridge spans the gap. A hoist, the lifting component of a crane, travels along the bridge. If the bridge is rigidly supported on two or more legs running on two fixed rails at ground level, the crane is called a gantry crane (USA, ASME B30 series) or a ''goliath crane'' (UK, BS 466). Unlike mobile or construction cranes, overhead cranes are typically used for either manufacturing or maintenance applications, where efficiency or downtime are critical factors. History In 1876 Sampson Moore in England designed and supplied the first ever electric overhead crane, which was used to hoist guns at the Royal Arsenal in Woolwich, London. Since that time Alliance Machine, now defunct, holds an AISE citation for one of the earliest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Press
A hydraulic press is a machine press using a hydraulic cylinder to generate a compressive force. It uses the hydraulic equivalent of a mechanical lever, and was also known as a Bramah press after the inventor, Joseph Bramah, of England. He invented and was issued a patent on this press in 1795. As Bramah (who is also known for his development of the flush toilet) installed toilets, he studied the existing literature on the motion of fluids and put this knowledge into the development of the press. Main principle The hydraulic press depends on Pascal's principle-the pressure throughout a closed system is constant. One part of the system is a piston acting as a pump, with a modest mechanical force acting on a small cross-sectional area; the other part is a piston with a larger area which generates a correspondingly large mechanical force. Only small-diameter tubing (which more easily resists pressure) is needed if the pump is separated from the press cylinder. Pascal's law: Pressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air is an important medium for transfer of energy in industrial processes, and is used for power tools such as air hammers, drills, wrenches, and others, as well as to atomize paint, to operate air cylinders for automation, and can also be used to propel vehicles. Brakes applied by compressed air made large railway trains safer and more efficient to operate. Compressed air brakes are also found on large highway vehicles. Compressed air is used as a breathing gas by underwater divers. It may be carried by the diver in a high pressure diving cylinder, or supplied from the surface at lower pressure through an air line or diver's umbilical. Similar arrangements are used in breathing apparatus used by firefighters, mine rescue workers and industrial workers in hazardous atmospheres. In Europe, 10 percent of all industrial electricity consumption is to produce compressed air—amountin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Hammer
A steam hammer, also called a drop hammer, is an industrial power hammer driven by steam that is used for tasks such as shaping forgings and driving piles. Typically the hammer is attached to a piston that slides within a fixed cylinder, but in some designs the hammer is attached to a cylinder that slides along a fixed piston. The concept of the steam hammer was described by James Watt in 1784, but it was not until 1840 that the first working steam hammer was built to meet the needs of forging increasingly large iron or steel components. In 1843 there was an acrimonious dispute between François Bourdon of France and James Nasmyth of Britain over who had invented the machine. Bourdon had built the first working machine, but Nasmyth claimed it was built from a copy of his design. Steam hammers proved to be invaluable in many industrial processes. Technical improvements gave greater control over the force delivered, greater longevity, greater efficiency and greater power. A stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, grilles, railings, light fixtures, furniture, sculpture, tools, agricultural implements, decorative and religious items, cooking utensils, and weapons. There was an historical distinction between the heavy work of the blacksmith and the more delicate operation of a whitesmith, who usually worked in Goldsmith, gold, Silversmith, silver, pewter, or the finishing steps of fine steel. The place where a blacksmith works is called variously a smithy, a forge or a blacksmith's shop. While there are many people who work with metal such as farriers, wheelwrights, and Armourer, armorers, in former times the blacksmith had a general knowledge of how to make and repair many things, from the most complex of weapons and armor to simple things ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Shipping Board
The United States Shipping Board (USSB) was established as an emergency agency by the 1916 Shipping Act (39 Stat. 729), on September 7, 1916. The United States Shipping Board's task was to increase the number of US ships supporting the World War I efforts. United States Shipping Board program ended on March 2, 1934. Initiation The United States' maritime position had been eroding for decades with some Congressional concern, some remedies actually worsening the situation, with European shipping companies dominating overseas trade and just over 10% of the value of trade carried in U.S. owned ships. The 1916 act was the result of Congressional efforts to create a board to address the problem dating from 1914. At this time the legislation was not a part of any war effort with specific intent as stated in the act: :"An Act to establish a United States Shipping Board for the purpose of encouraging, developing, and creating a naval auxiliary and naval reserve and a Merchant Marine to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, on the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by France to the north, east and west. The principality is home to 38,682 residents, of whom 9,486 are Monégasque nationals; it is widely recognised as one of the most expensive and wealthiest places in the world. The official language of the principality is French. In addition, Monégasque (a dialect of Ligurian), Italian and English are spoken and understood by many residents. With an area of , it is the second-smallest sovereign state in the world, after Vatican City. Its make it the most densely-populated sovereign state in the world. Monaco has a land border of and the world's shortest coastline of approximately ; it has a width that varies between . The hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidewheel Steamer
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine that drives paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, where the first uses were wheelers driven by animals or humans. In the early 19th century, paddle wheels were the predominant way of propulsion for steam-powered boats. In the late 19th century, paddle propulsion was largely superseded by the screw propeller and other marine propulsion systems that have a higher efficiency, especially in rough or open water. Paddle wheels continue to be used by small, pedal-powered paddle boats and by some ships that operate tourist voyages. The latter are often powered by diesel engines. Paddle wheels The paddle wheel is a large steel framework wheel. The outer edge of the wheel is fitted with numerous, regularly spaced paddle blades (called floats or buckets). The bottom quarter or so of the wheel travels under water. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
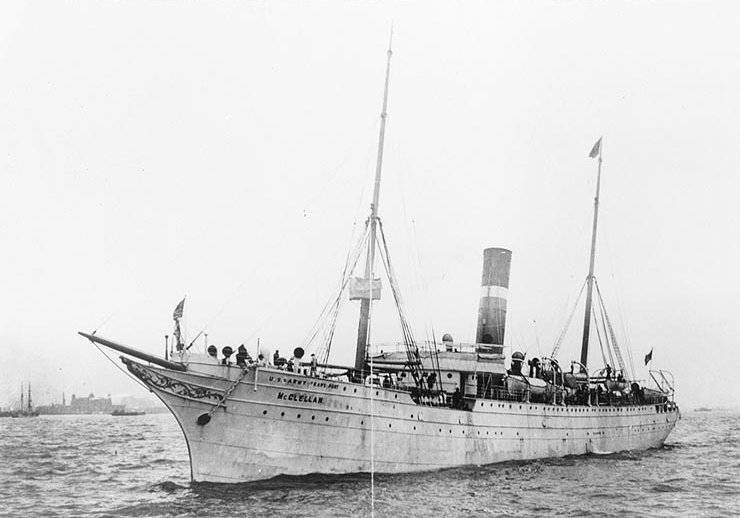
USAT McClellan
USAT ''McClellan'' was a United States Army transport ship that saw service during the Spanish–American War and World War I. She also participated in the occupation of Veracruz in 1914. ''McClellan'' was originally SS ''Port Victor'', a steel-hulled passenger-cargo screw steamer built for Anglo-Australian service in the 1880s. Eventually converted into an early example of a refrigeration ship, ''Port Victor'' continued in Australian service until shortly before her sale in 1898 to the United States government for use as a transport during the Spanish–American War. After the war, she was renamed USAT ''McClellan'' and employed as a U.S. Army transport for more than twenty years, supplying the garrisons in Cuba, Puerto Rico and the Philippines. Sold in 1919, she briefly returned to mercantile service under the name SS ''Hastier'', until being damaged by a fire in 1920 and subsequently scrapped. Construction and design ''Port Victor'' was built by Andrew Leslie & Co. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Association Of Machinists
The International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers (IAM) is an AFL–CIO/ CLC trade union representing approx. 646,933 workers as of 2006 in more than 200 industries with most of its membership in the United States and Canada. Origin On May 5, 1888, Thomas W. Talbot, a railroad machinist in Atlanta, Georgia, founded the Order of United Machinists and Mechanical Engineers. Talbot and 18 others had been members in the Knights of Labor. Talbot believed that a union needed to be formed for railroad machinists that would resist wage cuts. He wanted to provide insurance against unemployment, illness, and accidents but also wanted railroad machinists to be recognized for their craft skill. Unlike the Knights of Labor, who accepted everyone, Talbot's union accepted only white U.S. citizens, preferably native-born. The union excluded blacks, women, and non-citizens, and had secret passwords. Despite the secrecy, the order spread beyond Georgia, thanks in part to "boomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |