|
Uniform Limit Theorem
In mathematics, the uniform limit theorem states that the uniform limit of any sequence of continuous functions is continuous. Statement More precisely, let ''X'' be a topological space, let ''Y'' be a metric space, and let ƒ''n'' : ''X'' → ''Y'' be a sequence of functions converging uniformly to a function ƒ : ''X'' → ''Y''. According to the uniform limit theorem, if each of the functions ƒ''n'' is continuous, then the limit ƒ must be continuous as well. This theorem does not hold if uniform convergence is replaced by pointwise convergence. For example, let ƒ''n'' : , 1nbsp;→ R be the sequence of functions ƒ''n''(''x'') = ''xn''. Then each function ƒ''n'' is continuous, but the sequence converges pointwise to the discontinuous function ƒ that is zero on closed subset of ''YX'' under the uniform metric. In the case where ''Y'' is Complete metric spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drini Nonuniformconvergence SVG
The Drin (; sq, Drin or ; mk, Дрим, Drim ) is a river in Southern and Southeastern Europe with two distributaries one discharging into the Adriatic Sea and the other one into the Buna River. Its catchment area extends across Albania, Kosovo, Serbia, Greece, Montenegro and North Macedonia. The river and its tributaries form the Gulf of Drin, an ocean basin that encompasses the northern Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast. At long, the Drin is the longest river of Albania of which passes across Albania and the remainder through Kosovo and North Macedonia. It starts at the confluence of its two headwaters, namely the Black Drin and White Drin. It originates in the mountainous northern mountain range, flows westwards through the Albanian Alps and Dukagjin Highlands, and eventually drains into the Adriatic Sea, between Shëngjin and Durrës. Numerous lakes and reservoirs are formed by the river or flow into it such as the Fierza Lake and Koman Lake. Located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Metric Space
In mathematical analysis, a metric space is called complete (or a Cauchy space) if every Cauchy sequence of points in has a limit that is also in . Intuitively, a space is complete if there are no "points missing" from it (inside or at the boundary). For instance, the set of rational numbers is not complete, because e.g. \sqrt is "missing" from it, even though one can construct a Cauchy sequence of rational numbers that converges to it (see further examples below). It is always possible to "fill all the holes", leading to the ''completion'' of a given space, as explained below. Definition Cauchy sequence A sequence x_1, x_2, x_3, \ldots in a metric space (X, d) is called Cauchy if for every positive real number r > 0 there is a positive integer N such that for all positive integers m, n > N, d\left(x_m, x_n\right) < r. Complete space A metric space is complete if any of the following equivalent conditions are satisfied: :#Every [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice Hall
Prentice Hall was an American major educational publisher owned by Savvas Learning Company. Prentice Hall publishes print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market, and distributes its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. Prentice Hall became known as a publisher of trade books by authors such as Norman Vincent Peale; elementary, secondary, and college textbooks; loose-leaf information services; and professional books. Prentice Hall acquired the training provider Deltak in 1979. Prentice Hall was acquired by Gulf+Western in 1984, and became part of that company's publishing division Simon & Schuster. S&S sold several Prentice Hall subsidiaries: Deltak and Resource Systems were sold to National Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Inequality
In mathematics, the triangle inequality states that for any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than or equal to the length of the remaining side. This statement permits the inclusion of degenerate triangles, but some authors, especially those writing about elementary geometry, will exclude this possibility, thus leaving out the possibility of equality. If , , and are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, with no side being greater than , then the triangle inequality states that :z \leq x + y , with equality only in the degenerate case of a triangle with zero area. In Euclidean geometry and some other geometries, the triangle inequality is a theorem about distances, and it is written using vectors and vector lengths ( norms): :\, \mathbf x + \mathbf y\, \leq \, \mathbf x\, + \, \mathbf y\, , where the length of the third side has been replaced by the vector sum . When and are real numbers, they can be viewed as vectors in , and the tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighbourhood (mathematics)
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a neighbourhood (or neighborhood) is one of the basic concepts in a topological space. It is closely related to the concepts of open set and interior. Intuitively speaking, a neighbourhood of a point is a set of points containing that point where one can move some amount in any direction away from that point without leaving the set. Definitions Neighbourhood of a point If X is a topological space and p is a point in X, then a of p is a subset V of X that includes an open set U containing p, p \in U \subseteq V \subseteq X. This is also equivalent to the point p \in X belonging to the topological interior of V in X. The neighbourhood V need be an open subset X, but when V is open in X then it is called an . Some authors have been known to require neighbourhoods to be open, so it is important to note conventions. A set that is a neighbourhood of each of its points is open since it can be expressed as the union of open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Up until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity, and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
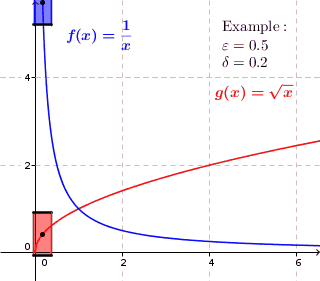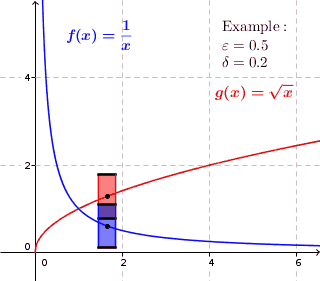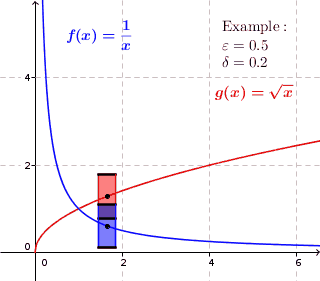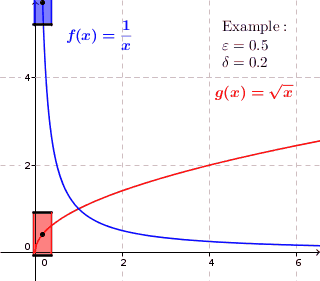
Uniform Continuity
In mathematics, a real function f of real numbers is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a positive real number \delta such that function values over any function domain interval of the size \delta are as close to each other as we want. In other words, for a uniformly continuous real function of real numbers, if we want function value differences to be less than any positive real number \epsilon, then there is a positive real number \delta such that , f(x) - f(y), 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every x,y \in X with d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every x,y \in X , , x - y, 0 \; \forall x \in X \; \forall y \in X : \, d_1(x,y) 0 , \forall x \in X , and \forall y \in X ) are used. * Alternatively, f is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a function of all positive real numbers \varepsilon, \delta(\varepsilon) representing the maximum positive real number, such that for every x,y \in X if d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every y \in X w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Norm
In mathematical analysis, the uniform norm (or ) assigns to real- or complex-valued bounded functions defined on a set the non-negative number :\, f\, _\infty = \, f\, _ = \sup\left\. This norm is also called the , the , the , or, when the supremum is in fact the maximum, the . The name "uniform norm" derives from the fact that a sequence of functions converges to under the metric derived from the uniform norm if and only if converges to uniformly. If is a continuous function on a closed and bounded interval, or more generally a compact set, then it is bounded and the supremum in the above definition is attained by the Weierstrass extreme value theorem, so we can replace the supremum by the maximum. In this case, the norm is also called the . In particular, if is some vector such that x = \left(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n\right) in finite dimensional coordinate space, it takes the form: :\, x\, _\infty := \max \left(\left, x_1\ , \ldots , \left, x_n\\right). Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banach Space
In mathematics, more specifically in functional analysis, a Banach space (pronounced ) is a complete normed vector space. Thus, a Banach space is a vector space with a metric that allows the computation of vector length and distance between vectors and is complete in the sense that a Cauchy sequence of vectors always converges to a well-defined limit that is within the space. Banach spaces are named after the Polish mathematician Stefan Banach, who introduced this concept and studied it systematically in 1920–1922 along with Hans Hahn and Eduard Helly. Maurice René Fréchet was the first to use the term "Banach space" and Banach in turn then coined the term " Fréchet space." Banach spaces originally grew out of the study of function spaces by Hilbert, Fréchet, and Riesz earlier in the century. Banach spaces play a central role in functional analysis. In other areas of analysis, the spaces under study are often Banach spaces. Definition A Banach space is a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Metric
In mathematical analysis, the uniform norm (or ) assigns to real- or complex-valued bounded functions defined on a set the non-negative number :\, f\, _\infty = \, f\, _ = \sup\left\. This norm is also called the , the , the , or, when the supremum is in fact the maximum, the . The name "uniform norm" derives from the fact that a sequence of functions converges to under the metric derived from the uniform norm if and only if converges to uniformly. If is a continuous function on a closed and bounded interval, or more generally a compact set, then it is bounded and the supremum in the above definition is attained by the Weierstrass extreme value theorem, so we can replace the supremum by the maximum. In this case, the norm is also called the . In particular, if is some vector such that x = \left(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n\right) in finite dimensional coordinate space, it takes the form: :\, x\, _\infty := \max \left(\left, x_1\ , \ldots , \left, x_n\\right). Metric an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a set whose complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points. In a complete metric space, a closed set is a set which is closed under the limit operation. This should not be confused with a closed manifold. Equivalent definitions By definition, a subset A of a topological space (X, \tau) is called if its complement X \setminus A is an open subset of (X, \tau); that is, if X \setminus A \in \tau. A set is closed in X if and only if it is equal to its closure in X. Equivalently, a set is closed if and only if it contains all of its limit points. Yet another equivalent definition is that a set is closed if and only if it contains all of its boundary points. Every subset A \subseteq X is always contained in its (topological) closure in X, which is denoted by \operatorname_X A; that is, if A \subseteq X then A \subseteq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |