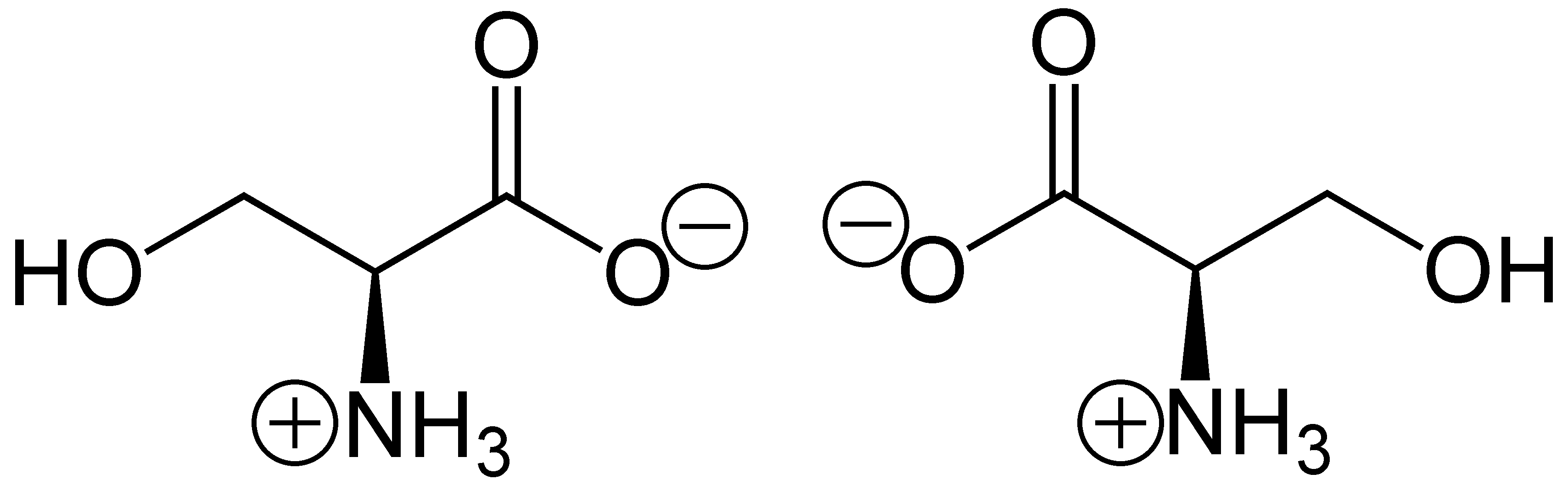|
Undecylprodigiosin
Undecylprodigiosin is an alkaloid produced by some Actinomycetes bacteria. It is a member of the prodiginines group of natural products and has been investigated for potential antimalarial activity. Natural sources Undecylprodigiosin is a secondary metabolite found in some Actinomycetes, for example ''Actinomadura madurae'', ''Streptomyces coelicolor'' and '' Streptomyces longisporus''. Production Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of undecylprodigiosin starts with PCP apoprotein which is transformed into the holoprotein using acetyl CoA and PPtase then adenylation occurs utilizing L-proline and ATP. The resulting molecule is then oxidized by dehydrogenase enzyme. Elongation by decarboxylative condensation with malonyl CoA is followed by another decarboxylative condensation with L-serine using α-oxamine synthase (OAS) domain. The compound is then cyclized, oxidized with dehydrogenase and methylated with SAM to give 4-methoxy-2,2′-bipyrrole-5-carboxaldehyde (MBC) intermediate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodiginines
The prodiginines are a family of red tripyrrole dyestuffs produced by Gammaproteobacteria (e.g. ''Serratia marcescens'') as well as some Actinomycetota (e.g. ''Streptomyces coelicolor''). The group is named after prodigiosin (prodiginine) and is biosynthesized through a common set of enzymes. They are interesting due to their history and their varied biological activity. Structural types Prodigiosin colour.svg, Prodigiosin Cycloprodigiosin.svg, Cycloprodigiosin Cyclononylprodigiosin.svg, Cyclononylprodigiosin Undecylprodigiosin coloured.svg, Undecylprodigiosin Butyl-meta-cycloheptylprodiginine.svg, Butyl-meta-cycloheptylprodiginine Natural sources The prodiginines are secondary metabolites originally noted in ''Serratia'' species, especially ''Serratia marcescens''. They are also found in Actinomycetes, for example ''Streptomyces coelicolor'' and some marine bacteria, including ''Hahella chejuensis'' and ''Pseudoalteromonas denitrificans''. Cyclononylprodigiosin was isolated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenylation
Adenylylation, more commonly known as AMPylation, is a process in which an adenosine monophosphate (AMP) molecule is covalently attached to the amino acid side chain of a protein. This covalent addition of AMP to a hydroxyl side chain of the protein is a posttranslational modification. Adenylylation involves a phosphodiester bond between a hydroxyl group of the molecule undergoing adenylylation, and the phosphate group of the adenosine monophosphate nucleotide (i.e. adenylic acid). Enzymes that are capable of catalyzing this process are called AMPylators. The known amino acids to be targeted in the protein are tyrosine and threonine, and sometimes serine. When charges on a protein undergo a change, it affects the characteristics of the protein, normally by altering its shape via interactions of the amino acids which make up the protein. AMPylation can have various effects on the protein. These are properties of the protein like, stability, enzymatic activity, co-factor binding, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Streptomycetes are characterised by a complex secondary metabolism. They produce over two-thirds of the clinically useful antibiotics of natural origin (e.g., neomycin, streptomycin, cypemycin, grisemycin, bottromycins and chloramphenicol). The antibiotic streptomycin takes its name directly from ''Streptomyces''. Streptomycetes are infrequent pathogens, though infections in humans, such as mycetoma, can be caused by '' S. somaliensis'' and '' S. sudanensis'', and in plants can be caused by '' S. cavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful. Often, the aim is to discover a new route of synthesis for a target molecule for which there already exist known routes. Sometimes, however, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malonyl CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid. Functions It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and commits them to fatty acid chain synthesis. Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase. One molecule of acetyl-CoA joins with a molecule of bicarbonate,Nelson D, Cox M (2008) ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry''. 5th Ed: p. 806 requiring energy rendered from ATP. Malonyl-CoA is utilised in fatty acid biosynthesis by the enzyme malonyl coenzyme A:acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT). MCAT serves to transfer malonate from malonyl-CoA to the terminal thiol of ''holo''-acyl carrier protein (ACP). Polyketide biosynthesis MCAT is also involved in bacterial polyketide biosynthesis. The enzyme MCAT together with an acyl carrier protein (ACP), and a polyketide synthase (PKS) and chain-length f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarboxylative Condensation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases ( EC number 4.1.1). In organic chemistry The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of a carboxyl group () with a hydrogen atom: :RCO2H -> RH + CO2 Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. Metal salts, especially copper compounds, facilitate the reaction via the intermediacy of metal carboxylate complexes. Decarboxylation of aryl carboxylates can generate the equivalent of the corresponding aryl anion, which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydrogenase
A dehydrogenase is an enzyme belonging to the group of oxidoreductases that oxidizes a substrate by reducing an electron acceptor, usually NAD+/NADP+ or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMN. Like all catalysts, they catalyze reverse as well as forward reactions, and in some cases this has physiological significance: for example, alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde in animals, but in yeast it catalyzes the production of ethanol from acetaldehyde. IUBMB Classification Oxidoreductases, enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, constitute Class EC 1 of the IUBMB classification of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Any of these may be called dehydrogenases, especially those in which NAD+ is the electron acceptor (oxidant), but reductase is also used when the physiological emphasis on reduction of the substrate, and oxidase is used ''only'' when O2 is the electron acceptor. The systematic name of an oxidoreductase is "donor:acceptor oxidore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |