|
Uncinocarpus Reesii
''Uncinocarpus reesii'' is a species of saprotrophic microfungi that grows in soil and on keratinous materials such as hair, feathers and skin. It was the first species to be designated as part of the genus ''Uncinocarpus'', owing in part to its characteristic development of hooked (uncinate) appendages. As the closest non-pathogenic relative of ''Coccidioides immitis'' and ''Coccidioides posadasii, C. posadasii'', it has become a subject of research interest. History and taxonomy ''Uncinocarpus reesii'' was first recognized under the name ''Gymnoascus uncinatus'' by German taxonomist species:Michael Emil Eduard Eidam, Michael Emil Eduard Eidam in 1893. The species is named after Robert Rees, an Australian mycologist who provided isolates of ''G. uncinatus'' to Lynne Sigler and G.F. Orr, who in 1976 proposed the re-designation of this species as the first a new genus: ''Uncinocarpus''. This redesignation was based largely in part due to the species' characteristic development of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprotrophic
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (for example ''Mucor'') and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes; saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( sapro- 'rotten material' + -phyte 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of saprotrophs and their internal nutrition, as well as the main two types of fungi that are most often referred to, as well as describes, visually, the process of saprotrophic nutrition through a diagram of hyph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
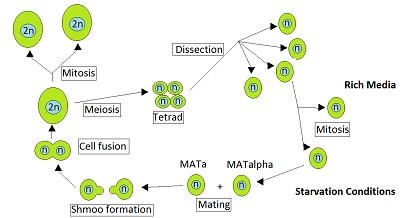
Heterothallic
Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals. The term is applied particularly to distinguish heterothallic fungi, which require two compatible partners to produce sexual spores, from homothallic ones, which are capable of sexual reproduction from a single organism. In heterothallic fungi, two different individuals contribute nuclei to form a zygote. Examples of heterothallism are included for ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus'', ''Penicillium marneffei'' and ''Neurospora crassa''. The heterothallic life cycle of ''N. crassa'' is given in some detail, since similar life cycles are present in other heterothallic fungi. Life cycle of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' The yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' is heterothallic. This means that each yeast cell is of a certain mating type and can only mate with a cell of the other mating type. During vegetative growth that ordinarily occurs when nutrients are abundant, ''S. cerev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onygenales
The Onygenales are an order of fungi in the class Eurotiomycetes and division Ascomycota. The order's last common ancestor is estimated to have lived 150 million years ago. Onygenales can consume and break down keratin, the main component of the outer layer of skin. They are primarily found on animals, droppings, and areas frequented by animals. Many are dimorphic, and can change from mold to yeast form depending on their environment. Many onygenalean fungi are pathogens. One species, ''Trichophyton rubrum'', is the primary cause of athlete's foot. This order also includes Coccidioides implicated in Valley fever. The Onygenales are important as emerging human pathogens because of the rising rates of immunosuppression due to live-organ transplant, HIV/AIDS, and autoimmune disorders such as lupus erythematosus Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracoccidioides
The Ajellomycetaceae are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota, class Eurotiomycetes Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more tha .... The family contains eight genera. References Onygenales Ascomycota families Taxa described in 2004 {{Eurotiomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidioides
''Coccidioides'' is a genus of dimorphic ascomycetes in the family Onygenaceae. Member species are the cause of coccidioidomycosis, also known as San Joaquin Valley fever, an infectious fungal disease largely confined to the Western Hemisphere and endemic in the Southwestern United States. The host acquires the disease by respiratory inhalation of spores disseminated in their natural habitat. The causative agents of coccidioidomycosis are ''Coccidioides immitis'' and ''Coccidioides posadasii''. Both ''C. immitis'' and ''C. posadasii'' are indistinguishable during laboratory testing and commonly referred in literature as ''Coccidioides''. Clinical presentation Coccidioidomycosis is amazingly diverse in terms of its scope of clinical presentation, as well as clinical severity. About 60% of ''Coccidioides'' infections as determined by serologic conversion are asymptomatic. The most common clinical syndrome in the other 40% of infected patients is an acute respiratory ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascospore
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. ''Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. ''Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some ''Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the "bourrelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascocarp
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buff (colour)
Buff (latin ''bubalinus'') is a light brownish yellow, ochreous colour, typical of buff leather. Buff is a mixture of yellow ochre and white: two parts of white lead and one part of yellow ochre produces a good buff, or white lead may be tinted with French ochre alone. As an RYB quaternary colour, it is the colour produced by an equal mix of the tertiary colours citron and russet. Etymology The first recorded use of the word ''buff'' to describe a colour was in ''The London Gazette'' of 1686, describing a uniform to be "...a Red Coat with a Buff-colour'd lining". It referred to the colour of undyed buffalo leather, such as soldiers wore as some protection: an eyewitness to the death in the Battle of Edgehill (1642) of Sir Edmund Verney noted "he would neither put on arms rmouror buff coat the day of the battle". Such buff leather was suitable for ''buffing'' or serving as a ''buffer'' between polished objects. It is not clear which bovine "''buffalo''" referred to, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinocarpus Reesii Colony
''Uncinocarpus'' is a genus of fungi within the Onygenaceae family. The name is derived from the Latin word ''uncinus'', meaning "hook" and the Greek word ''karpos'' (καρπός), meaning "fruit". It was distinguished from the genus ''Gymnoascus'' based on keratinolytic capacity, ascospore morphology and the development of hooked, occasionally spiraling appendages. Alternatively, ''Uncinocarpus'' species may possess helically coiled or smooth, wavy appendages, or lack appendages altogether, an example of such species being '' U. orissi''. Being a close non-pathogenic relative of the pathogenic dimorphic fungi Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii, which cause Coccidioidomycosis, it is used in genomic research to help develop human vaccination, which might alleviate the Valley fever A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onygenaceae
The Onygenaceae are a family (biology), family of fungi in the Ascomycota, class Eurotiomycetes. Genera These are the genera that are in the Onygenaceae, according to a 2021 review of fungal classification. Following the genus name is the Author citation (botany), taxonomic authority (those who first circumscribed the genus; standardized author abbreviations are used), year of publication, and the estimated number of species. * ''Amauroascus'' – 15 spp. * ''Aphanoascus'' – 18 spp. * ''Apinisia'' – 3 spp. * ''Arachnotheca'' – 1 sp. * ''Ascocalvatia'' – 1 sp. * ''Auxarthron'' – 13 spp. * ''Auxarthronopsis'' – 2 spp. * ''Bifidocarpus'' – 2 spp. * ''Byssoonygena'' – 1 sp. * ''Canomyces'' – 1 sp. * ''Castanedomyces'' – 1 sp. * ''Chlamydosauromyces'' – 1 sp. * ''Chrysosporium'' – 66 spp. * ''Coccidioides'' – 6 spp. * ''Currahomyces'' – 1 sp. * ''Kuehniella'' – 2 spp. * ''Leucothecium'' – 3 spp. * ''Malbranchea'' – 23 spp. * ''Myoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |