|
Ultra Trencher 1
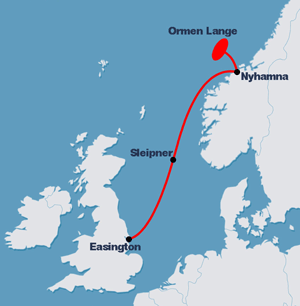
Ultra Trencher 1 (UT1) is (as of 2008) the world's largest submersible robot, used for burying submarine pipelines in a trench in the sea floor. Roland Piquepaille"The world’s biggest subsea robot" ZDNet.com It has a mass of 60 tons and measures 7.8 metres long, 7.8 metres wide, and 5.6 metres tall. It costs roughly £10 million. It can move at a speed of 2 to 3 knots when submerged and can trench pipelines with a 1-meter diameter in water up to 1,500 metres deep. It uses a pair of "jet swords" to create the trench by injecting pressurized water into the sediment. UT1 is manufactured by the Newcastle upon Tyne company Soil Machine Dynamics Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former t .... References Robotic submarines {{robot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersible
A submersible is a small watercraft designed to operate underwater. The term "submersible" is often used to differentiate from other underwater vessels known as submarines, in that a submarine is a fully self-sufficient craft, capable of independent cruising with its own power supply and air renewal system, whereas a submersible is usually supported by a nearby ship, surface vessel, very large floating structure, platform, shore team or sometimes a larger submarine. In common usage by the general public, however, the word "submarine" may be used to describe a craft that is by the technical definition actually a submersible. There are many types of submersibles, including both crewed and uncrewed craft, otherwise known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Submersibles have many uses worldwide, such as oceanography, underwater archaeology, ocean exploration, adventure, equipment maintenance and recovery, and underwater videography. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' ( ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' (TOPIO) to industrial robots, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Autonomous things are expected to proliferate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Pipeline
A submarine pipeline (also known as marine, subsea or offshore pipeline) is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench.Dean, p. 338-340Gerwick, p. 583-585 In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it crosses water expanses, such as small seas, straits and rivers.Palmer & King, p. 2-3 Submarine pipelines are used primarily to carry oil or gas, but transportation of water is also important. A distinction is sometimes made between a ''flowline'' and a pipeline.Bai & Bai, p. 22 The former is an ''intrafield'' pipeline, in the sense that it is used to connect subsea wellheads, manifolds and the platform ''within'' a particular development field. The latter, sometimes referred to as an ''export pipeline'', is used to bring the resource to shore. Sizeable pipeline construction projects need to take into account many factors, such as the offshore ecology, geohazards and environmental loading – they are often undertaken by multidisciplinary, interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit). In geology, trenches result from erosion by rivers or by geological movement of tectonic plates. In civil engineering, trenches are often created to install underground utilities such as gas, water, power and communication lines. In construction, trenches are dug for foundations of buildings, retaining walls and dams, and for cut-and-cover construction of tunnels. In archaeology, the "trench method" is used for searching and excavating ancient ruins or to dig into strata of sedimented material. In geotechnical engineering, trenches serve for locating faults and investigating deep soil properties. In trench warfare, soldiers occupy trenches to protect them against weapons fire. Trenches are dug by use of manual tools such as shovels and pickaxes, or by heavy equipment such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile definition in 1970, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for the diameter of a sphere. In more modern usage, the length d of a diameter is also called the diameter. In this sense one speaks of diameter rather than diameter (which refers to the line segment itself), because all diameters of a circle or sphere have the same length, this being twice the radius r. :d = 2r \qquad\text\qquad r = \frac. For a convex shape in the plane, the diameter is defined to be the largest distance that can be formed between two opposite parallel lines tangent to its boundary, and the is often defined to be the smallest such distance. Both quantities can be calculated efficiently using rotating calipers. For a curve of constant width such as the Reuleaux triangle, the width and diameter are the same because all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manometric u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water (fluvial processes), but also wind (aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. Glacial moraine deposits and till are ice-transported sediments. Classification Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain shape, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle Upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is also the most populous city of North East England. Newcastle developed around a Roman settlement called Pons Aelius and the settlement later took the name of a castle built in 1080 by William the Conqueror's eldest son, Robert Curthose. Historically, the city’s economy was dependent on its port and in particular, its status as one of the world's largest ship building and repair centres. Today, the city's economy is diverse with major economic output in science, finance, retail, education, tourism, and nightlife. Newcastle is one of the UK Core Cities, as well as part of the Eurocities network. Famous landmarks in Newcastle include the Tyne Bridge; the Swing Bridge; Newcastle Castle; St Thomas’ Church; Grainger Town including G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Machine Dynamics
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter Organic matter, organic material, or natural organic matter refers to the large source of carbon-based compounds found within natural and engineered, terrestrial, and aquatic environments. It is matter composed of organic compounds that have c ..., minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a Porosity, porous phase that holds Soil gas, gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-state of matter, state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, terrain, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |