|
Uffizi 16, Francesco Ferrucci
The Uffizi Gallery (; it, Galleria degli Uffizi, italic=no, ) is a prominent art museum located adjacent to the Piazza della Signoria in the Historic Centre of Florence in the region of Tuscany, Italy. One of the most important Italian museums and the most visited, it is also one of the largest and best known in the world and holds a collection of priceless works, particularly from the period of the Italian Renaissance. After the ruling House of Medici died out, their art collections were given to the city of Florence under the famous ''Patto di famiglia'' negotiated by Anna Maria Luisa, the last Medici heiress. The Uffizi is one of the first modern museums. The gallery had been open to visitors by request since the sixteenth century, and in 1765 it was officially opened to the public, formally becoming a museum in 1865. History The building of the Uffizi complex was begun by Giorgio Vasari in 1560 for Cosimo I de' Medici so as to accommodate the offices of the Florentine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uffizi Gallery Logo
The Uffizi Gallery (; it, Galleria degli Uffizi, italic=no, ) is a prominent art museum located adjacent to the Piazza della Signoria in the Historic Centre of Florence in the region of Tuscany, Italy. One of the most important Italian museums and the most visited, it is also one of the largest and best known in the world and holds a collection of priceless works, particularly from the period of the Italian Renaissance. After the ruling House of Medici died out, their art collections were given to the city of Florence under the famous ''Patto di famiglia'' negotiated by Anna Maria Luisa, the last Medici heiress. The Uffizi is one of the first modern museums. The gallery had been open to visitors by request since the sixteenth century, and in 1765 it was officially opened to the public, formally becoming a museum in 1865. History The building of the Uffizi complex was begun by Giorgio Vasari in 1560 for Cosimo I de' Medici so as to accommodate the offices of the Florentine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; it, Toscana ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of about 3.8 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence (''Firenze''). Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its influence on high culture. It is regarded as the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance and of the foundations of the Italian language. The prestige established by the Tuscan dialect's use in literature by Dante Alighieri, Petrarch, Giovanni Boccaccio, Niccolò Machiavelli and Francesco Guicciardini led to its subsequent elaboration as the language of culture throughout Italy. It has been home to many figures influential in the history of art and science, and contains well-known museums such as the Uffizi and the Palazzo Pitti. Tuscany is also known for its wines, including Chianti, Vino Nobile di Montepulciano, Morellino di Scansano, Brunello di Montalcino and white Vernaccia di San Gimignano. Having a strong linguisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statues In Niches Outside The Uffizi Gallery, Florence
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size; a sculpture that represents persons or animals in full figure but that is small enough to lift and carry is a statuette or figurine, whilst one more than twice life-size is a colossal statue. Statues have been produced in many cultures from prehistory to the present; the oldest-known statue dating to about 30,000 years ago. Statues represent many different people and animals, real and mythical. Many statues are placed in public places as public art. The world's tallest statue, ''Statue of Unity'', is tall and is located near the Narmada dam in Gujarat, India. Color Ancient statues often show the bare surface of the material of which they are made. For example, many people associate Greek classical art with white marble sculpture, but there is evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loggiato Degli Uffizi
The Loggiato is the semi-enclosed courtyard ( it, cortile) space between the two long galleries of the Uffizi Gallery located adjacent to the Piazza della Signoria in the historic center of Florence, capital of Tuscany, Italy. Because the facade of the arcaded corridor parallel to the Arno River also continues the sculptural display of the cortile, it can also be included in the description. History and Description In addition, to hosting the entrance to the museum housed in the upper galleries, the loggiato is known for its display of statues of ''famous Tuscans'' housed in niches carved from the inner ground floor pilasters. It is stated that Cosimo I de Medici for his original plan for the Uffizi planned to display statues of famous Tuscans in the ground floor. In 1574, just before the death of Cosimo, the sculptor Vincenzo Danti had his statue of the former Duke placed in the ground floor. His son, Francesco, in 1584 substituted this statue with one by Giambologna, standing on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
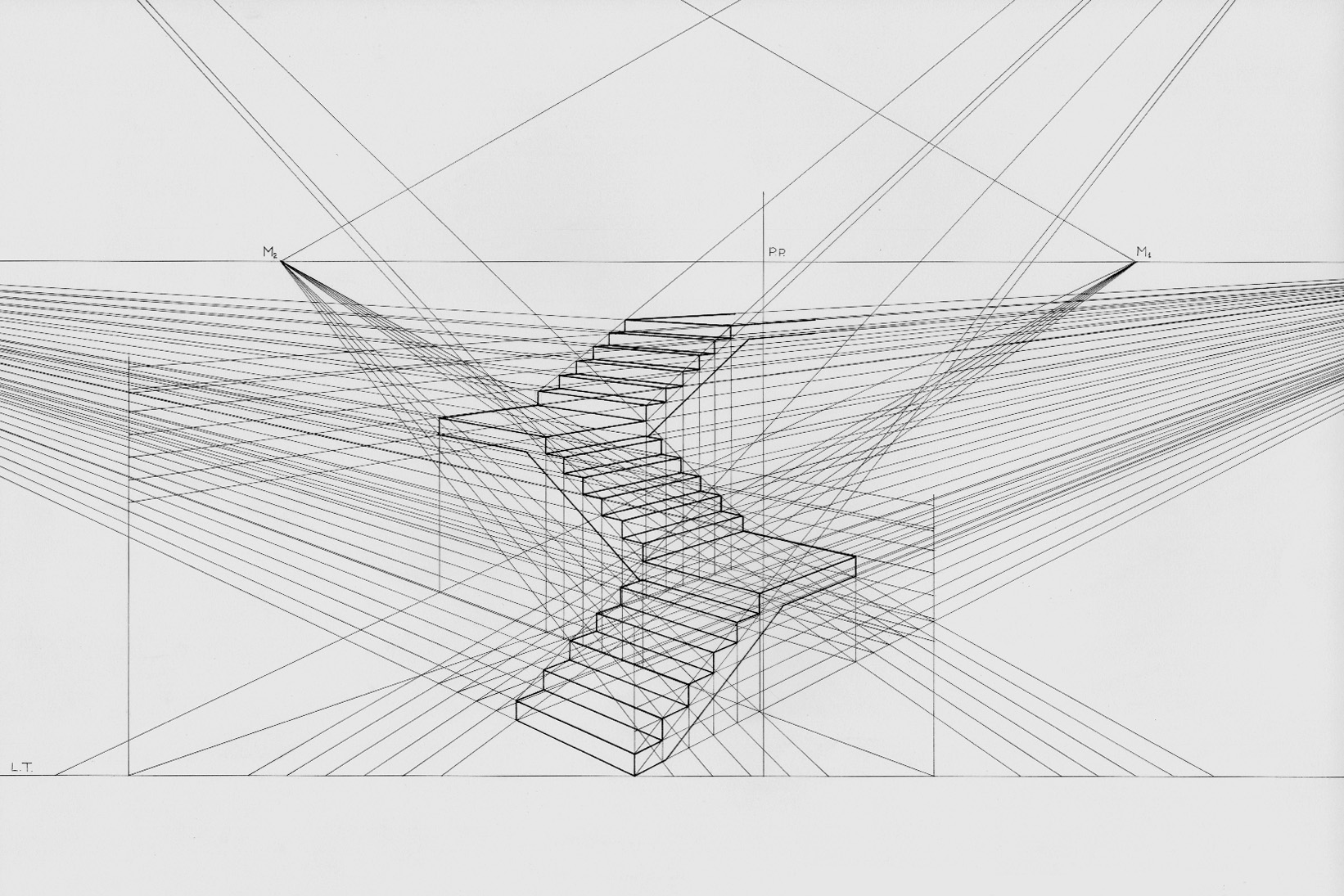
Perspective (visual)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigfried Giedion
Sigfried Giedion (sometimes misspelled Siegfried Giedion; 14 April 1888, Prague – 10 April 1968, Zürich) was a Bohemian-born Swiss historian and critic of architecture. His ideas and books, ''Space, Time and Architecture'', and ''Mechanization Takes Command'', had an important conceptual influence on the members of the Independent Group at the Institute of Contemporary Arts in the 1950s. Giedion was a pupil of Heinrich Wölfflin. He was the first secretary-general of the Congrès International d'Architecture Moderne, and taught at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard University, and the ETH-Zurich. In ''Space, Time & Architecture'' (1941), Giedion wrote an influential standard history of modern architecture, while ''Mechanization Takes Command'' established a new kind of historiography. Biography Sigfried Giedion was the son of a textile manufacturer from Zugersee. He graduated from the University of Vienna in 1913 with a degree in engineering. Not wanting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardo Buontalenti
Bernardo Buontalenti (), byname of Bernardo Delle Girandole ( 1531 – June 1608), was an Italian stage designer, architect, theatrical designer, military engineer and artist and inventor of italian ice cream. Biography Buontalenti was born in Florence. He entered the service of the Medici as a youth and remained with them the rest of his life. He is said to have been instructed in painting by Salviati and Bronzino, in sculpture by Michelangelo Buonarroti, in architecture by Giorgio Vasari, and in miniature painting under Giulio Clovio. He executed a number of miniatures for Francesco, the son of Cosimo I. More than a painter, he was celebrated as an architect; in this role he was much employed in the design of fortifications, villas, and gardens and is considered one of the most important architects of the Mannerist period. He was also a great mechanic, and an excellent mathematician. In 1562 he travelled to Spain. His first known work is from 1568, the Palazzo di Bianca Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfonso Parigi The Elder
Alfonso Parigi (died 1590) was an Italian architect and designer working in Florence for the Grand Duke of Tuscany. His major commission was the completion of Giorgio Vasari's Palazzo degli Uffizi. His main works are all in Florence, and include: *The palazzo of the Archiconfraternità di Misericordia, an ancient charitable foundation devoted to helping the wounded and sick, rebuilt 1575–78, partly remodelled ito designs by Stefano Diletti, 1781. * At Santa Trinita he rebuilt the convent cloister, working to designs of Buontalenti, beginning in 1584. His son Giulio worked also as architect for the House of Medici The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Mug .... References * 1590 deaths Architects from Florence 16th-century Italian architects Year of birth unknown [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosimo I De' Medici, Grand Duke Of Tuscany
Cosimo I de' Medici (12 June 1519 – 21 April 1574) was the second Duke of Florence from 1537 until 1569, when he became the first Grand Duke of Tuscany, a title he held until his death. Life Rise to power Cosimo was born in Florence on 12 June 1519, the son of the famous condottiere Ludovico de' Medici (known as Giovanni delle Bande Nere) and his wife Maria Salviati, herself a granddaughter of Lorenzo the Magnificent. He was the grandson of Caterina Sforza, the Countess of Forlì and Lady of Imola. Cosimo came to power in 1537 at age 17, just after the 26-year-old Duke of Florence, Alessandro de' Medici, was assassinated. Cosimo was from a different branch of the Medici family, descended from Giovanni il Popolano, the great-grandson of Giovanni di Bicci de' Medici, founder of the Medici Bank. It was necessary to search for a successor outside of the "senior" branch of the Medici family descended from Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici, since the only male child of Alessandro, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giorgio Vasari
Giorgio Vasari (, also , ; 30 July 1511 – 27 June 1574) was an Italian Renaissance Master, who worked as a painter, architect, engineer, writer, and historian, who is best known for his work ''The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects'', considered the ideological foundation of all art-historical writing, and the basis for biographies of several Renaissance artists, including Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo. Vasari designed the ''Tomb of Michelangelo'' in the Basilica of Santa Croce, Florence that was completed in 1578. Based on Vasari's text in print about Giotto's new manner of painting as a ''rinascita'' (rebirth), author Jules Michelet in his ''Histoire de France'' (1835) suggested adoption of Vasari's concept, using the term ''Renaissance'' (rebirth, in French) to distinguish the cultural change. The term was adopted thereafter in historiography and still is in use today. Life Vasari was born prematurely on 30 July 1511 in Arezzo, Tuscany. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uffizi Gallery - Michelangelo Painting "Tondo Doni"
The Uffizi Gallery (; it, Galleria degli Uffizi, italic=no, ) is a prominent art museum located adjacent to the Piazza della Signoria in the Historic Centre of Florence in the region of Tuscany, Italy. One of the most important Italian museums and the most visited, it is also one of the largest and best known in the world and holds a collection of priceless works, particularly from the period of the Italian Renaissance. After the ruling House of Medici died out, their art collections were given to the city of Florence under the famous ''Patto di famiglia'' negotiated by Anna Maria Luisa, the last Medici heiress. The Uffizi is one of the first modern museums. The gallery had been open to visitors by request since the sixteenth century, and in 1765 it was officially opened to the public, formally becoming a museum in 1865. History The building of the Uffizi complex was begun by Giorgio Vasari in 1560 for Cosimo I de' Medici so as to accommodate the offices of the Florentine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
