|
USS Thach (FFG-43)
USS ''Thach'' (FFG-43), an , was the only ship of the United States Navy named for Admiral John Thach, a Naval Aviator during World War II, who invented the Thach Weave dogfighting tactic. Construction and design ''Thach'' was laid down on 6 March 1981 by the Todd Pacific Shipyards, Los Angeles Division, San Pedro, California; launched on 18 December 1982; sponsored by Mrs. Madalyn J. Thach, widow of the namesake; and commissioned on 17 March 1984 at Long Beach. ''Thach''s mission was to provide anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine protection for carrier battle groups, naval expeditionary forces, replenishment groups, convoys, and other military and merchant shipping. The new direction for the naval service remained focused on the ability to project power from the sea in the critical littoral regions for the world. Success in the warfare environment of the 1990s and beyond required thorough evaluation, rapid decision-making and almost instantaneous response to any pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogfight
A dogfight, or dog fight, is an aerial battle between fighter aircraft conducted at close range. Dogfighting first occurred in Mexico in 1913, shortly after the invention of the airplane. Until at least 1992, it was a component in every major war, though with steadily declining frequency. Since then, longer-range weapons have made dogfighting largely obsolete. Modern terminology for air-to-air combat is air combat maneuvering (ACM), which refers to tactical situations requiring the use of individual basic fighter maneuvers (BFM) to attack or evade one or more opponents. This differs from aerial warfare, which deals with the strategy involved in planning and executing various missions. Etymology The term ''dogfight'' has been used for centuries to describe a melee: a fierce, fast-paced close quarters battle between two or more opponents. The term gained popularity during World War II, although its origin in air combat can be traced to the latter years of World War I. One of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 by both sides. Iraq's primary rationale for the attack against Iran cited the need to prevent Ruhollah Khomeini—who had spearheaded Iran's Islamic Revolution in 1979—from exporting the new Iranian ideology to Iraq; there were also fears among the Iraqi leadership of Saddam Hussein that Iran, a theocratic state with a population predominantly composed of Shia Muslims, would exploit sectarian tensions in Iraq by rallying Iraq's Shia majority against the Baʽathist government, which was officially secular and dominated by Sunni Muslims. Iraq also wished to replace Iran as the power player in the Persian Gulf, which was not seen as an achievable objective prior to the Islamic Revolution because of Pahlavi Iran's economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
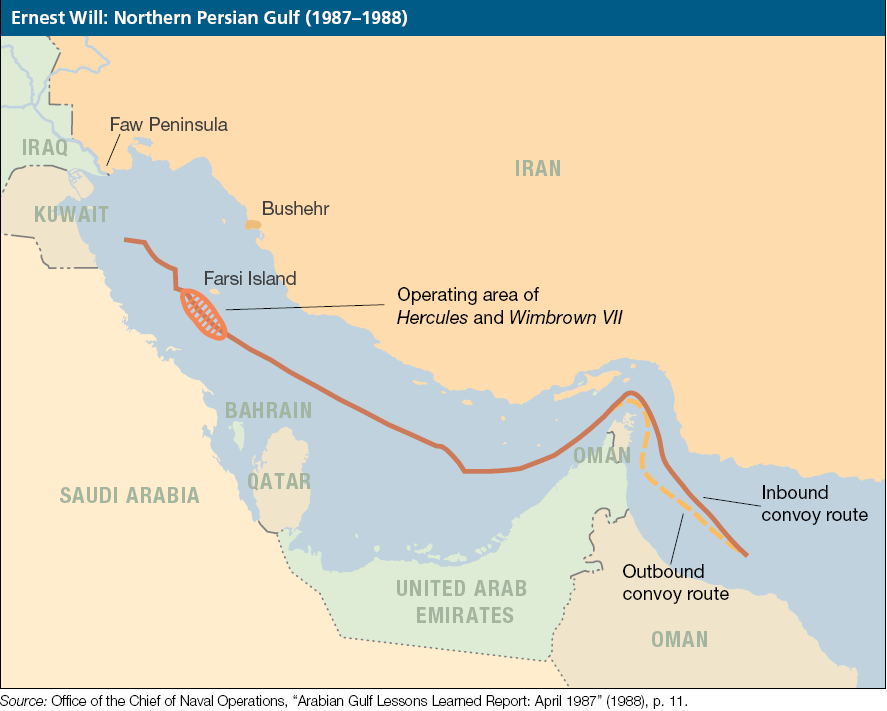
Operation Earnest Will
Operation Earnest Will (24 July 1987 – 26 September 1988) was the American military protection of Kuwaiti-owned tankers from Iranian attacks in 1987 and 1988, three years into the Tanker War phase of the Iran–Iraq War. It was the largest naval convoy operation since World War II. The U.S. Navy warships that escorted the tankers, part of U.S. Naval Forces Central Command, were the operations' most visible part, but U.S. Air Force AWACS radar planes provided surveillance and U.S. Army special-operations helicopters hunted for possible attackers. Other U.S. Navy vessels participated in Operation Earnest Will. They were then under the command of the U.S. Navy's Seventh Fleet which had primary responsibility for combat operations in the Persian Gulf. The numerous ships used in Operation Earnest Will mostly consisted of Carrier Battle Groups, Surface Action Groups and ships from the Pacific's Third and Seventh Fleets and the Mediterranean-based Sixth Fleet. They generally operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
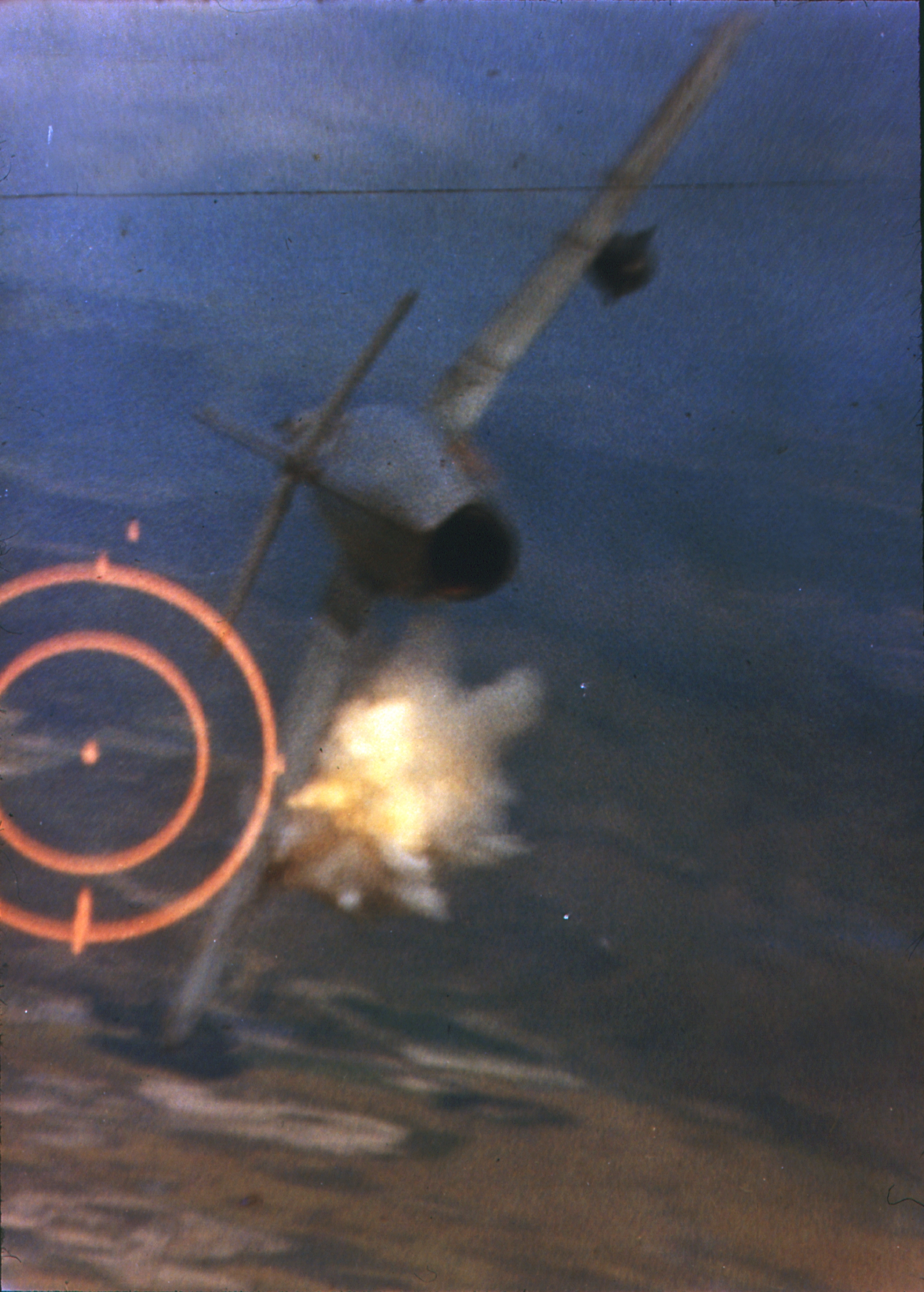
Operation Nimble Archer
Operation Nimble Archer was the 19 October 1987 attack on two Iranian oil platforms in the Persian Gulf by United States Navy forces. The attack was a response to Iran's missile attack three days earlier on , a reflagged Kuwaiti oil tanker at anchor off Kuwait. The action occurred during Operation Earnest Will, the effort to protect Kuwaiti shipping amid the Iran–Iraq War. Iran subsequently filed a lawsuit against the United States for reparations at the International Court of Justice. The Court ruled, by 14 votes to two, that the retaliatory attacks by the U.S. Navy against certain Iranian oil platforms in the Persian Gulf in 1987 and 1988 constituted an unlawful use of force but did not violate 1955 Treaty of Amity. Operation On 16 October, ''Sea Isle City'' was in Kuwaiti waters, waiting to be loaded. It had been escorted there by U.S. warships, but was not under their protection at the time. An Iranian Silkworm missile launched from the Iranian-occupied Al-Faw Peninsula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
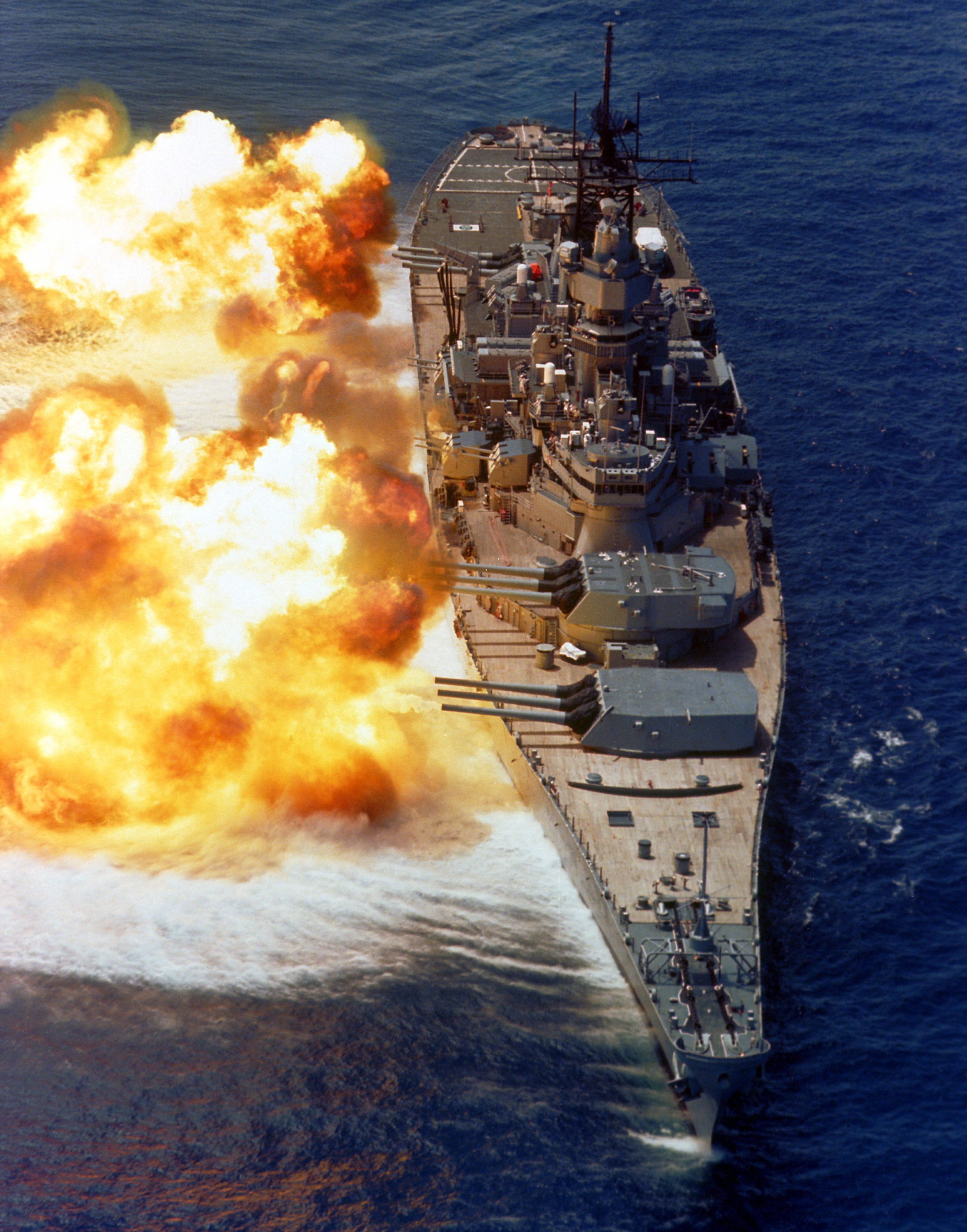
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ironclad warship,Stoll, J. ''Steaming in the Dark?'', Journal of Conflict Resolution Vol. 36 No. 2, June 1992. now referred to by historians as pre-dreadnought battleships. In 1906, the commissioning of into the United Kingdom's Royal Navy heralded a revolution in the field of battleship design. Subsequent battleship designs, influenced by HMS ''Dreadnought'', were referred to as "dreadnoughts", though the term eventually became obsolete as dreadnoughts became the only type of battleship in common use. Battleships were a symbol of naval dominance and national might, and for decades the battleship was a major factor in both diplomacy and military strategy.Sondhaus, L. ''Naval Warfare 1815–1914'', . A global arms race in battleship cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer Squadron 21
A destroyer squadron is a naval squadron or flotilla usually consisting of destroyers rather than other types of vessel. In some navies other vessels, such as frigates, may be included. In English the word "squadron" tends to be used for larger and "flotilla" for smaller vessels; both may be used for destroyer units. Similar formations are used in non-English-speaking countries, e.g., the "escadrille"—which would translate directly as "squadron"—in France. Royal Navy The Royal Navy began to form units of destroyers after the introduction of 'torpedo boat destroyers' in the early 1900s though pre-World War Two they were usually designated flotillas. RN destroyer units are listed in the main article above examples of some destroyer squadrons below. * 1st Destroyer Squadron, 1947-1970 * 2nd Destroyer Squadron, 1956-1971 * 3rd Destroyer Squadron, 1945-2001 * 4th Destroyer Squadron, 1948-1959 * 5th Destroyer Squadron, 1947-2002 US Navy The U.S. Navy acronym for a destroyer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DC-10
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas. The DC-10 was intended to succeed the DC-8 for long-range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; it was introduced on August 5, 1971, by American Airlines. The trijet has two turbofans on underwing pylons and a third one at the base of the vertical stabilizer. The twin-aisle layout has a typical seating for 270 in two classes. The initial DC-10-10 had a range for transcontinental flights. The DC-10-15 had more powerful engines for hot and high airports. The DC-10-30 and −40 models (with a third main landing gear leg to support higher weights) each had intercontinental ranges of up to . The KC-10 Extender (based on the DC-10-30) is a U.S. Air Force tanker. A design flaw in the original cargo doors caused a poor safety record in early operations. Following the American Airlines Flight 191 crash (the deadliest aviation accident in US history), the US Federal Aviati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the direction of flow: * a rotating gas compressor * a combustor * a compressor-driving turbine. Additional components have to be added to the gas generator to suit its application. Common to all is an air inlet but with different configurations to suit the requirements of marine use, land use or flight at speeds varying from stationary to supersonic. A propelling nozzle is added to produce thrust for flight. An extra turbine is added to drive a propeller (turboprop) or ducted fan (turbofan) to reduce fuel consumption (by increasing propulsive efficiency) at subsonic flight speeds. An extra turbine is also required to drive a helicopter rotor or land-vehicle transmission (turboshaft), marine propeller or electrical generator (power turbine). Greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikorsky SH-60 Seahawk
The Sikorsky SH-60/MH-60 Seahawk (or Sea Hawk) is a twin turboshaft engine, multi-mission United States Navy helicopter based on the United States Army UH-60 Black Hawk and a member of the Sikorsky S-70 family. The most significant modifications are the folding main rotor and a hinged tail to reduce its footprint aboard ships. The U.S. Navy uses the H-60 airframe under the model designations SH-60B, SH-60F, HH-60H, MH-60R, and MH-60S. Able to deploy aboard any air-capable frigate, destroyer, cruiser, fast combat support ship, expeditionary transfer dock, amphibious assault ship, littoral combat ship or aircraft carrier, the Seahawk can handle anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-surface warfare (ASUW), naval special warfare (NSW) insertion, search and rescue (SAR), combat search and rescue (CSAR), vertical replenishment (VERTREP), and medical evacuation (MEDEVAC). Design and development Origins During the 1970s, the U.S. Navy began looking for a new helicopter to replace the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Battle Group
A carrier battle group (CVBG) is a naval fleet consisting of an aircraft carrier capital ship and its large number of escorts, together defining the group. The ''CV'' in ''CVBG'' is the United States Navy hull classification code for an aircraft carrier. The first naval task forces built around carriers appeared just prior to and during World War II. The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) was the first to assemble many carriers into a single task force, known as ''Kido Butai''. This task force was used with devastating effect in the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Kido Butai operated as the IJN's main carrier battle group until four of its carriers were sunk at the Battle of Midway. In contrast, the United States Navy deployed its large carriers in separate formations, with each carrier assigned its own cruiser and destroyer escorts. These single-carrier formations would often be paired or grouped together for certain assignments, most notably the Battle of the Coral Sea and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |