|
Triumf Front Signboard
TRIUMF is Canada's national particle accelerator centre. It is considered Canada's premier physics laboratory, and consistently regarded as one of the world's leading subatomic physics research centers. Owned and operated by a consortium of universities, it is on the south campus of one of its founding members, the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia. It houses the world's largest cyclotron, a source of 520 MeV protons, which was named an IEEE Milestone in 2010. Its accelerator-focused activities involve particle physics, nuclear physics, nuclear medicine, materials science, and detector and accelerator development. Over 500 scientists, engineers, technicians, tradespeople, administrative staff, postdoctoral fellows, and students work at the site. It attracts over 1000 national and international researchers every year, and has generated over $1 billion in economic activity over the last decade. To develop TRIUMF's research priorities, physicists base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January 26, 1932, granted: February 20, 1934 A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention. The cyclotron was the first "cyclical" accelerator. The primary accelerators before the development of the cyclotron were electrostatic accelerators, such as the Cockcroft–Walton accelerator and Van de Graaff generator. In these accelerators, particles would cross an accelerating electric field only once. Thus, the energy gained by the particles was limited by the maximum elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triumf Front Signboard
TRIUMF is Canada's national particle accelerator centre. It is considered Canada's premier physics laboratory, and consistently regarded as one of the world's leading subatomic physics research centers. Owned and operated by a consortium of universities, it is on the south campus of one of its founding members, the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia. It houses the world's largest cyclotron, a source of 520 MeV protons, which was named an IEEE Milestone in 2010. Its accelerator-focused activities involve particle physics, nuclear physics, nuclear medicine, materials science, and detector and accelerator development. Over 500 scientists, engineers, technicians, tradespeople, administrative staff, postdoctoral fellows, and students work at the site. It attracts over 1000 national and international researchers every year, and has generated over $1 billion in economic activity over the last decade. To develop TRIUMF's research priorities, physicists base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
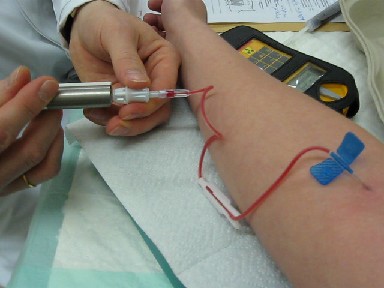
Technetium-99m
Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope in the world. Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role, because it emits readily detectable gamma rays with a photon energy of 140 keV (these 8.8 pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The relatively "short" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiation exposure low. The same characteristics make the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSERC
The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC; french: Conseil de recherches en sciences naturelles et en génie du Canada, CRSNG) is the major federal agency responsible for funding natural sciences and engineering research in Canada. NSERC directly funds university professors and students as well as Canadian companies to perform research and training. With funding from the Government of Canada, NSERC supports the research of over 41,000 students, trainees and professors at universities and colleges in Canada with an annual budget of CA$1.1 billion in 2015. Its current director is Alejandro Adem. NSERC, combined with the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), forms the major source of federal government funding to post-secondary research. These bodies are sometimes collectively referred to as the "Tri-Council" or "Tri-Agency". History NSERC came into existence on 1 May 1978 under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
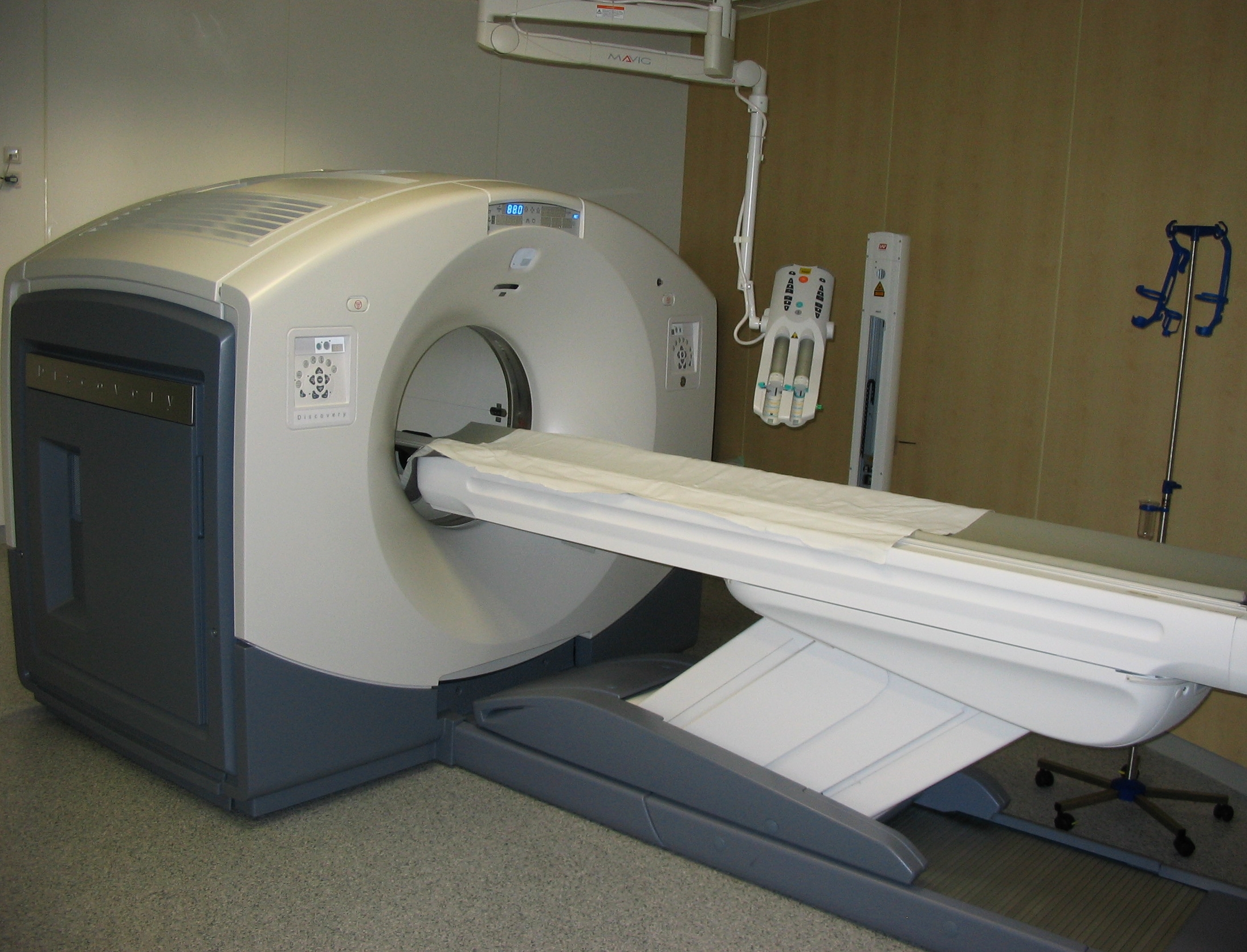
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fullerene
A fullerene is an allotrope of carbon whose molecule consists of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The molecule may be a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, tube, or many other shapes and sizes. Graphene (isolated atomic layers of graphite), which is a flat mesh of regular hexagonal rings, can be seen as an extreme member of the family. Fullerenes with a closed mesh topology are informally denoted by their empirical formula C''n'', often written C''n'', where ''n'' is the number of carbon atoms. However, for some values of ''n'' there may be more than one isomer. The family is named after buckminsterfullerene (C60), the most famous member, which in turn is named after Buckminster Fuller. The closed fullerenes, especially C60, are also informally called buckyballs for their resemblance to the standard ball of association football ("soccer"). Nested closed fullerenes have been named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigel Smith (physicist) , English musical band manager who formed 1990s British boy band Take That
{{hndis, Smith, Nigel ...
Nigel Smith may refer to: * Nigel Smith (footballer, born 1958), English football defender * Nigel Smith (footballer, born 1969), English football striker * Nigel Smith (racing driver) (born 1951), British businessman and retired auto racing driver * Nigel Smith (alpine skier) (born 1964), British former alpine skier * Nigel Smith (literature scholar), British literature professor * Nigel Martin-Smith Nigel Martin-Smith is a Manchester-based English musical band manager. He helped form the 1990s British boy band Take That. Biography Early career Martin-Smith entered the entertainment industry in the early 1980s working as a casting agent fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Bagger
Jonathan Anders Bagger (born August 7, 1955) is an American theoretical physicist, specializing in high energy physics and string theory. He is known for the Bagger–Lambert–Gustavsson action. Biography Bagger received his bachelor's degree in 1977 from Dartmouth College. He spent the academic year 1977–1978 at the University of Cambridge as a Churchill Scholar. In 1978 he became a graduate student in physics at Princeton University, where he received his PhD in 1983. His doctoral thesis ''Matter Couplings in Supergravity Theories'' was supervised by Edward Witten. Bagger was a postdoc from 1983 to 1986 at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center. He was from 1986 to 1989 an associate professor at Harvard University. At Johns Hopkins University he became in 1989 a full professor, holding a professorial chair there until 2014. In 2014 Bagger was appointed director of TRIUMF, Canada’s national laboratory for particle and nuclear physics. Bagger’s research deals with high-ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigel Lockyer
Nigel Stuart Lockyer (born 5 November 1952) is a British-American experimental particle physicist. He was the Director of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), in Batavia, Illinois, the leading particle physics laboratory in the United States, from September 2013 to April 2022. Prior to becoming Fermilab's Director, Lockyer served as Director of TRIUMF, Canada's national laboratory for particle and nuclear physics, from May 2007 to September 2013, and was a Professor of Physics at the University of British Columbia and University of Pennsylvania. He was born in Scotland, raised in Canada, and attended graduate school in the United States. Early life and career Lockyer was born in Annan, Scotland. He received his Bachelor of Science degree in 1975 from York University in Toronto, and in 1980 obtained his Ph.D. from Ohio State University. After receiving his Ph.D., Lockyer spent four years at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory at Stanford University as a post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Astbury
Alan Astbury (1934–2014) was a Canadian physicist, emeritus professor at the University of Victoria, and director of the Tri-Universities Meson Facility (TRIUMF) laboratory. Early life and education He was born in Crewe, England, to Jane and Harold Astbury. His mother worked in a bakery and his father was an engineer for the Co-op Dairy. He went to Nantwich and Acton Grammar School. Although he was a good cricketer and footballer - he played for Crewe Schoolboys along with Chelsea and England player Frank Blunstone - his parents discouraged a career in football. Academic career In 1953, he joined the University of Liverpool, gaining a first-class honours degree in 1956 followed by a PhD in 1959 under Alec Merrison and Hugh Muirhead. He won a Leverhulme Research Fellowship to work on Liverpool's 380 MeV, 1.83m (72 inch) synchrocyclotron, the world's second-largest at the time. The team's work confirmed parity violation in muon capture. He joined Kenneth Crowe's group at B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Vogt
Erich Wolfgang Vogt, (November 12, 1929 - February 19, 2014) was a Canadian physicist. Born into a pacifist Mennonite family in Steinbach, Manitoba Vogt received a Bachelor of Science degree in 1951 and a Master of Science degree in 1952 from the University of Manitoba. He received a Ph.D. from Princeton University in 1955 under the direction of Eugene Wigner. In 1965, he started teaching at the University of British Columbia. From 1975 to 1981, he was the Vice President (Faculty & Student Affairs). He retired in 1994, although he came back in 2000 to teach several 100 level physics courses. He is best known as one of the founders of TRIUMF, Canada's national laboratory of nuclear and particle physics, which utilizes a particle accelerator, located on the University of British Columbia. He was the director from 1981 to 1994. Vogt co-authored and edited 24 volumes of ''Advances of Nuclear Physics'' with John W. Neagle. In 1976, he was made an Officer of the Order of Canada for his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Reginald Richardson
John Reginald Richardson (1912 in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada – 25 November 1997 in Fremont, California) was a Canadian-American physicist and one of the dominant figures in cyclotron development. His many achievements include participation in the first demonstration of phase stability, the development of the first synchrocyclotron and the first sector-focused cyclotron. Richardson grew up in Vancouver until his family emigrated to the US in 1922. He studied physics at UCLA and was a doctoral student in nuclear physics of Ernest Orlando Lawrence at the University of California, Berkeley, receiving his PhD in 1937. After a year at the University of Michigan, he became Assistant Professor at the University of Illinois. From 1942 he worked on electromagnetic isotope separation for the Manhattan Project in Berkeley and Oak Ridge (calutron). In 1946, after the discovery of the phase stability and the synchrotron principle by Weksler and Edwin McMillan, he collaborated with a group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |