|
Trams In Wuhan
Trams in Wuhan may refer to any one of the tram systems currently operational in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China. The first tram started revenue service in Wuhan is the Auto-city T1 Line, which began on July 28, 2017. Subsequently, Optics Valley tram started revenue service from April 1, 2018. Systems Auto-city trams Auto-city T1 line () started revenue service on July 28, 2017, and is the first line of the Auto-city trams. It runs from Chelun Square to Deshenggang in Hanyang District for a length of with 22 stations. At Chelun Square it is transferable to Zhuanyang Boulevard Station on Line 3, Wuhan Metro. The planned Auto-city tram system consists of 14 lines, ranging and has some 277 stations. The line's 21 tramcars were built by CRRC Zhuzhou Locomotive. File:Outside of a Auto-city tram.jpg, Outside of an Auto-city tram File:A signboard for Auto-city trams in Interchange Cannel.jpg, A signboard for Auto-city trams in Interchange Channel File:Inside of the car of Auto-city tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei, Hubei Province in the China, People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the List of cities in China by population, ninth-most populous Chinese city and one of the nine National Central City, National Central Cities of China. The name "Wuhan" came from the city's historical origin from the conglomeration of Wuchang District, Wuchang, Hankou District, Hankou, and Hanyang District, Hanyang, which are collectively known as the "Three Towns of Wuhan" (). Wuhan lies in the eastern Jianghan Plain, at the confluence of the Yangtze river and its largest tributary, the Han River (Hubei), Han River, and is known as "Nine Provinces' Thoroughfare" (). Wuhan has historically served as a busy city port for commerce and trading. Other historical events taking place in Wuhan include the Wuchang Uprising of 1911, which led to the end of 2,000 years of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
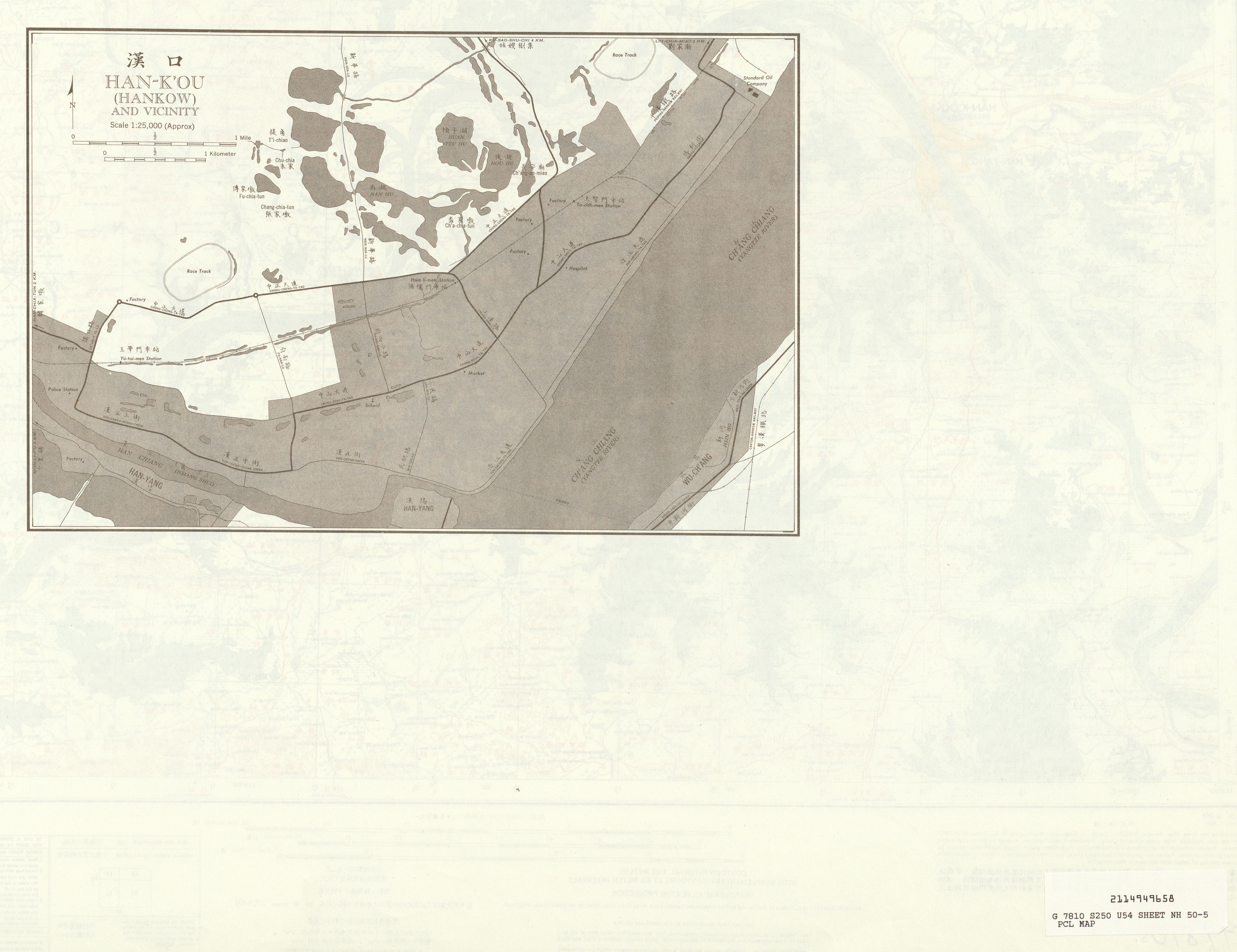
Hankou
Hankou, alternately romanized as Hankow (), was one of the three towns (the other two were Wuchang and Hanyang) merged to become modern-day Wuhan city, the capital of the Hubei province, China. It stands north of the Han and Yangtze Rivers where the Han flows into the Yangtze. Hankou is connected by bridges to its triplet sister towns Hanyang (between Han and Yangtze) and Wuchang (on the south side of the Yangtze). Hankou is the main port of Hubei province and the single largest port in the middle reaches of Yangtze. History The city's name literally means "Mouth of the Han", from its position at the confluence of the Han with the Yangtze River. The name appears in a Tang Dynasty poem by Liu Changqing. Other historical names for the city include Xiakou (), Miankou (), and Lukou (). Hankou, from the Ming to late Qing, was under the administration of the local government in Hanyang, although it was already one of the four major national markets ( :zh:四大名镇) in Ming dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympic Sports Center Station (Wuhan)
Olympic Sports Center station may refer to: *Aoti Zhongxin (Olympic Sports Center) station, on Line 8 of the Beijing Subway, China * Olympic Sports Center station (Chongqing Rail Transit), on the Loop line, China * Olympic Sports Center station (Hangzhou Metro), on Line 6 and Line 7, China * Olympic Sports Center station (Ningbo Rail Transit), on Line 4, China * Olympic Sports Center station (Changzhou Metro), on Line 1 (Changzhou Metro), China * Olympic Sports Center station (Lanzhou Metro), on Line 1 (Lanzhou Metro) Line 1 of the Lanzhou Metro is a subway line in Lanzhou running from to , has 20 stations and is long. It opened on 23 June 2019. History Line 1 started construction on July 9, 2012. Line 1 is with 20 stations. The line is completely undergrou ..., China * Olympic Sports Center station (Zhengzhou Metro), on Line 6 and Line 14 of the Zhengzhou Metro, China * Huangcun station, formerly Olympic Sports Center station, on Line 4 and Line 21 of the Guangzhou Metro, Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhan–Xianning Intercity Railway
Parameters The Wuhan–Xianning intercity railway (), commonly abbreviated as ''Wu-Xian intercity railway'', is a high-speed commuter railway line in Hubei Province of China with double tracks. It connects the provincial capital Wuhan with the city of Xianning, with a number of intermediate stops throughout Wuhan's southern suburbs. The railway is part of Wuhan Metropolitan Area intercity railway system. The railway line is long, and includes 13 stations, from Wuhan's Wuchang railway station to Xianning South railway station in Xianning. Intermediate stations is include Nanhu East railway station (in Wuhan's Guanggu area), several stations in Wuhan's suburban Jiangxia District and in Xianning City (Xian'an District). Although there are already two railway lines between Wuhan and Xianning (the Wuhan–Guangzhou high-speed railway and the older "conventional" Beijing–Guangzhou Railway), the new railway is supposed to complement them, rather than compete with them. Unlike the Wu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Track
Green track (also grassed track or lawn track) is a type of railway track in which the track bed and surrounding area are planted with sod, grass turf or other vegetation as ground cover. It is a popular way of making railways more visually appealing, particularly for trams and light rail, and providing additional urban green space. Aside from the visual improvement, the vegetation provides a number of positive effects, such as noise control, noise reduction, less air pollution, Surface runoff, rainwater runoff mitigation, and reduced urban heat island, urban heat island effect. History The first green tracks were installed in 1905 along in Berlin. Due to the technical challenges they posed, many green tracks were phased out in the following decades, but beginning in the mid-1980s, green tracks have seen a resurgence. Impact Green tracks have a number of positive impacts on the urban environment. Green tracks reduce surface runoff by retaining an estimated 50-70% of the precipit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles
CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles Co., Ltd. () is a Chinese rolling stock manufacturer and a division of the CRRC. While the CRV emerged in 2002, the company's roots date back to the establishment of the Changchun Car Company in 1954. The company became a division of CNR Corporation before its merger with CSR to form the present CRRC. It has produced a variety of rolling stock for customers in China and abroad, including locomotives, passenger cars, multiple units, rapid transit and light rail vehicles. It has established technology transfer partnerships with several foreign railcar manufacturers, including Bombardier Transportation, Alstom, and Siemens Mobility. Joint Ventures In 2004 Alstom won the first high speed train contract in China, supporting CRRC to build 60 CRH5 high speed trains. In November 2016, CRRC won Melbourne suburban train contract for Evolution Rail as Public Private Partnership with Downer Group, Plenary Group. Changchun Bombardier Railway Vehicles Co. Ltd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics Valley Of China
Donghu New Technology Development Zone (), also referred to as Optics Valley () or Guanggu, is a New Technology Development Zone in Wuhan, China. It was established in 1988. In 1991 it was approved as one of the National Economic and Technological Development Zones of China. In 2011 it was designated as a New Technology Development Zone for Optical technology, and since then self-labeled as the "Optics Valley" of China. ,湖北省民营经济网,2008年5月28日查阅。 The Development Zone is situated east of in Wuhan, west of |
Xingfuqiao Station (Wuhan)
Xingfuqiao () is a Metro station, station on Line 5 (Chengdu Metro), Line 5 of the Chengdu Metro in China. It was opened on 27 December 2019. References Railway stations in China opened in 2019 Chengdu Metro stations {{Sichuan-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail. The vehicles are called streetcars or trolleys (not to be confused with trolleybus) in North America and trams or tramcars elsewhere. The first two terms are often used interchangeably in the United States, with ''trolley'' being the preferred term in the eastern US and ''streetcar'' in the western US. ''Streetcar'' or ''tramway'' are preferred in Canada. In parts of the United States, internally powered buses made to resemble a streetcar are often referred to as "trolleys". To avoid further confusion with trolley buses, the American Public Transportation Association (APTA) refers to them as "trolley-replica buses". In the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRRC Zhuzhou Locomotive
CRRC Zhuzhou Locomotive Co., Ltd. is one of the electric locomotive manufacturers in China. It is one of the subsidiaries of CRRC. History Predecessor Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Works was founded in 1936. CRRC Zhuzhou Locomotive Co., Ltd. On 31 August 2005, CSR Group Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Co., Ltd. was spin-off from the locomotive works; the original legal entity of the locomotive works became an intermediate holding company for CSR Group only. After the formation of listed company CSR Corporation Limited, the limited company "CSR Group Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive" became part of the listed portion of the group, and the intermediate holding company remained unlisted. The limited company also renamed to CSR Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Co., Ltd., In 2015 the company was renamed into CRRC Zhuzhou Locomotive Co., Ltd. (). Joint ventures Siemens Traction Equipment Ltd. (STEZ), is a joint venture between Siemens (50%), Zhuzhou CRRC Times Electric (30%) and CRRC Zhuzhou Loco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)