|
Torrington And Marland Railway
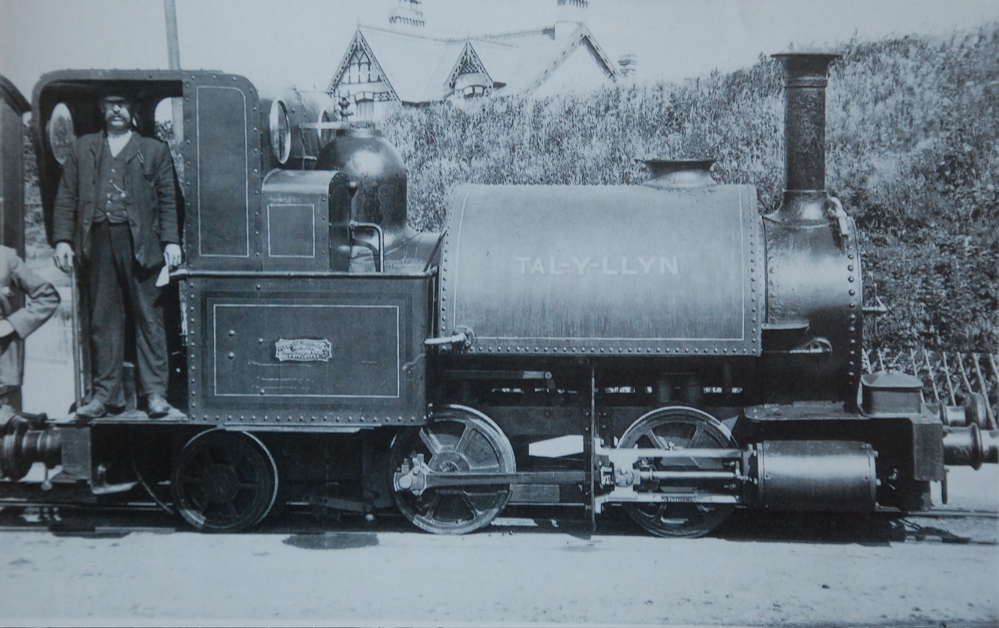
The Torrington and Marland Railway was a narrow gauge built to carry clay from the quarries at Clay Moor to Torrington in north Devon. History The line was surveyed in 1879 by John Barraclough Fell who was also the consulting engineer to the nearby Pentewan Railway. Fell's survey was notable for its use of ten wooden viaducts, which were an unusual feature for a British railway. The railway was a private line, built to serve clay traffic, but part of the agreement with the landowners over whose land it passed was that it would carry local passengers. Steam locomotives were used on both the main railway and the internal lines in the clay pits. In 1925 the main line was replaced with a standard gauge branch of the North Devon and Cornwall Junction Light Railway. The Torrington and Marland was cut back to a 1½ mile stub and the internal quarry lines. These continued in use until 1971 when the line finally closed. Locomotives {, class="wikitable" !Number !Name !Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
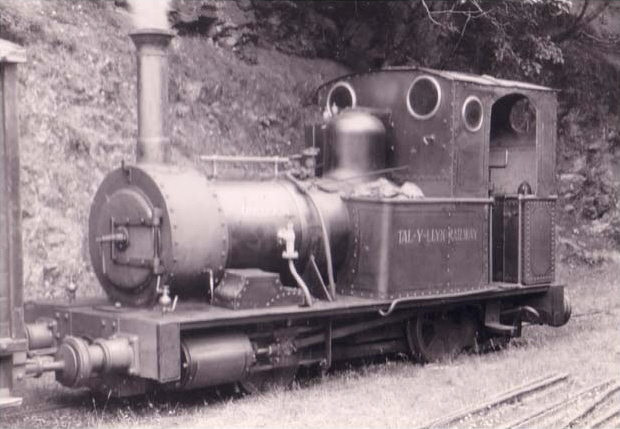
Black, Hawthorn & Co
Black, Hawthorn and Company was a steam locomotive manufacturer with a works situated in Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, UK. John Coulthard and Son The Quarry Field Works was opened in 1835 by John and Ralph Coulthard, known as John Coulthard and Son which became R. Coulthard and Company in 1853 when the partnership was dissolved. Their first loco was York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway number 156, a to the Jenny Lind pattern. There followed more of the same and several engines. Although the works numbers went up to 100, probably only twenty were new, since the company carried out a great deal of rebuilding work. Black, Hawthorn & Co In 1865 Ralph Coulthard retired and the works was taken over by William Black and Thomas Hawthorn, who concentrated on industrial tank locomotives, both four and six coupled. The company supplied steam locomotives to collieries and works, particularly in North East England. They also built a number of crane engines. Some of the locomotives were very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3 Ft Gauge Railways In England
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarka Trail
The Tarka Trail is a series of footpaths and cyclepaths (rail trails) around north Devon, England that follow the route taken by the fictional Tarka the Otter in the book of that name. It covers a total of in a figure-of-eight route, centred on Barnstaple. The section between Braunton and Meeth is car-free, level and mostly tarmacked, and is shared by pedestrians and cyclists, with horseriding also permitted on part of it. The remainder of the route covers a wide variety of landscapes, including wooded river valleys, moorland, coastal cliffs and sandy beaches. Walking varies between easy through to moderate and strenuous, depending on the location, but, in general, it is comprehensively waymarked. The trails are a popular tourist destination and bicycle hire businesses are available for those who wish to cycle along suitable sections of the trail. A section of the Trail is part of National Cycle Network route number 27 and forms part of the route known as the Devon Coas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Narrow Gauge Railways
There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant common carriers to small, short-lived industrial railways. Many notable events in British railway history happened on narrow-gauge railways including the first use of steam locomotives, the first public railway and the first heritage railway, preserved railway. History Early railways: before 1865 The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in coal mines to guide wooden Quarry tub, tubs. Because of the restricted loading gauge of the tunnels and the need for the tubs to be small enough to be pushed by one man, these railways were almost all narrow gauge. These underground lines often had short above-ground sections as well. After the start of the Industrial Revolution it became possible to create railways with iron tracks and wheels, which reduced the friction involved in moving wagons and made longer horse-hauled trains possible. These could mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrap
Scrap consists of Recycling, recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap Waste valorization, has monetary value, especially recovered metals, and non-metallic materials are also recovered for recycling. Once collected, the materials are sorted into types — typically metal scrap will be crushed, shredded, and sorted using mechanical processes. Scrap recycling is important for creating a more sustainable economy or creating a circular economy, using significantly less energy and having far less environmental impact than producing metal from ore. Metal recycling, especially of structural steel, Ship breaking, ships, used manufactured goods, such as Vehicle recycling, vehicles and white goods, is a major industrial activity with complex networks of wrecking yards, sorting facilities and recycling plants. Processing Scrap metal originates both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avonside Engine Company
The Avonside Engine Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Avon Street, St. Philip's, Bristol, England between 1864 and 1934. However the business originated with an earlier enterprise Henry Stothert and Company. Origins The firm was originally started by Henry Stothert in 1837 as Henry Stothert and Company. Henry was the son of George Stothert (senior), founder of the nearby Bath engineering firm of Stothert & Pitt. Henry's brother, also named George, was manager of the same firm. The company was given an order for two broad gauge () Firefly class express passenger engines ''Arrow'' and ''Dart'', with driving wheels, delivered for the opening of the Great Western Railway (GWR) from Bristol to Bath on 31 August 1840. This was soon followed by an order for eight smaller Sun class engines with driving wheels. Stothert, Slaughter and Company Edward Slaughter joined the company in 1841, when it became known as Stothert, Slaughter and Company. By 1844 their works were n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fletcher Jennings
Fletcher, Jennings & Co. was an engineering company at Lowca near Whitehaven, Cumberland, England. Overview Fletcher and Jennings took over the business of Tulk and Ley in 1857. From then, until 1884, the company concentrated on four and six-coupled industrial tank locomotives, although other goods such as bridge girders, and blast-furnace shells for the burgeoning local iron industry, were also produced. By then nearly two hundred locomotives had been built and the company acquired limited liability as Lowca Engineering Company Ltd. In 1905, the name changed again to the New Lowca Engineering Company Ltd., but the company was receiving fewer orders. After a disastrous fire in 1912, all production ceased and the company being finally wound up in 1927. Surviving locomotives Preserved locomotives manufactured by the company include: Other locomotives Other locomotives manufactured by the company include: *Brigham Hall/Rothersyke of the Cleator & Workington junction rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Lewin
Stephen Lewin (c. 18221913) was an English architect, artist, civil engineer and iron-founder, who was a builder of steamboats and steam locomotives. Initially he worked in Boston, Lincolnshire, Boston in Lincolnshire as a civil engineer with his father William Lewin, who was an assistant to John Rennie the Elder. His should not be confused with his son, Stephen Samuel Lewin (c. 18481909), a successful artist who specialised in historical works often featuring cavaliers and figures in 17th-century costumes. Architectural practice After working with his civil engineer father, Lewin then set up an architectural practice in Boston and at the same time published a notable series of engravings of Medieval churches in the Parts of Holland in Lincolnshire. He was involved in the civic life in Boston and was Mayor in 1860-2 and 1861-2. His younger brother, Charles Augustus Lewin had moved to Poole in Dorset in 1856 as a timber merchant. In 1863, Lewin, who had entered into a partnership ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Devon And Cornwall Junction Light Railway
The North Devon and Cornwall Junction Light Railway was a railway built to serve numerous ball clay pits that lay in the space between the London and South Western Railway's Torrington branch, an extension of the North Devon Railway group, and Halwill, an important rural junction on the North Cornwall Railway and its Okehampton to Bude Line. Ball clay was an important mineral but its weight and bulk required efficient transportation; the material had been brought to main line railways by a gauge tramway. Expanding volumes prompted conversion to a light railway—requiring less complex engineering and operational procedures than a full railway—and it was opened on 27 July 1925.St John Thomas, David (editor), Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: Volume 1 - the West Country; David & Charles, Newton Abbot, 3rd edition 1966) Passengers were carried in addition to the mineral traffic, but the business largely consisted of workers at the ball clay pits themselves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow Gauge Railway
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structure gauges, and lighter rails, they can be less costly to build, equip, and operate than standard- or broad-gauge railways (particularly in mountainous or difficult terrain). Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often used in mountainous terrain, where engineering savings can be substantial. Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often built to serve industries as well as sparsely populated communities where the traffic potential would not justify the cost of a standard- or broad-gauge line. Narrow-gauge railways have specialised use in mines and other environments where a small structure gauge necessitates a small loading gauge. In some countries, narrow gauge is the standard; Japan, Indonesia, Taiwan, New Zealand, South Africa, and the Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with approximately 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, and Uzbekistan. The distance between the inside edges of the rails is defined to be 1435 mm except in the United States and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in U.S. customary/Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches" which is equivalent to 1435.1mm. History As railways developed and expanded, one of the key issues was the track gauge (the distance, or width, between the inner sides of the rails) to be used. Different railways used different gauges, and where rails of different gauge met – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |