|
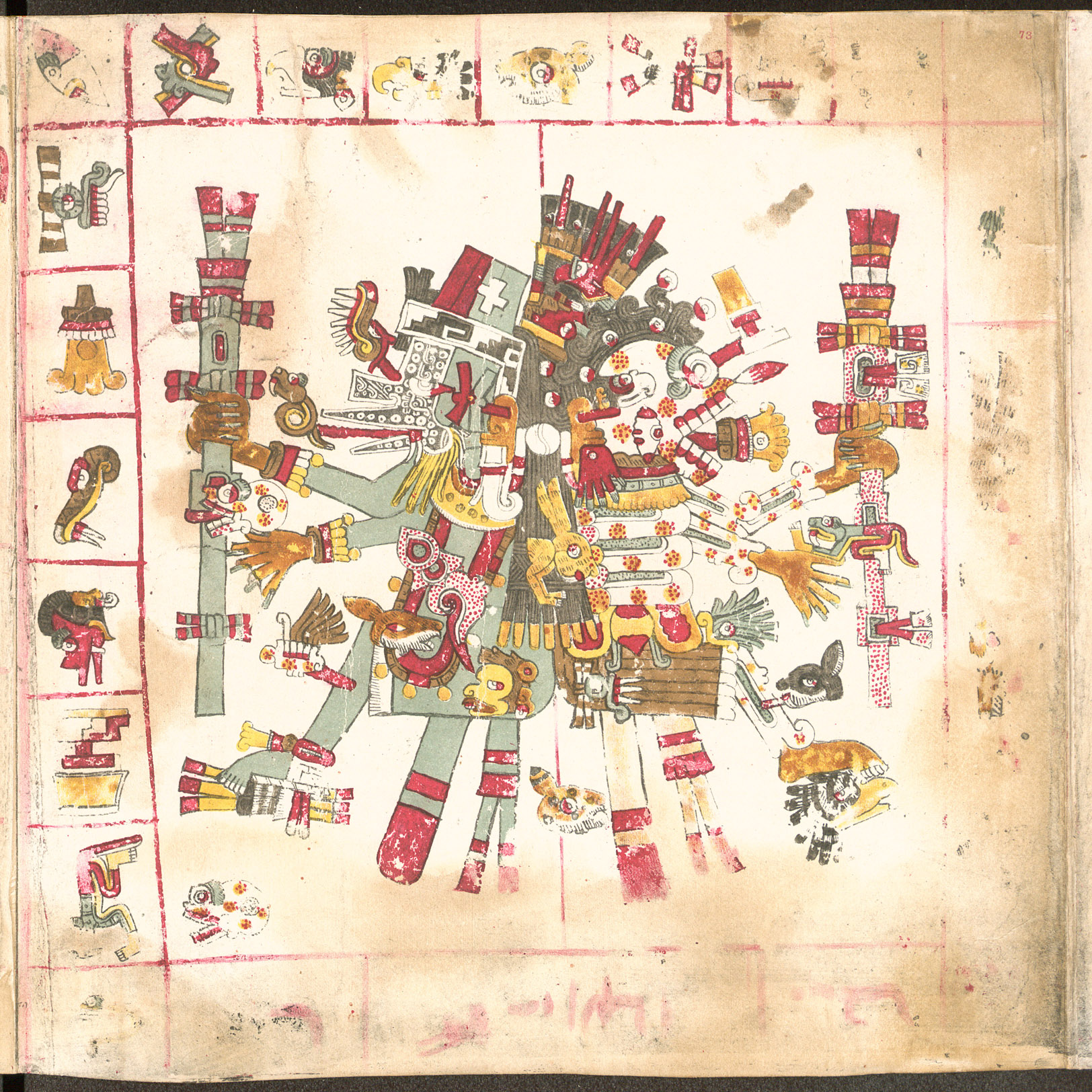
Tlaltecuhtli Stone Carving
Tlaltecuhtli (Classical Nahuatl ''Tlāltēuctli'', ) is a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican deity worshipped primarily by the Mexica (Aztec) people. Sometimes referred to as the "earth monster," Tlaltecuhtli's dismembered body was the basis for the world in the Aztec creation story of the fifth and final cosmos. In carvings, Tlaltecuhtli is often depicted as an anthropomorphic being with splayed arms and legs. Considered the source of all living things, she had to be kept sated by human sacrifices which would ensure the continued order of the world. According to a source, in the creation of the Earth, the gods did not tire of admiring the liquid world, no oscillations, no movements, so Tezcatlipoca and Quetzalcoatl thought that the newly created world should be inhabited. And for this, they made Tlalcihuatl, 'Lady of the earth', come down from heaven, and Tlaltecuhtli, 'Lord of the earth', would be her consort. Tezcatlipoca and Quetzalcoatl create the Earth from the body of Cipactli, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tezcatlipocas
In Aztec mythology, Creator-gods are the only four Tezcatlipocas, the children of the creator couple Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl "Lord and Lady of Duality", "Lord and Lady of the Near and the Close", "Father and Mother of the Gods", "Father and Mother of us all", who received the gift of the ability to create other living beings without childbearing. They reside atop a mythical thirteenth heaven Ilhuicatl-Omeyocan "the place of duality". Each of the four sons takes a turn as Sun, these suns are the Five Suns, sun of earth, the Five Suns, sun of air, the Five Suns, sun of fire, the Five Suns, sun of water (Tlaloc, rain god replaces Xipe-Totec). Each world is destroyed. The present era, Five Suns, the Fifth Sun is ushered in when a lowly god, Nanahuatzin sacrifices himself in fire and becomes Tonatiuh, the Fifth Sun. In his new position of power he refuses to go into motion until the gods make sacrifice to him. In an elaborate ceremony, Quetzalcoatl cuts the hearts out of each of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Mythology
Aztec mythology is the body or collection of myths of the Aztec civilization of Central Mexico. The Aztecs were Nahuatl-speaking groups living in central Mexico and much of their mythology is similar to that of other Mesoamerican cultures. According to legend, the various groups who were to become the Aztecs arrived from the north into the Anahuac valley around Lake Texcoco. The location of this valley and lake of destination is clear – it is the heart of modern Mexico City – but little can be known with certainty about the origin of the Aztec. There are different accounts of their origin. In the myth the ancestors of the Mexica/Aztec came from a place in the north called Aztlan, the last of seven ''nahuatlacas'' (Nahuatl-speaking tribes, from ''tlaca'', "man") to make the journey southward, hence their name "Azteca." Other accounts cite their origin in Chicomoztoc, "the place of the seven caves," or at Tamoanchan (the legendary origin of all civilizations). The Mexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deluge (mythology)
A flood myth or a deluge myth is a myth in which a great flood, usually sent by a deity or deities, destroys civilization, often in an act of divine retribution. Parallels are often drawn between the flood waters of these myths and the primaeval waters which appear in certain creation myths, as the flood waters are described as a measure for the cleansing of humanity, in preparation for rebirth. Most flood myths also contain a culture hero, who "represents the human craving for life". The flood-myth motif occurs in many cultures, including the Mesopotamian flood stories, Native American in North America, the Genesis flood narrative, ''manvantara-sandhya'' in Hinduism, and Deucalion and Pyrrha in Greek mythology. Mythologies One example of a flood myth is the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Many scholars believe that this account was copied from the Akkadian '' Atra-Hasis'', which dates to the 18th century BCE. In the Gilgamesh flood myth, the highest god, Enlil, decides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cōātlīcue
Coatlicue (; nci, cōātl īcue, , "skirt of snakes"), wife of Mixcōhuātl, also known as (, "mother of the gods") is the Aztec goddess who gave birth to the moon, stars, and Huītzilōpōchtli, the god of the sun and war. The goddesses Toci "our grandmother" and Cihuacōātl "snake woman", the patron of women who die in childbirth, were also seen as aspects of Cōātlīcue. Etymology The goddess' Classical Nahuatl name can be rendered both ''Cōātlīcue'' and ''Cōātl īcue'', from '' cōātl'' "snake" and '' īcue'' "her skirt", roughly meaning " he who hasthe skirt of snakes". The name ''Tēteoh īnnān'', from '' tēteoh'', plural of '' teōtl'' "god", + '' īnnān'' "their mother", refers directly to her maternal role. Myths Coatlicue is represented as a woman wearing a skirt of writhing snakes and a necklace made of human hearts, hands, and skulls. Her feet and hands are adorned with claws and her breasts are depicted as hanging flaccid from pregnancy. Her face is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Calendar Stone
The Aztec sun stone ( es, Piedra del Sol) is a late post-classic Mexica sculpture housed in the National Anthropology Museum in Mexico City, and is perhaps the most famous work of Mexica sculpture. It measures in diameter and thick, and weighs . Shortly after the Spanish conquest, the monolithic sculpture was buried in the Zócalo, the main square of Mexico City. It was rediscovered on 17 December 1790 during repairs on the Mexico City Cathedral. Following its rediscovery, the sun stone was mounted on an exterior wall of the cathedral, where it remained until 1885.Getty Museum, "Aztec Calendar Stone" ''getty.edu'', accessed 22 August 2018 Early scholars initially thought that the stone was carved in the 1470s, though modern research suggests that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moctezuma II
Moctezuma Xocoyotzin ( – 29 June 1520; oteːkˈsoːmaḁ ʃoːkoˈjoːt͡sĩn̥), nci-IPA, Motēuczōmah Xōcoyōtzin, moteːkʷˈsoːma ʃoːkoˈjoːtsin variant spellings include Motewksomah, Motecuhzomatzin, Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecuhzoma, Motēuczōmah, Muteczuma, and referred to retroactively in European sources as Moctezuma II, was the ninth Emperor of the Aztec Empire (also known as Mexica Empire), reigning from 1502 or 1503 to 1520. Through his marriage with queen Tlapalizquixochtzin of Ecatepec, one of his two wives, he was also king consort of that ''altepetl''. The first contact between the indigenous civilizations of Mesoamerica and Europeans took place during his reign, and he was killed during the initial stages of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, when conquistador Hernán Cortés and his men fought to take over the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan. During his reign, the Aztec Empire reached its greatest size. Through warfare, Moctezuma expanded the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
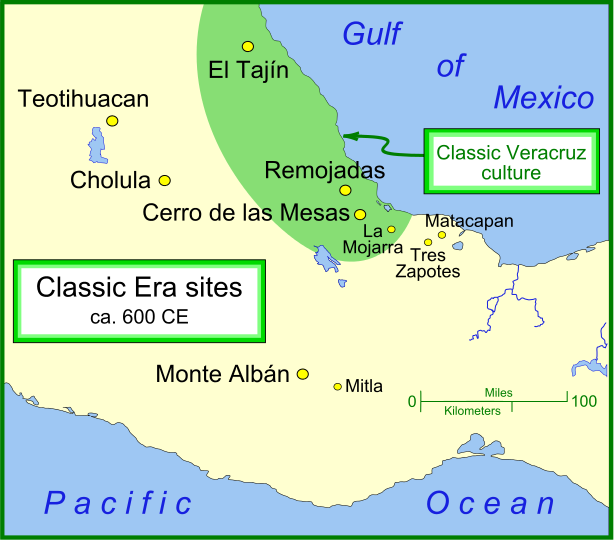
El Tajín
El Tajín is a pre-Columbian archeological site in southern Mexico and is one of the largest and most important cities of the Mesoamerican chronology, Classic era of Mesoamerica. A part of the Classic Veracruz culture, El Tajín flourished from 600 to 1200 CE and during this time numerous temples, palaces, Mesoamerican ballcourt, ballcourts, and pyramids were built. From the time the city fell, in 1230, to 1785, no European seems to have known of its existence, until a government inspector chanced upon the Pyramid of the Niches. El Tajín, named after the Totonac rain god, was named a World Heritage site in 1992, due to its cultural importance and its architecture. This architecture includes the use of decorative niches and cement in forms unknown in the rest of Mesoamerica. Its best-known monument is the Pyramid of the Niches, but other important monuments include the Arroyo Group, the North and South Ballcourts and the palaces of Tajín Chico. In total there have been 20 ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuauhxicalli
A ''cuauhxicalli'' or ''quauhxicalli'' (, meaning "eagle gourd bowl") was an altar-like stone vessel used by the Aztec to hold human hearts extracted in sacrificial ceremonies. A cuauhxicalli would often be decorated with animal motifs, commonly eagles or jaguars. Another kind of cuauhxicalli is the Chacmool-type, which is shaped as a reclining person holding a bowl on his belly. Gallery File:20041229-Ocelotl-Cuauhxicalli (Museo Nacional de Antropología) MQ.jpg, Jaguar-shaped cuauhxicalli in the National Museum of Anthropology of Mexico File:Mighty carved stone eagle.jpg, Cuauhxicalli in the shape of an eagle, from the Templo Mayor The (Spanish: Main Temple) was the main temple of the Mexica people in their capital city of Tenochtitlan, which is now Mexico City. Its architectural style belongs to the late Postclassic period of Mesoamerica. The temple was called ' in ... File:Cuauhxicalli, National Anthropology Museum, Mexico City.webm, Video of a cuauhxicalli, Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)