|
Tiyan
The Ezhavas () are a community with origins in the region of India presently known as Kerala, where in the 2010s they constituted about 23% of the population and were reported to be the largest Hindu community. They are also known as ''Ilhava'', ''Irava'', ''Izhava'' and ''Erava'' in the south of the region; as ''Chovas'', ''Chokons'' and ''Chogons'' in Central Travancore; and as ''Thiyyar'', ''Tiyyas'' and ''Theeyas'' in the Malabar region. Some are also known as ''Thandan'', which has caused administrative difficulties due to the presence of a distinct caste of Thandan in the same region. The Malabar Ezhava Pullapilly (1976) pp. 31–32 group have claimed a higher ranking in the Hindu caste system than do the others, although from the perspective of the colonial and subsequent administrations they were treated as being of similar rank. Nossiter (1982) p. 30 Ezhava dynasties such as the Mannanar existed in Kerala. Pullapilly (1976) pp. 31–32 The Chekavar, a warrior section wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thandan
Thandan or Thandayan is the honorary title given to the headman of the Thiyya community people in Palakkad, Thrissur district, who reside in the Indian State of Kerala. Thandan is the hereditary headman of a Thiyyar tara (village) and is a Thiyyar by caste. He is appointed by the senior Rani of the Zamorin's family or by a local Raja in territories outside the Zamorin's jurisdiction. Thandan becomes the of the or . They are designated as Other Backward Classes by the Government of Kerala as per anthropological studies conducted by the Kerala Institute of Research, and Development Studies. Status ''Thandan'' was the most commonly-used title to represent the highest privilege among the Thiyyar of the Malabar area. The most notable Thiyyar of the Malabars received the title as Thandan for their service to the state either in the administration of Malabar district Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malaba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalaripayattu
Kalaripayattu (; also known simply as Kalari) is an Indian martial art that originated in modern-day Kerala, a state on the southwestern coast of India. Kalaripayattu is known for its long-standing history within Indian martial arts, and is one of the oldest surviving martial arts in India. Kalaripayattu is mentioned in the Vadakkan Pattukal, a collection of ballads written about the Chekavar of the Malabar region of Kerala. In the Vadakkan Pattukal, it is stated that the cardinal principle of Kalaripayattu was that knowledge of the art be used to further worthy causes, and not for the advancement of one's own selfish interests. Kalaripayattu is a martial art designed for the ancient battlefield (the word "Kalari" meaning "battlefield"), with weapons and combative techniques that are unique to Kerala. Like most Indian martial arts, Kalaripayattu contains rituals and philosophies inspired by Hinduism. The art also bases medical treatments upon concepts found in the ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disruptive Editing
Disruption, disruptive, or disrupted may refer to: Business *Creative disruption, disruption concept in a creative context, introduced in 1992 by TBWA's chairman Jean-Marie Dru *Disruptive innovation, Clayton Christensen's theory of industry disruption by new technology or products Psychology and sociology *Disruptive behavior disorders, a class of mental health disorders *Disruptive physician, a physician whose obnoxious behaviour upsets patients or other staff *Social disruption, a radical alteration, transformation, dysfunction or breakdown of social life Other uses *Cell disruption is a method or process in cell biology for releasing biological molecules from inside a cell *''Disrupted: My Misadventure in the Start Up Bubble'', a 2016 book by Daniel Lyons *Disruption (adoption) is also the term for the cancellation of an adoption of a child before it is legally completed *Disruption (of schema), in the field of computer genetic algorithms *Disruption of 1843, the divergence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
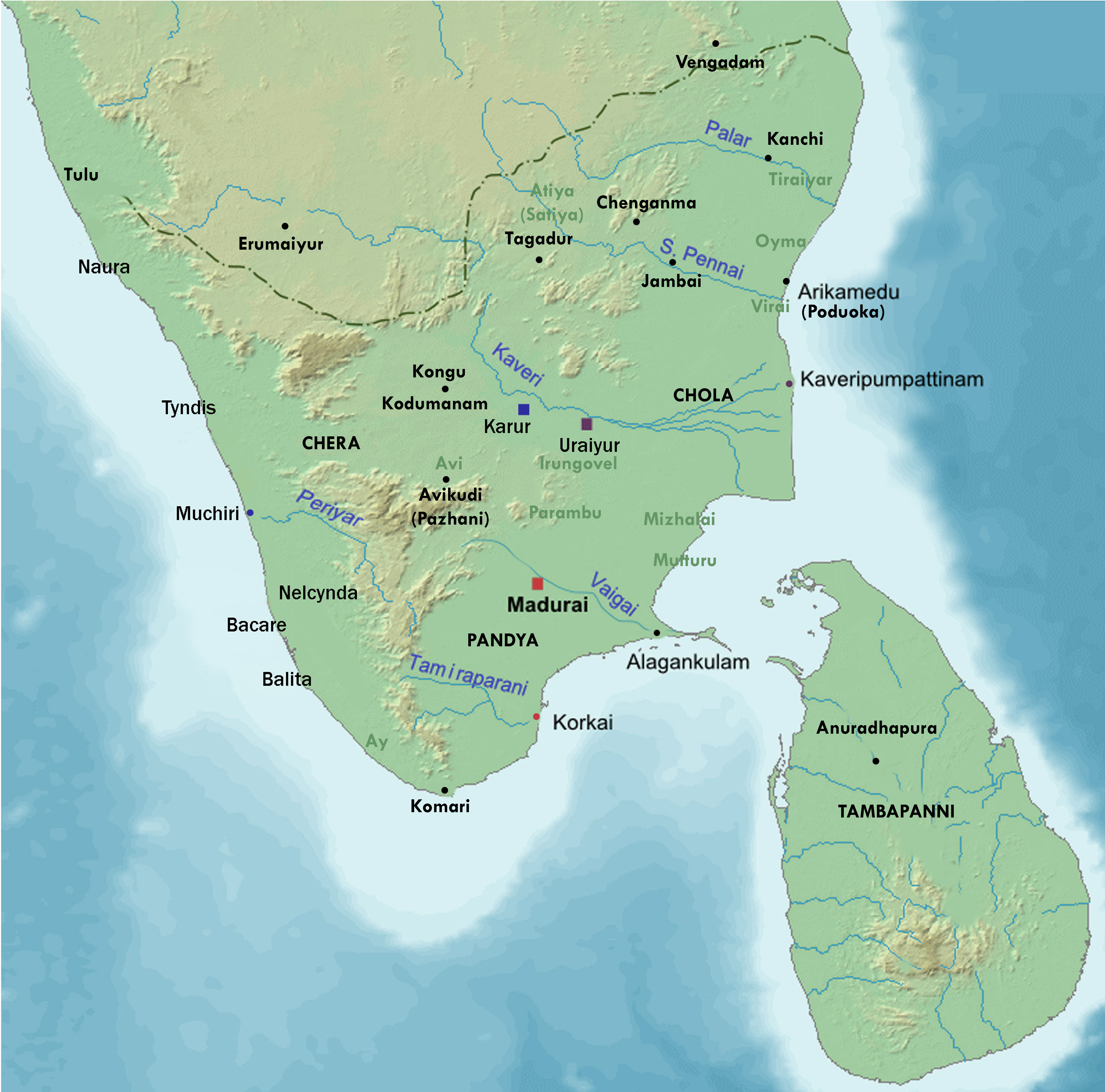
Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE during the reign of Ashoka of the Maurya Empire. As one of the Three Crowned Kings of Tamilakam, along with the Chera and Pandya, the dynasty continued to govern over varying territories until the 13th century CE. The Chola Empire was at its peak under the Medieval Cholas in the mid-9th century CE. The heartland of the Cholas was the fertile valley of the Kaveri River. They ruled a significantly larger area at the height of their power from the later half of the 9th century till the beginning of the 13th century. They unified peninsular India south of the Tungabhadra River, and held the territory as one state for three centuries between 907 and 1215 CE.K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, ''A History of South India'', p 157 Under Rajaraja I and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallava
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana dynasty, with whom they had formerly served as feudatories. The Pallavas became a major South Indian power during the reign of Mahendravarman I (600–630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630–668 CE), and dominated the southern Andhra Region and the northern parts of the Tamil region for about 600 years, until the end of the 9th century. Throughout their reign, they remained in constant conflict with both the Chalukyas of Badami in the north, and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola and Pandyas in the south. The Pallavas were finally defeated by the Chola ruler Aditya I in the 9th century CE. The Pallavas are most noted for their patronage of Hindu temple architecture, the finest example being the Shore Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Mamallapuram. Kancheepuram served as the capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naṟṟiṇai
''Naṟṟiṇai'' ( ta, நற்றிணை meaning ''excellent tinai''), is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the first of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. The collection – sometimes spelled as Natrinai or Narrinai – contains both ''akam'' (love) and ''puram'' (war, public life) category of poems. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' anthology contains 400 poems, mainly of 9 to 12 lines, but a few with 8 to 13 lines each. According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems were likely composed between 100–300 CE based on the linguistics, style and dating of the authors. While Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar , dates some poems to the 1st century BCE. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' manuscript colophon states that it was compiled under the patronage of the Pandyan king named ''Pannatu Tanta Pantiyan Maran Valuti'', but the compiler remained anonymous. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuṟuntokai
Kuṟuntokai ( ta, குறுந்தொகை, meaning ''the short-collection'') is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the second of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. The collection belongs to the ''akam'' (love) category, and each poem consists of 4 to 8 lines each (except poem 307 and 391 which have 9 lines). The Sangam literature structure suggests that the original compilation had 400 poems, but the surviving ''Kuruntokai'' manuscripts have 402 poems. According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, these poems were likely composed between 100 CE and 300 CE based on the linguistics, style and dating of the authors. Kamil Zvelebil, a Tamil literature and history scholar, states that the majority of the poems in the ''Kuruntokai'' were likely composed between the 1st century BCE and the 2nd century CE. The ''Kuruntokai'' manuscript colophon states that it was compiled by Purikko (உரை), however nothing is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akanaṉūṟu
The ''Akananuru'' (, literally "four hundred oemsin the akam genre"), sometimes called ''Nedunthokai'' (''lit.'' "anthology of long poems"), is a classical Tamil poetic work and one of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. It is a collection of 400 love poems with invocatory poem dedicated to Shiva. The collected poems were composed by 144 poets, except 3 poems which are by anonymous author(s). The poems range between 13 and 31 lines, and are long enough to include more details of the subject, episode and its context. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, they are "one of the most valuable collections" from ancient Tamil history perspective. The ''Akananuru'' anthology is notable for its mathematical arrangement: the odd number poems are dedicated to ''palai'' (arid landscape); poem number ten and its multiples (10, 20, 30, etc., up to 400) are ''neytal'' (coastal landscape); poems bearing number 2 and then in inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eelattu Poothanthevanar
Eelattu Poothanthevanar () was one of the earliest known classical Ceylon (present day Sri Lanka) Tamil poets from the Sangam period. He hailed from the ancient international port of Manthai (''Manthottam/ Manthoddam'' in Tamil, Manthota in derived Sinhalese) in Ceylon, the ruins of which are in present-day Mannar District, Sri Lanka. His poems were included in the Tamil language anthologies of the Sangam literature compiled in Tamilakam before 250 CE Writing in the city of Madurai, he praises the valour of the contemporaneous King Pasum Poon Pandyan, who, as per the '' Narkudi Velalar Varalaru'', reigned from 275 to 240 BCE. Seven of his poetic verses feature in the '' Akananuṟu'', '' Natriṇai'' and '' Kurunthokai''. Other Sri Lankan Tamil poets whose contemporary work feature in the anthologies include Pūtan Ila Naganar and Marudan Ila Naganar. Contribution to the Sangam literature Eelattu Poothanthevanar has written two Sangam verses, including one each in Akananuru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paṭṭiṉappālai
__NOTOC__ ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'' ( ta, பட்டினப் பாலை) is a Tamil poem in the ancient Sangam literature. It contains 301 lines, of which 296 lines are about the port city of Kaveripoompattinam, the early Chola kingdom and the Chola king Karikalan. The remaining 5 lines are on the proposed separation by a man who wants to move there and the separation pain of his wife who would miss her husband's love. Of the 301 lines, 153 are in the ''vanci'' meter and the rest are in ''akaval''. It is sometimes referred to as ''Vancinetumpattu'', or the "long song in the vanci meter". The poem was composed by Katiyalur Uruttirankannanar, sometime around 1st century and 2nd century CE, states Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar. The title ''Pattinappalai'' is combination of two words, ''pattinam'' (city) and ''palai'' (desert, metonymically "separation, love division"). The poem has a lengthy initial section on the harbor capital city of the ancient Cholas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language—one of the longest surviving classical languages in the world—is widely spoken in the state and serves as its official language. The state lies in the southernmost part of the Indian peninsula, and is bordered by the Indian union territory of Puducherry and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh, as well as an international maritime border with Sri Lanka. It is bounded by the Western Ghats in the west, the Eastern Ghats in the north, the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait to the south-east, and the Indian Ocean in the south. The at-large Tamilakam region that has been inhabited by Tamils was under several regimes, such as the Sangam era rulers of the Chera, Chola, and Pandya cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madurai
Madurai ( , also , ) is a major city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District. As of the 2011 census, it was the third largest Urban agglomeration in Tamil Nadu after Chennai and Coimbatore and the 44th most populated city in India. Located on the banks of River Vaigai, Madurai has been a major settlement for two millennia and has a documented history of more than 2500 years. It is often referred to as "Thoonga Nagaram", meaning "the city that never sleeps". Madurai is closely associated with the Tamil language. The third Tamil Sangam, a major congregation of Tamil scholars said to have been held in the city. The recorded history of the city goes back to the 3rd century BCE, being mentioned by Megasthenes, the Greek ambassador to the Maurya empire, and Kautilya, a minister of the Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya. Signs of human settlements and Roman trade links dating back to 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |