|
Tituba
Tituba Indian was an enslaved woman who was one of the first to be accused of witchcraft during the Salem witch trials of 1692-1693. She was brought to colonial Massachusetts from Barbados by Samuel Parris, the minister of Salem Village. She was pivotal in the trials because she confessed to witchcraft when examined by the authorities, giving credence to the accusations. She accused the two other women, Sarah Good and Sarah Osborne, of the same crime. She was imprisoned for over a year but never went to trial. It is unknown what happened to her after the case against her was dismissed by a grand jury in May 1693. Early life Tituba's husband was John Indian, an Indigenous man whose origins are unknown, but he may have been from Central or South America, Tibitó, Colombia to be precise. It is said that she was named after her town or tribe. Tituba may have originally been from Barbados. Many historians, such as Elaine Breslaw and Charles Upham, gathered that Tituba was a Native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salem Witch Trials
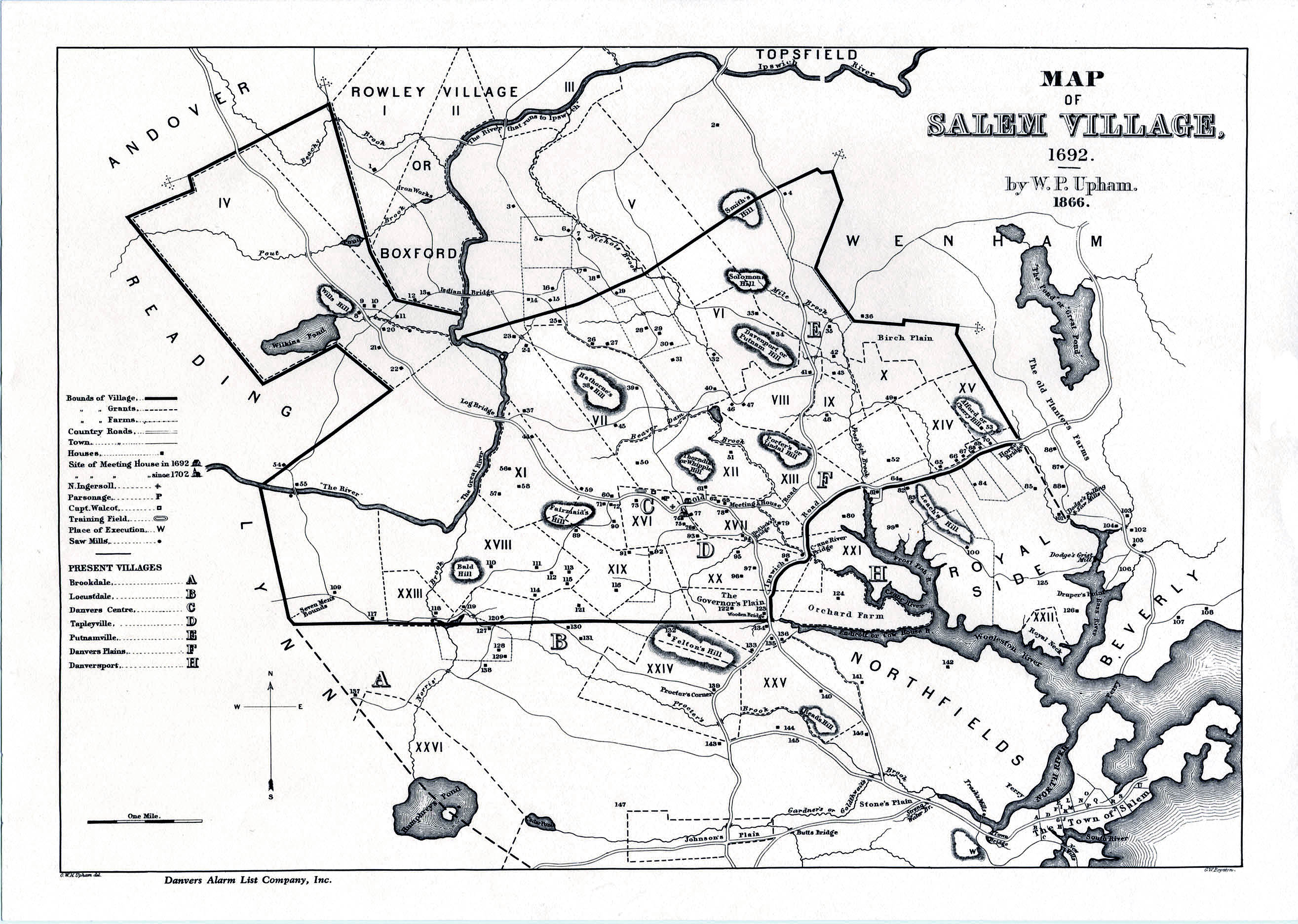
The Salem witch trials were a series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts between February 1692 and May 1693. More than 200 people were accused. Thirty people were found guilty, 19 of whom were executed by hanging (14 women and five men). One other man, Giles Corey, was pressed to death after refusing to enter a plea, and at least five people died in jail. Arrests were made in numerous towns beyond Salem and Salem Village (known today as Danvers), notably Andover and Topsfield. The grand juries and trials for this capital crime were conducted by a Court of Oyer and Terminer in 1692 and by a Superior Court of Judicature in 1693, both held in Salem Town, where the hangings also took place. It was the deadliest witch hunt in the history of colonial North America. Only fourteen other women and two men had been executed in Massachusetts and Connecticut during the 17th century. The episode is one of Colonial America's most no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salem Witch Trials
The Salem witch trials were a series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts between February 1692 and May 1693. More than 200 people were accused. Thirty people were found guilty, 19 of whom were executed by hanging (14 women and five men). One other man, Giles Corey, was pressed to death after refusing to enter a plea, and at least five people died in jail. Arrests were made in numerous towns beyond Salem and Salem Village (known today as Danvers), notably Andover and Topsfield. The grand juries and trials for this capital crime were conducted by a Court of Oyer and Terminer in 1692 and by a Superior Court of Judicature in 1693, both held in Salem Town, where the hangings also took place. It was the deadliest witch hunt in the history of colonial North America. Only fourteen other women and two men had been executed in Massachusetts and Connecticut during the 17th century. The episode is one of Colonial America's most no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Parris
Samuel Parris (1653February 27, 1720) was the Puritan minister in Salem Village, Massachusetts, during the Salem witch trials. He was also the father of one of the afflicted girls, and the uncle of another. Life and career Samuel Parris, son of Thomas Parris, was born in London, England to a family of modest financial success and religious nonconformity. Samuel emigrated to Boston in the early 1660s, where he attended Harvard College at his father's behest. When his father died in 1673, Samuel left Harvard to take up his inheritance in Barbados, where he maintained a sugar plantation. In 1680, after a hurricane hit Barbados, damaging much of his property, Parris sold a little of his land and returned to Boston, where he brought his slave Tituba and married Elizabeth Eldridge. Eldridge was noted by many as being incredibly beautiful, and was said to be one of the most beautiful women in Salem Village. Together they had three children, Thomas Parris, Elizabeth Parris, and Susannah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betty Parris (Salem Witch Trials)
Elizabeth "Betty" Parris (November 28, 1682 – March 21, 1760) was one of the young girls who accused other people of being witches during the Salem witch trials. The accusations made by Betty (Elizabeth) and her cousin Abigail Williams caused the direct death of 20 Salem residents: 19 were hanged, while another, Giles Corey, was pressed to death.Profile womenshistory.about.com; accessed December 23, 2014. Early life Her father, , was a well-known minister in the Salem Church. Her mother, Elizabeth Parris, died a few years after the witch trials. Her older brother Thomas Parris was born in 1681, and her younger sister Susanna Parris was born in 1687. Others l ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Osborne
Sarah Osborne (also variously spelled Osbourne, Osburne, or Osborn; née Warren, formerly Prince, (c. 1643 – May 10, 1692) was a colonist in the Massachusetts Bay colony and one of the first women to be accused of witchcraft in the Salem witch trials of 1692. Sarah Osborn was suggested to be a witch by Sarah Good. Sarah Good said she had been tormenting the girls. Early life and marriages Born Sarah Warren, Osborne was born in Watertown, Massachusetts in the Mid 1600s. She later married a prominent man by the name of Robert Prince. Prince was the brother-in-law and neighbor of Captain John Putnam, a member of the notable Putnam family. She moved with her husband to Salem Village in 1662, where the couple had two sons and a daughter: Joseph, James, and Elizabeth. Robert Prince died in 1674. Shortly following Robert Prince's death, Osborne hired an Irish indentured immigrant. Eventually, Alexander Osborne paid off his indenture, and the two married. Despite late Prince's wishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abigail Williams (Salem Witch Trials)
Abigail Williams (born c. 1681, date of death unknown) was an 11- or 12-year-old girl who, along with nine-year-old Betty Parris, was among the first of the children to falsely accuse their neighbors of witchcraft in 1692; these accusations eventually led to the Salem witch trials. Salem trials In early 1692, Abigail Williams was living with her relative, Betty Parris' father, the village pastor Samuel Parris, along with his two slaves Tituba and John Indian. Tituba was part of a group of three women—with Sarah Good and Sarah Osborne—who were the first to be arrested, on February 29, 1692, under the accusation that their spectres (ghosts) were afflicting the young girls in Parris' household. The three women were questioned separately but were aware of each other and, in a classic prisoner's dilemma, they were turned against each other. Sarah Good was the first interrogated and held to her innocence. Judge John Hathorne directed all "the children ... to look upon her a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Good
Sarah Good (, 1653 – , 1692)Contemporary records commonly used the Julian calendar and the Annunciation Style of enumerating months and years. By the Gregorian calendar and using modern style dating, all of the witch trial events in this article occurred in 1692. See also: Old Style and New Style dates; Dual dating was one of the first three women to be accused of witchcraft in the Salem witch trials, which occurred in 1692 in colonial Massachusetts. Biography Sarah Good was born in 1653, the daughter of a well-to-do tavern owner in Wenham, Massachusetts named John Solart. In 1669, when she was 16 years old, her father committed suicide. His 70-acre estate was valued around 500 pounds and he didn't leave a will. At the time of his death, the Solarts were one of many families involved in land disputes around Salem. The estate was divided mostly between his widow and two sons, with only a small allotment to be shared among seven daughters, however, even this was denied to the gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rachel Dyer
''Rachel Dyer: A North American Story'' is a Gothic historical novel by American writer John Neal. Published in 1828 in Maine, it is the first bound novel about the Salem witch trials. Though it garnered little critical notice in its day, it influenced works by Nathaniel Hawthorne, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, John Greenleaf Whittier, and Walt Whitman. It is best remembered for the American literary nationalism, American literary nationalist essay, "Unpublished Preface", that precedes the body of the novel. Following a darkly poetic narrative, the story centers on historical figure George Burroughs and fictional witch hysteria victim, Rachel Dyer. With about two-thirds of the story taking place in the courtroom, it follows the trials of multiple alleged witches. Themes include justice, sexual frustration, mistreatment of Native Americans in the United States, Indigenous Americans by Puritans, the myth of national American unity in the face of cultural pluralism, pluralist reali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greater Antilles and northern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. All these groups spoke related Arawakan languages. Name Early Spanish explorers and administrators used the terms ''Arawak'' and ''Caribs'' to distinguish the peoples of the Caribbean, with ''Carib'' reserved for indigenous groups that they considered hostile and ''Arawak'' for groups that they considered friendly. In 1871, ethnologist Daniel Garrison Brinton proposed calling the Caribbean populace "Island Arawak" due to their cultural and linguistic similarities with the mainland Arawak. Subsequent scholars shortened this convention to "Arawak", creating confusion between the island and mainland groups. In the 20th century, scholars such as Irving Rouse resumed using "Taíno" for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. Inhabited by Island Caribs, Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Amerindians, Spanish navigators took possession of Barbados in the late 15th century, claiming it for the Crown of Castile. It first appeared on a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese Empire claimed the island between 1532 and 1536, but abandoned it in 1620 with their only remnants being an introduction of wild boars for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An Kingdom of England, English ship, the ''Olive Blossom'', arrived in Barbados on 14 May 1625; its men took possession of the island in the name of James VI and I, King James I. In 1627, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapegoat
In the Bible, a scapegoat is one of a pair of kid goats that is released into the wilderness, taking with it all sins and impurities, while the other is sacrificed. The concept first appears in the Book of Leviticus, in which a goat is designated to be cast into the desert to carry away the sins of the community. Practices with some similarities to the scapegoat ritual also appear in Ancient Greece and Ebla. Origins Some scholars have argued that the scapegoat ritual can be traced back to Ebla around 2400 BC, from where it spread throughout the ancient Near East. Etymology The word "scapegoat" is an English translation of the Hebrew ( he, עזאזל), which occurs in Leviticus 16:8: The Brown–Driver–Briggs Hebrew Lexicon gives () as a reduplicative intensive of the stem , "remove", hence , "for entire removal". This reading is supported by the Greek Old Testament translation as "the sender away (of sins)". The lexicographer Gesenius takes to mean "averter", wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |