|
Tiras
Tiras ( he, ''Ṯīrās'') is, according to the Book of Genesis () and 1 Chronicles, the seventh and youngest son of Japheth in the Hebrew Bible. A brother of biblical Javan (associated with the Greek people), its geographical locale is sometimes associated by scholars with the Tershi or Tirsa, one of the groups which made up the Sea Peoples "thyrsenes" (Tyrrhenians), a naval confederacy which terrorized Egypt and other Mediterranean nations around 1200 BCE. These Sea People are referred to as "Tursha" in an inscription of Ramesses III, and as "Teresh of the Sea" on the Merneptah Stele. Some theologians associate Tiras with Thrace or the Etruscans. In 1838, the German theologian Johann Christian Friedrich Tuch suggested identifying Tiras with the Etruscans — who, according to Greek and Roman sources such as Herodotus (I, 94), had been living in Lydia as the Tyrsenoi before emigrating to Italy as early as the 8th century BC. Ancient and Medieval Identifications According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
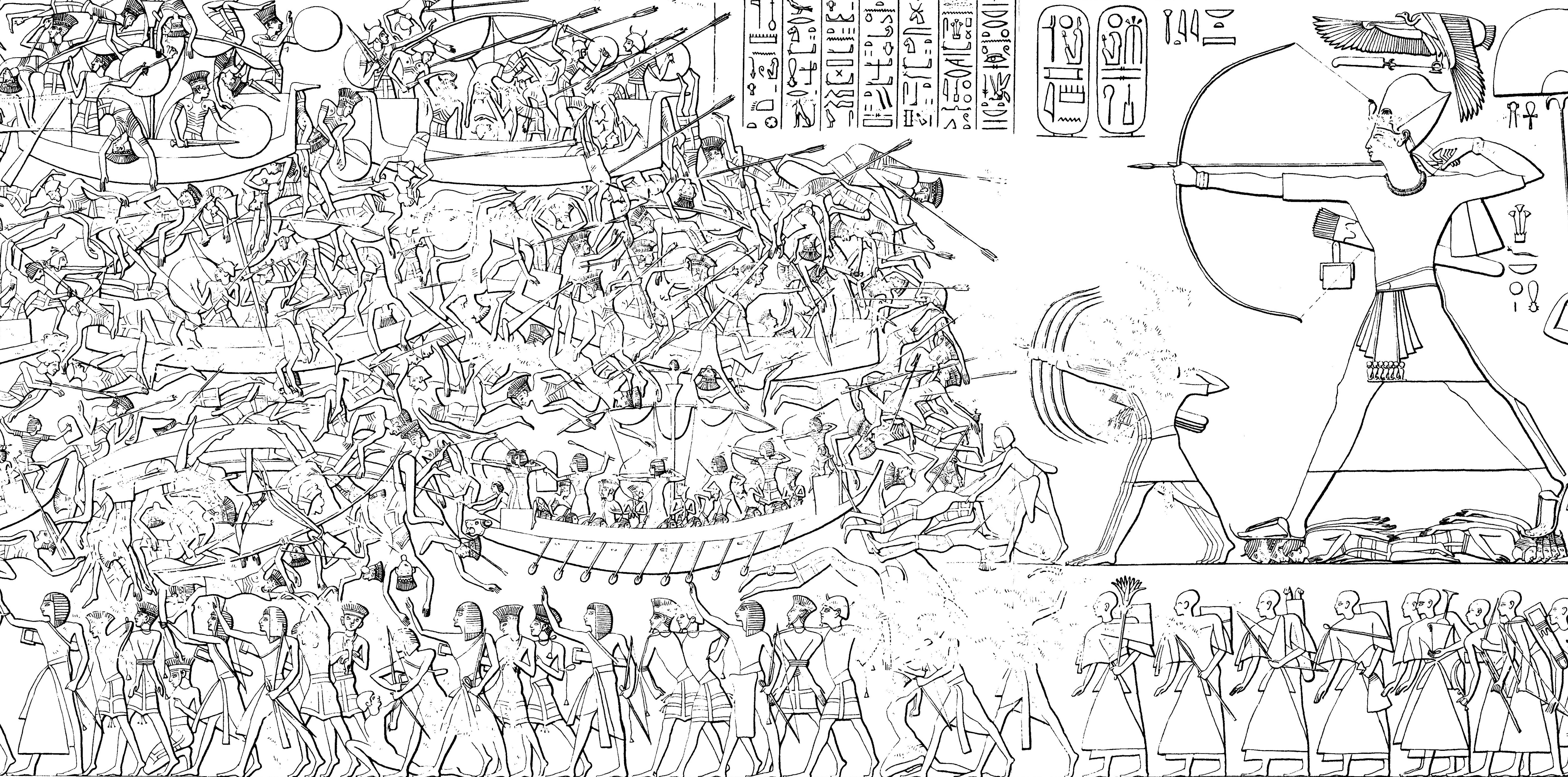
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japheth
Japheth ( he, יֶפֶת ''Yép̄eṯ'', in pausa ''Yā́p̄eṯ''; el, Ἰάφεθ '; la, Iafeth, Iapheth, Iaphethus, Iapetus) is one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis, in which he plays a role in the story of Noah's drunkenness and the curse of Ham, and subsequently in the Table of Nations as the ancestor of the peoples of the Aegean Sea, Anatolia, and elsewhere. In medieval and early modern European tradition he was considered to be the progenitor of the European peoples, Javakhishvili, Ivane (1950), ''Historical-Ethnological problems of Georgia, the Caucasus and the Near East''. Tbilisi, pp. 130–135 (in Georgian). while Islamic traditions also include the Chinese people among his descendants. Etymology The meaning of the name ''Japheth'' is disputable. There are two possible sources to the meaning of the name: * From Aramaic root , meaning ''to extend''. In this case, the name would mean ''may He extend'' (Rashi). * From Hebrew root , meaning ''beauty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaan (son Of Ham)
Canaan ( – ''Kənáʿan'', in pausa – ''Kənā́ʿan''), according to the ''Book of Genesis'' in the Hebrew Bible, was a son of Ham and grandson of Noah, as well as the father of the Canaanites. Etymology The English term ''Canaan'' (pronounced since c. AD 1500, due to the Great Vowel Shift) comes from the Hebrew (''knʿn''), via Greek ''Khanaan'' and Latin . It appears as in the Amarna letters (14th century BC), and is found on coins from Phoenicia in the last half of the 1st millennium. It first occurs in Greek in the writings of Hecataeus as ''Khna''(Χνᾶ). Scholars connect the name ''Canaan'' with , ''Kana'an'', the general Northwest Semitic name for this region. The etymology is uncertain. One explanation is that it has an original meaning of "lowlands", from a Semitic root "to be low, humble, depressed", in contrast with Aram, "highlands". An alternative suggestion derives the term from Hurrian ''Kinahhu'', purportedly referring to the colour purple, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cush (Bible)
Cush or Kush ( he, כּוּשׁ , ''Kūš''; gez, ኩሽ), according to the Hebrew Bible, was the oldest son of Ham and a grandson of Noah. He was the brother of Mizraim, Phut, and Canaan. Cush was the father of Nimrod, a king called the "first heroic warrior on earth". Cush is traditionally considered the ancestor of the "land of Cush", an ancient territory believed to have been located near the Red Sea. Cush is identified in the Bible with the Kingdom of Kush or ancient Sudan. The Cushitic languages are named after Cush. Identification Cush is a Hebrew name that is possibly derived from ''Kash'', the Egyptian name of Upper Nubia and later of the Nubian kingdom at Napata, known as the Kingdom of Kush.David M. Goldenberg (2003), ''The Curse of Ham: Race and Slavery in Early Judaism, Christianity, and Islam'', p. 18. The form ''Kush'' appears in Egyptian records as early as the reign of Mentuhotep II (21st century BC), in an inscription detailing his campaigns against the Nubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayk
Hayk ( hy, Հայկ, ), also known as Hayk Nahapet (, , ), is the legendary patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation. His story is told in the '' History of Armenia'' attributed to the Armenian historian Moses of Chorene (Movses Khorenatsi) and in the ''Primary History'' traditionally attributed to Sebeos. Fragments of the legend of Hayk are also preserved in the works of other authors, as well as in Armenian folk tradition. Etymology The name of the patriarch, ''Hayk'' (), is not exactly homophonous with the Armenian name for "Armenia," ''Haykʻ'' (). In Classical Armenian, ''Haykʻ'' is the nominative plural of ''hay'' (հայ), the Armenian word for "Armenian." While Robert W. Thomson considers the etymology of ''Haykʻ'' (Հայք) from ''Hayk'' (Հայկ) to be impossible, other scholars consider the connection between the two to be obvious and derive ''Hayk'' from ''hay''/''Haykʻ'' via the suffix ''-ik''. Martirosyan, Hrach (2010). ''Etymological Dictionary of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area between northern Greece, southern Russia, and north-western Turkey. They shared the same language and culture... There may have been as many as a million Thracians, diveded among up to 40 tribes." Thracians resided mainly in the Balkans (mostly Present (time), modern day Bulgaria, Turkey and Greece) but were also located in Anatolia, Anatolia (Asia Minor) and other locations in Eastern Europe. The exact origin of Thracians is unknown, but it is believed that proto-Thracians descended from a purported mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers, arriving from the rest of Asia and Africa through the Asia Minor (Anatolia). The proto-Thracian culture developed int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning"). Genesis is an account of the creation of the world, the early history of humanity, and of Israel's ancestors and the origins of the Jewish people. Tradition credits Moses as the author of Genesis, as well as the books of Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and most of Deuteronomy; however, modern scholars, especially from the 19th century onward, place the books' authorship in the 6th and 5th centuries BC, hundreds of years after Moses is supposed to have lived.Davies (1998), p. 37 Based on scientific interpretation of archaeological, genetic, and linguistic evidence, most scholars consider Genesis to be primarily mythological rather than historical. It is divisible into two parts, the primeval history (chapters 1–11) and the ancestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius.Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Put (biblical Figure)
Phut or Put ( he, ''Pūṭ''; Septuagint Greek ''Phoud'') is the third son of Ham (one of the sons of Noah), in the biblical Table of Nations (Genesis ; cf. 1 Chronicles ). The name Put (or Phut) is used in the Bible for Ancient Libya, but a few scholars proposed the Land of Punt known from Ancient Egyptian annals. Historical records Epiphanius writes: "Thus Mistrem was allotted Egypt, Cush Ethiopia, Put Axum, Ragman and Sabteka and edan, also called Judad the region bordering on Garama." Josephus writes: "Phut also was the founder of Libya, and called the inhabitants Phutites (''Phoutes''), from himself: there is also a river in the country of Moors which bears that name; whence it is that we may see the greatest part of the Grecian historiographers mention that river and the adjoining country by the appellation of Phut (''Phoute''): but the name it has now has been by change given it from one of the sons of Mezraim, who was called Lybyos." Pliny the Elder and Ptolemy''Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Jarir Al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari is known for his historical works and his expertise in Qur'anic exegesis (), but he has also been described as "an impressively prolific polymath".Lindsay Jones (ed.), ''Encyclopedia of religion'', volume 13, Macmillan Reference USA, 2005, p. 8943 He wrote works on a diverse range of subjects, including world history, poetry, lexicography, grammar, ethics, mathematics, and medicine. His most influential and best known works are his Quranic commentary, known in Arabic as , and his historical chronicle called '' History of the Prophets and Kings'' (), often referred to as ("al-Tabari's History"). Al-Tabari followed the Shafi'i madhhab for nearly a decade before he developed his own interpretation of Islamic jurisprudence. His understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |