|
Tihiro Ohkawa
was a Japanese people, Japanese physicist whose field of work was in Plasma (physics), plasma physics and fusion power. He was a pioneer in developing ways to generate electricity by nuclear fusion when he worked at General Atomics. Ohkawa died September 27, 2014 in La Jolla, California at the age of 86. Early life and career Ohkawa was born in Kanazawa on January 3, 1928. He studied physics at the University of Tokyo in 1950, and was a member of the Yoshio Nishina group for researching cosmic altitude radiation for 16 years even during the World War II. He was a researcher at CERN and at Midwestern State University before becoming a professor at the University of Tokyo. In 1960, he went to General Atomics, where he led a fusion research project and later became vice president and deputy chairman of the board. In 1994, Ohkawa left General Atomics to found TOYO Technologies. In 2004, he was co-founder of Nano Fusion Technologies with Masano Nishikawa for the development of micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanazawa
is the capital city of Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 466,029 in 203,271 households, and a population density of 990 persons per km2. The total area of the city was . Overview Cityscape File:もてなしドーム3.jpg, Kanazawa Station(2013) File:Omichoichibakan004.jpg, Ōmichō-Market(Ōmichō-Ichiba)(2013) File:Kanazawa view from Utatsuyama Park.jpg, Skyline of Kanazawa City(2017) File:Cityscape at downtown Kanazawa.jpg, CBD of Kanazawa File:Katamachi Crossing.jpg, Downtown of Katamachi Area (2022) Geography Kanazawa is located in north-western Ishikawa Prefecture in the Hokuriku region of Japan and is bordered by the Sea of Japan to the west and Toyama Prefecture to the east. The city sits between the Sai and Asano rivers. The eastern portion of the city is dominated by the Japanese Alps. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Hakusan National Park. Climate Kanazawa has a humid subtropical cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Isotopes
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (''t''1/2) for tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITER
ITER (initially the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, ''iter'' meaning "the way" or "the path" in Latin) is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy by replicating, on Earth, the fusion processes of the Sun. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for late 2025, it will be the world's largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment and the largest experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with ten times the plasma volume of any other tokamak operating today. The long-term goal of fusion research is to generate electricity. ITER's stated purpose is scientific research, and technological demonstration of a large fusion reactor, without electricity generation. ITER's goals are to achieve enough fusion to produce 10 ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIII-D (tokamak)
DIII-D is a tokamak that has been operated since the late 1980s by General Atomics (GA) in San Diego, USA, for the U.S. Department of Energy. The DIII-D National Fusion Facility is part of the ongoing effort to achieve magnetically confined fusion. The mission of the DIII-D Research Program is to establish the scientific basis for the optimization of the tokamak approach to fusion energy production. DIII-D was built on the basis of the earlier Doublet III, the third in a series of machines built at GA to experiment with tokamaks having non-circular plasma cross sections. This work demonstrated that certain shapes strongly suppressed a variety of instabilities in the plasma, which led to much higher plasma pressure and performance. DIII-D is so-named because the plasma is shaped like the letter D, a shaping that is now widely used on modern designs, and has led to the class of machines known as "advanced tokamaks." Advanced tokamaks are characterized by operation at high plasma β ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald William Kerst
Donald William Kerst (November 1, 1911 – August 19, 1993) was an American physicist who worked on advanced particle accelerator concepts (accelerator physics) and plasma physics. He is most notable for his development of the betatron, a novel type of particle accelerator used to accelerate electrons. A graduate of the University of Wisconsin, Kerst developed the first betatron at the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign, where it became operational on July 15, 1940. During World War II, Kerst took a leave of absence in 1940 and 1941 to work on it with the engineering staff at General Electric, and he designed a portable betatron for inspecting dud bombs. In 1943 he joined the Manhattan Project's Los Alamos Laboratory, where he was responsible for designing and building the Water Boiler, a nuclear reactor intended to serve as a laboratory instrument. From 1953 to 1957 Kerst was technical director of the Midwestern Universities Research Association, where he worked on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipole Magnet
Multipole magnets are magnet A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nicke ...s built from multiple individual magnets, typically used to control Charged particle beam, beams of charged particles. Each type of magnet serves a particular purpose. * Dipole magnets are used to bend the trajectory of particles * Quadrupole magnets are used to focus particle beams * Sextupole magnets are used to correct for chromaticity (accelerator), chromaticity introduced by quadrupole magnets Magnetic field equations The magnetic field of an ideal multipole magnet in an accelerator is typically modeled as having no (or a constant) component parallel to the nominal beam direction (z direction) and the transverse components can be written as complex numbers: B_x + i B_y = C_n \cdot ( x - iy )^ w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. , it was the leading candidate for a practical fusion reactor. Tokamaks were initially conceptualized in the 1950s by Soviet physicists Igor Tamm and Andrei Sakharov, inspired by a letter by Oleg Lavrentiev. The first working tokamak was attributed to the work of Natan Yavlinsky on the T-1 in 1958. It had been demonstrated that a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that wind around the torus in a helix. Devices like the z-pinch and stellarator had attempted this, but demonstrated serious instabilities. It was the development of the concept now known as the safety factor (labelled ''q'' in mathematical notation) that guided tokamak development; by arranging the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midwestern Universities Research Association
The Midwestern Universities Research Association (MURA) was a collaboration between 15 universities with the goal of designing and building a particle accelerator for the Midwestern United States. It existed between 1953–1967, but could not achieve its goal in this time and lost funding. It was thought that President John F. Kennedy would have supported the MURA machine, while one of President Lyndon B. Johnson's first actions was the shutdown of the MURA machine and laboratory. In its formative years, Donald Kerst was the director of MURA. At this institution, Keith Symon invented the FFAG accelerator, independently to Tihiro Ohkawa, which combines several concepts of cyclotrons and synchrotrons. FFAG concepts were extensively developed in MURA. The proposed MURA accelerators were scaling FFAG synchrotrons, meaning that orbits of any momentum are photographic enlargements of those of any other momentum. The concept of FFAG acceleration was revived in the early 1980s,Martin, S.; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Kolomensky
Andrei, Andrey or Andrej (in Cyrillic script: Андрэй , Андрей or Андреј) is a form of Andreas/Ἀνδρέας in Slavic languages and Romanian. People with the name include: *Andrei of Polotsk (–1399), Lithuanian nobleman *Andrei Alexandrescu, Romanian computer programmer *Andrey Amador, Costa Rican cyclist *Andrei Arlovski, Belarusian mixed martial artist *Andrey Arshavin, Russian football player *Andrej Babiš, Czech prime minister *Andrey Belousov (born 1959), Russian politician *Andrey Bolotov, Russian agriculturalist and memoirist *Andrey Borodin, Russian financial expert and businessman *Andrei Broder, Romanian-Israeli American computer scientist and engineer *Andrei Chikatilo, prolific and cannibalistic Russian serial killer and rapist *Andrei Denisov (weightlifter) (born 1963), Israeli Olympic weightlifter *Andrey Ershov, Russian computer scientist *Andrey Esionov, Russian painter *Andrei Glavina, Istro-Romanian writer and politician *Andrei Gromyko (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Symon
Keith Randolph Symon (March 25, 1920 – December 16, 2013) was an American physicist working in the fields of accelerator physics and plasma physics. Symon graduated summa cum laude, Phi Beta Kappa, from Harvard in 1942 with a BA in Philosophy and Mathematics. In 1948 he was awarded a PhD in Physics. He taught physics at Wayne State University in Detroit until 1955. Symon was professor of physics at the University of Wisconsin until his retirement in 1992 when he became emeritus professor. From 1956 to 1967 he was on the staff of the Midwestern Universities Research Association (MURA), a collaboration of Big Ten universities, the University of Chicago and Notre Dame. In 1982 and 1983 he was acting director of the Madison Academic Computing Center and from 1983 to 1985, acting director of the UW-Madison Synchrotron Radiation Center. His textbook, "Mechanics", has been a staple in physics classes since publication of the first edition in 1953. It has been published in multiple lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
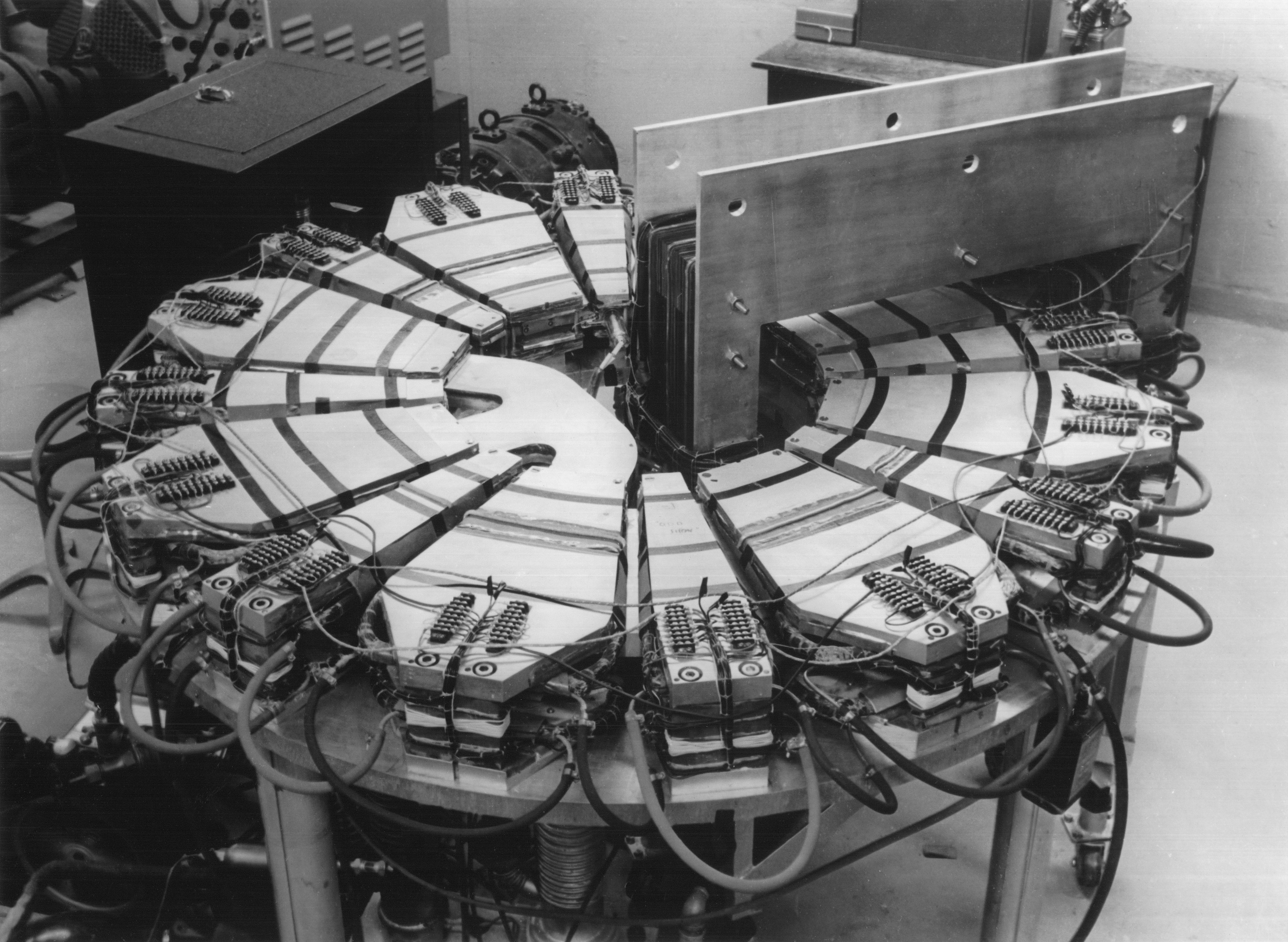
Fixed-field Alternating Gradient Accelerator
A Fixed-Field alternating gradient Accelerator (FFA; also abbreviated FFAG) is a circular particle accelerator concept that can be characterized by its time-independent magnetic fields (''fixed-field'', like in a cyclotron) and the use of alternating gradient strong focusing (as in a synchrotron). In all circular accelerators, magnetic fields are used to bend the particle beam. Since the magnetic force required to bend the beam increases with particle energy, as the particles accelerate, either their paths will increase in size, or the magnetic field must be increased over time to hold the particles in a constant size orbit. Fixed-field machines, such as cyclotrons and FFAs, use the former approach and allow the particle path to change with acceleration. In order to keep particles confined to a beam, some type of focusing is required. Small variations in the shape of the magnetic field, while maintaining the same overall field direction, are known as weak focusing. Strong, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |