|
Thyssagetae
The Thyssagetae ( grc, Θυσσαγέται) were an ancient tribe described by Herodotus as occupying a district to the north-east of Scythia, separated from the Budini by a "desert" that took seven days to cross.Herodotus. ''Histories'', 4.22.1: "...after the desert, if one inclines somewhat to the east, the Thyssagetae are reached, a numerous nation quite distinct from any other, and living by the chase." The Thyssagetae therefore seem to have occupied the southern end of the Ural Mountains, north of the Caspian Sea. According to the 19th Century archaeologist Sir Ellis Minns, the form of their name suggests that the Thyssagetae spoke an Iranian language, such as Scythian or Sarmatian, like the neighbouring Massagetae (on the north-east shores of the Caspian).Ellis Hovell Minns, (2011; orig. 1903), ''Scythians and Greeks: A Survey of Ancient History and Archaeology on the North Coast of the Euxine from the Danube to the Caucasus'', Cambridge, Cambridge University Press p. 107. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' and plural ''Getae'' may be derived from a Greek exonym: the area was the hinterland of Greek colonies on the Black Sea coast, bringing the Getae into contact with the ancient Greeks from an early date. Although it is believed that the Getae were related to their westward neighbours, the Dacians, several scholars, especially in the Romanian historiography, posit that the Getae and the Dacians were the same people. Ethnonym The ethnonym ''Getae'' was first used by Herodotus. The root was also used for the Tyragetae, Thyssagetae, Massagetae, and others. Getae and Dacians Ancient sources Strabo, one of the first ancient sources to mention Getae and Dacians, stated in his ''Geographica'' ( 7BC – 20AD) that the Dacians lived in the wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science .. * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians .. * : "All contemporary historians, archeologists and li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chusovaya River
The Chusovaya (russian: Чусова́я) is a river flowing in Perm Krai, Sverdlovsk Oblast and Chelyabinsk Oblast of Russia. A tributary of the Kama, which in turn is a tributary of the Volga, it discharges into the Chusovskoy Cove of the Kamsky Reservoir. The river is remarkable in that it originates on the eastern slopes of the Ural Mountains in Asia, crosses the mountains, and mostly runs on their western slopes in Europe. The Chusovaya River is widely used as a source of water. In particular, its water is taken from the Volchikhinsky Reservoir, , to the Verkhneisetsky Reservoir to supply the major city of Yekaterinburg. Fifteen smaller reservoirs are spread over about 150 tributaries of the river. There are numerous metal and coal mines along the Chusovaya, and the river was intensively used to deliver their production to the western Russia. However, industrial navigation nearly halted with the development of railways in the early 20th century. Chusovoy is the major remaini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
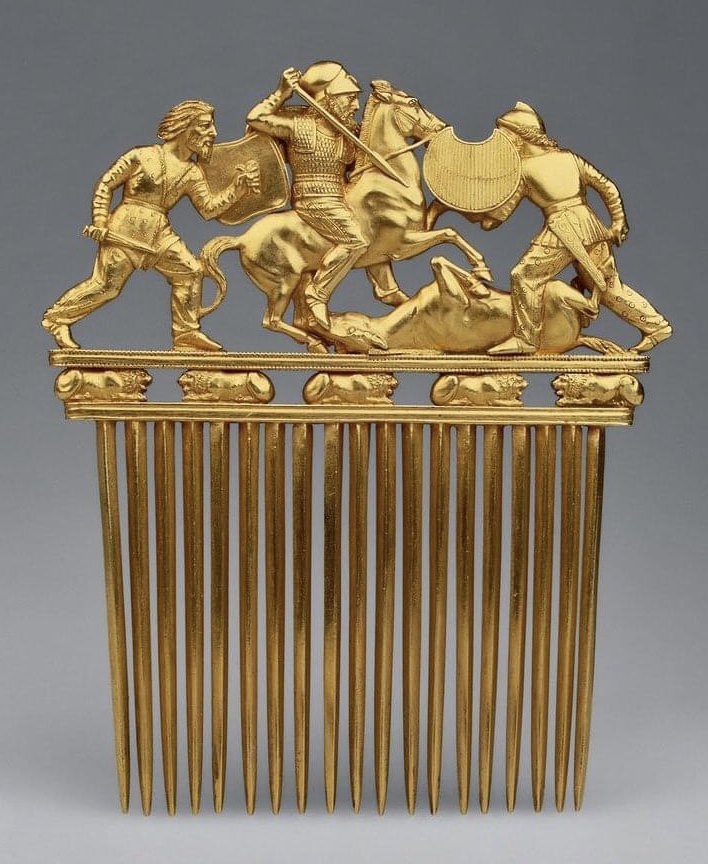
Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translation of Iranian “wearers of pointed caps”: "The (who wear pointed caps) were known to Greek authors as the , a direct translation of the Old Persian name" were an ancient Eastern Iranian Saka people who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia and were part of the wider Scythian cultures. The Massagetae rose to power in the 8th to 7th centuries BCE, when they kickstarted a series of events with wide-reaching consequences by expelling the Scythians out of Central Asia and into the Caucasian and Pontic Steppes. The Massagetae are most famous for their queen Tomyris's defeating and killing of Cyrus, the founder of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The Massagetae declined after the 3rd century BCE, after which they merged with some other trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
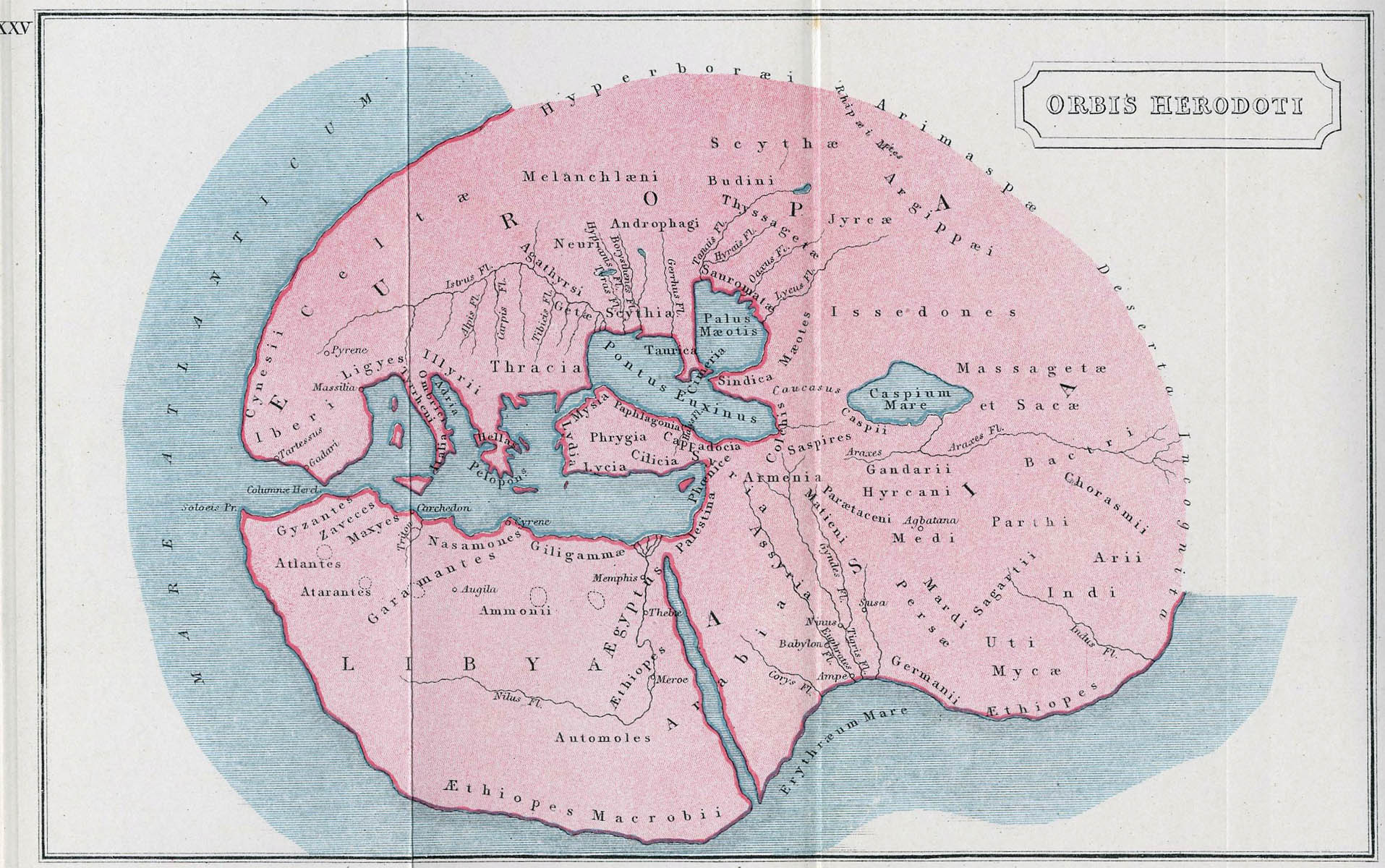
Orbis Herodoti
Orbis may refer to: Companies * Orbis Business Intelligence, a British private intelligence firm * Orbis Technology, a British bookmaker software company now called OpenBet * Orbis (Polish travel agency), a Polish travel agency, established in 1920 Entertainment * ''Orbis'' (audio drama), a Doctor Who audio play * ''Orbis Pictus'' (film), a 1997 Slovak film Historical * The "Orbis Terrarum", a map of the world created by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa in 20 A.D. * Orbis, Rhineland-Palatinate, a municipality in the Donnersbergkreis district, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany * ''Orbis Pictus'', a 1658 children's book by Czech educator Jan Ámos Komenský Publishing * Orbis Books, a U.S. publishing imprint of the Maryknoll order * Orbis Publishing, a British publisher of partworks and books * Orbis Pictus Award, awarded by the National Council of Teachers of English for outstanding children's nonfiction literature * ''Orbis'', a 2002 alternative history novel by Scott Mackay Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribes Described Primarily By Herodotus
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflicting theoretical understandings of social and kinship structures, and also reflecting the problematic application of this concept to extremely diverse human societies. The concept is often contrasted by anthropologists with other social and kinship groups, being hierarchically larger than a lineage or clan, but smaller than a chiefdom, nation or state. These terms are equally disputed. In some cases tribes have legal recognition and some degree of political autonomy from national or federal government, but this legalistic usage of the term may conflict with anthropological definitions. In the United States, Native American tribes are legally considered to have "domestic dependent nation" status within the territorial United States, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadic Groups In Eurasia
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pastoral tribes slowly decreased, reaching an estimated 30–40 million nomads in the world . Nomadic hunting and gathering—following seasonally available wild plants and game—is by far the oldest human subsistence method. Pastoralists raise herds of domesticated livestock, driving or accompanying them in patterns that normally avoid depleting pastures beyond their ability to recover. Nomadism is also a lifestyle adapted to infertile regions such as steppe, tundra, or ice and sand, where mobility is the most efficient strategy for exploiting scarce resources. For example, many groups living in the tundra are reindeer herders and are semi-nomadic, following forage for their animals. Sometimes also described as "nomad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Peoples Of Russia
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
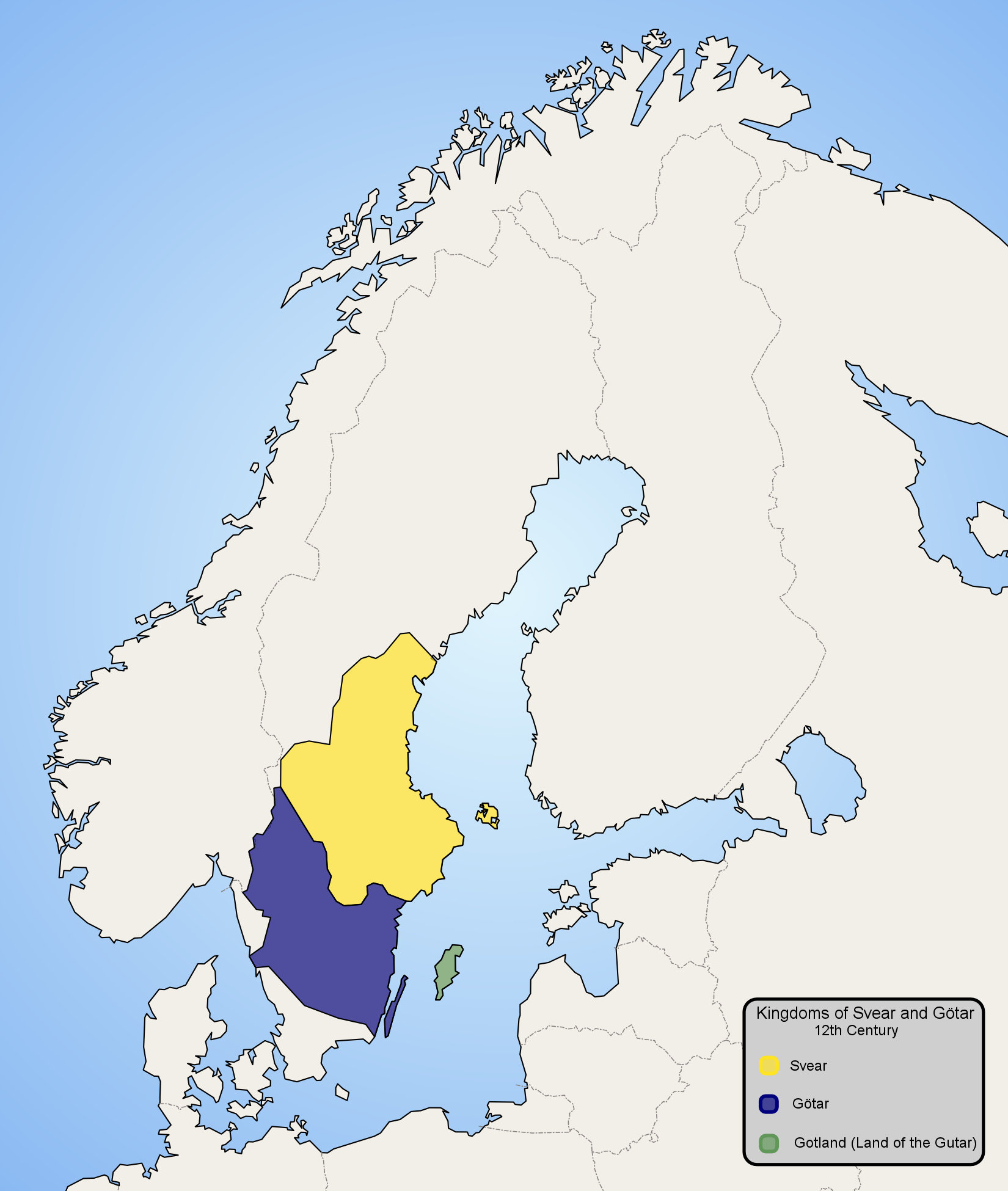
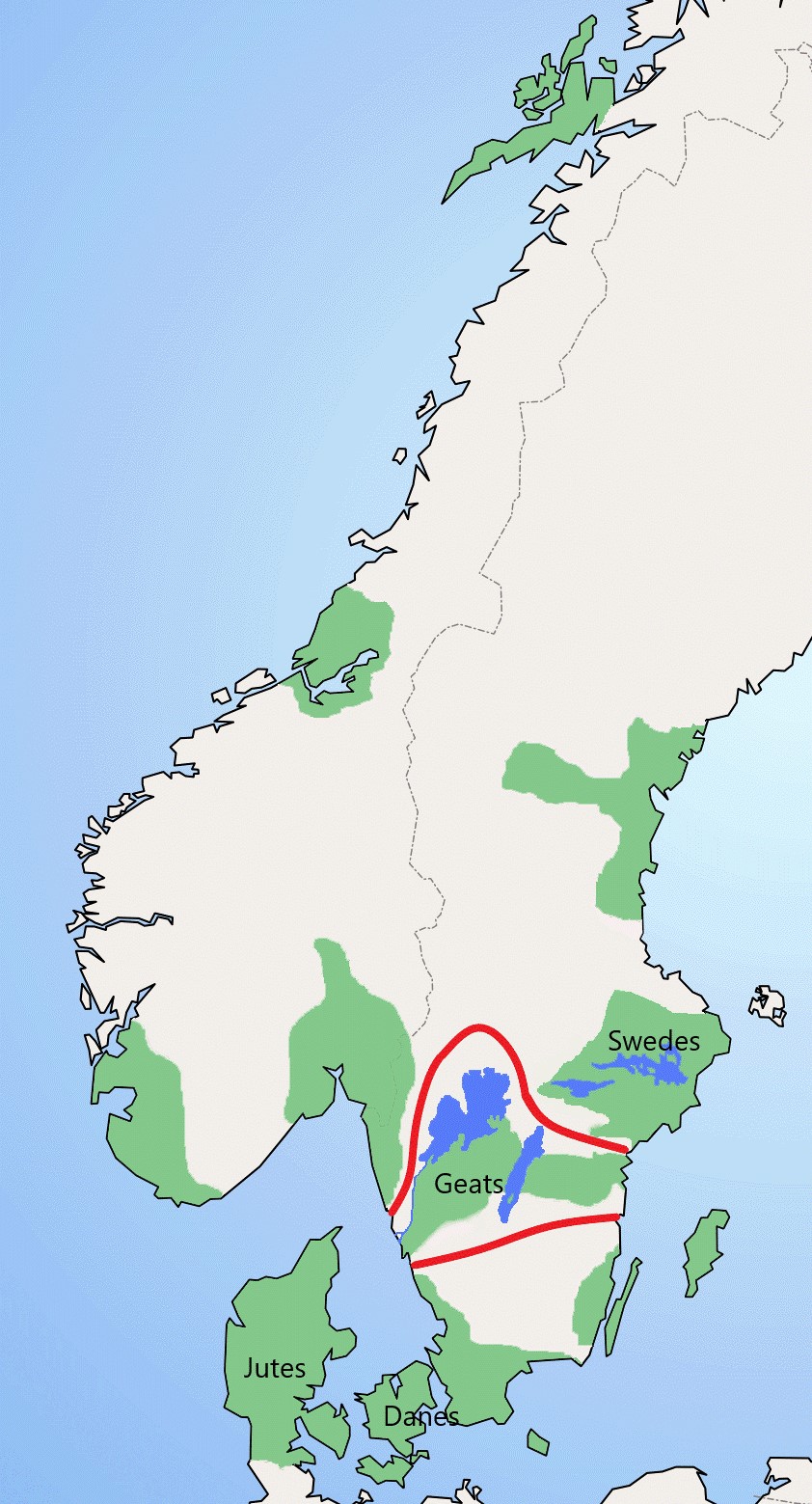
Gutes
The Gutes (old west norse ''Gotar'', old gutnish ''Gutar'') were a North Germanic tribe inhabiting the island of Gotland. The ethnonym is related to that of the ''Goths'' (''Gutans''), and both names were originally Proto-Germanic *''Gutaniz''. Their language is called Gutnish (''gutniska''). They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with historical Swedes and Geats. Name The name of the Gutes in Old West Norse is ''Gotar (adj. gotneskr)'', which is the same as that used for the Goths. Old Norse sources such as the sagas do not distinguish between the Goths and the Gutes. In accordance, the Old East Norse term for both Goths and Gutes seems to have been ''Gutar'' (adj. ''gutniskr''). Only the Goths and Gutes bear this name among all the Germanic tribes, even if ''Geat'' is closely related. The fact that the ethnonym is identical to ''Goth'' may be the reason why they are not mentioned as a special group until Jordanes' Getica, where they may be those who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geats
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyragetae
The Tyrageti, Tyragetae, or Tyrangitae (, Strabo vii.; Ptol. iii. 5. § 25), literally, the Getae of the Tyras, were a sub-tribe of the Getae, situated on the river ''Tyras'' (modern-day Dniester in Moldova and Ukraine). They were regarded as an immigrant tribe of European Sarmatia dwelling E. of the river Tyras, near the Carpii and Tagri, and, according to Ptolemy, the northern neighbours of Lower Moesia. Pliny Pliny may refer to: People * Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'') * Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ... (v. 12. s. 26) calls them, with more correct orthography, Tyragetae, and represents them as dwelling on a large island in the Tyras. References * External links Ancient tribes in Romania Getic tribes {{Ancient-Thrace-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of Ukraine. It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average discharge (hydrology), discharge at delta – between and – and of drainage basin. It is widely regarded as the Rivers in Russia, national river of Russia. The hypothetical old Russian state, the Rus' Khaganate, arose along the Volga . Historically, the river served as an important meeting place of various Eurasian civilizations. The river flows in Russia through forests, Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |